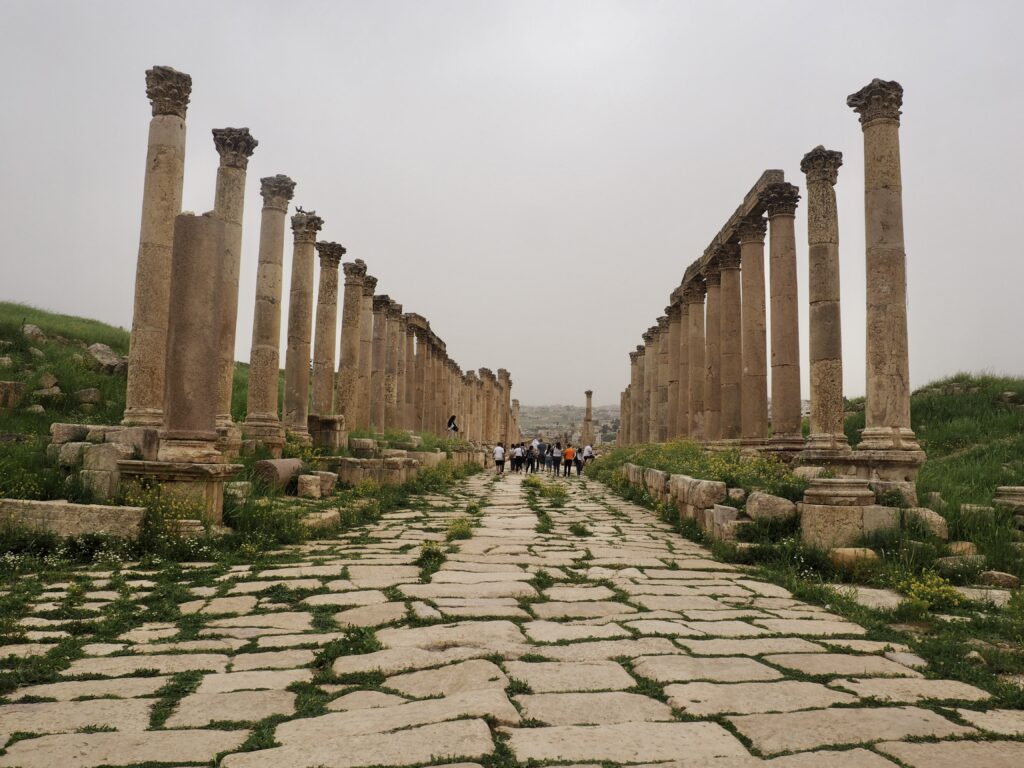
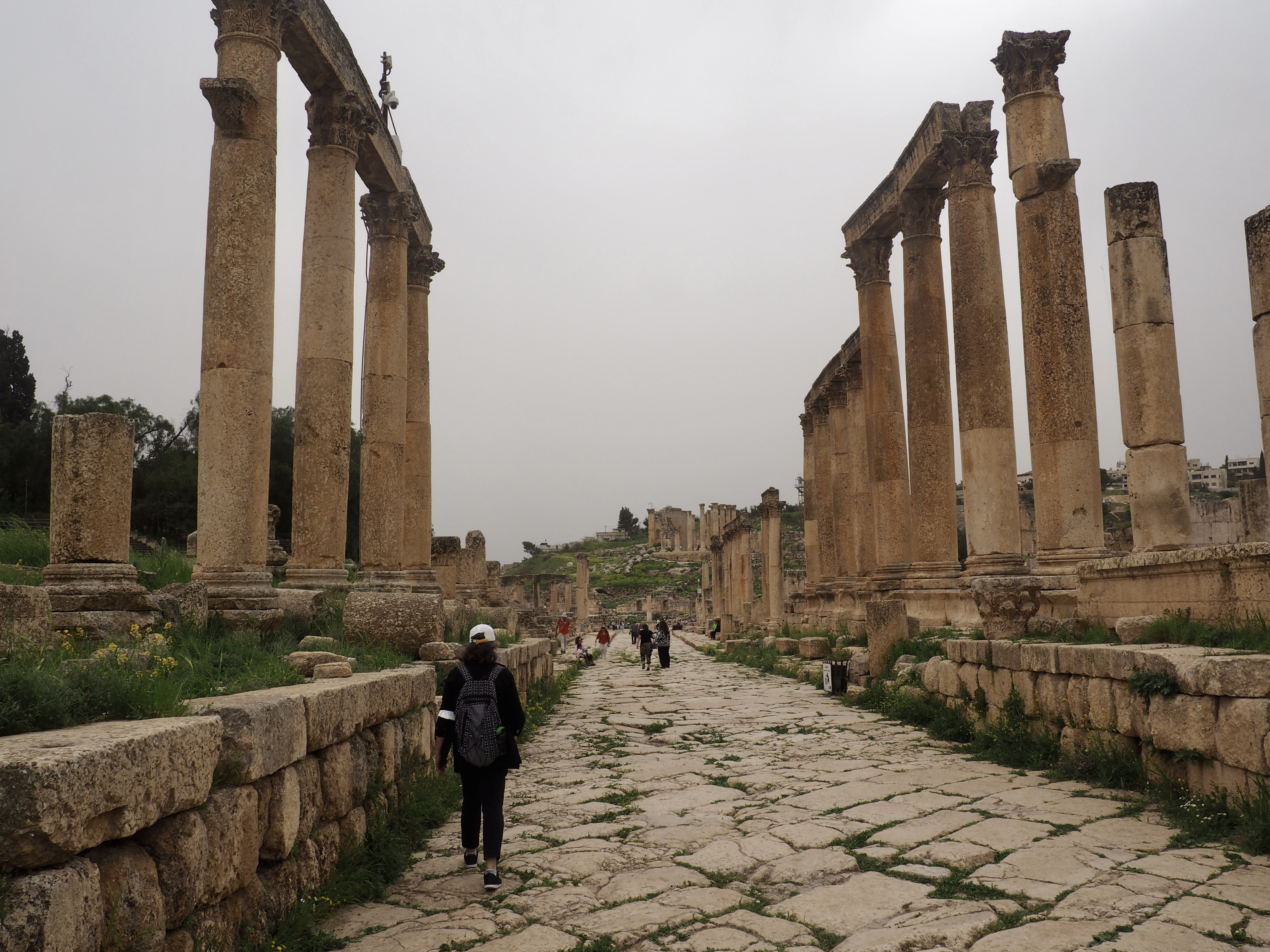
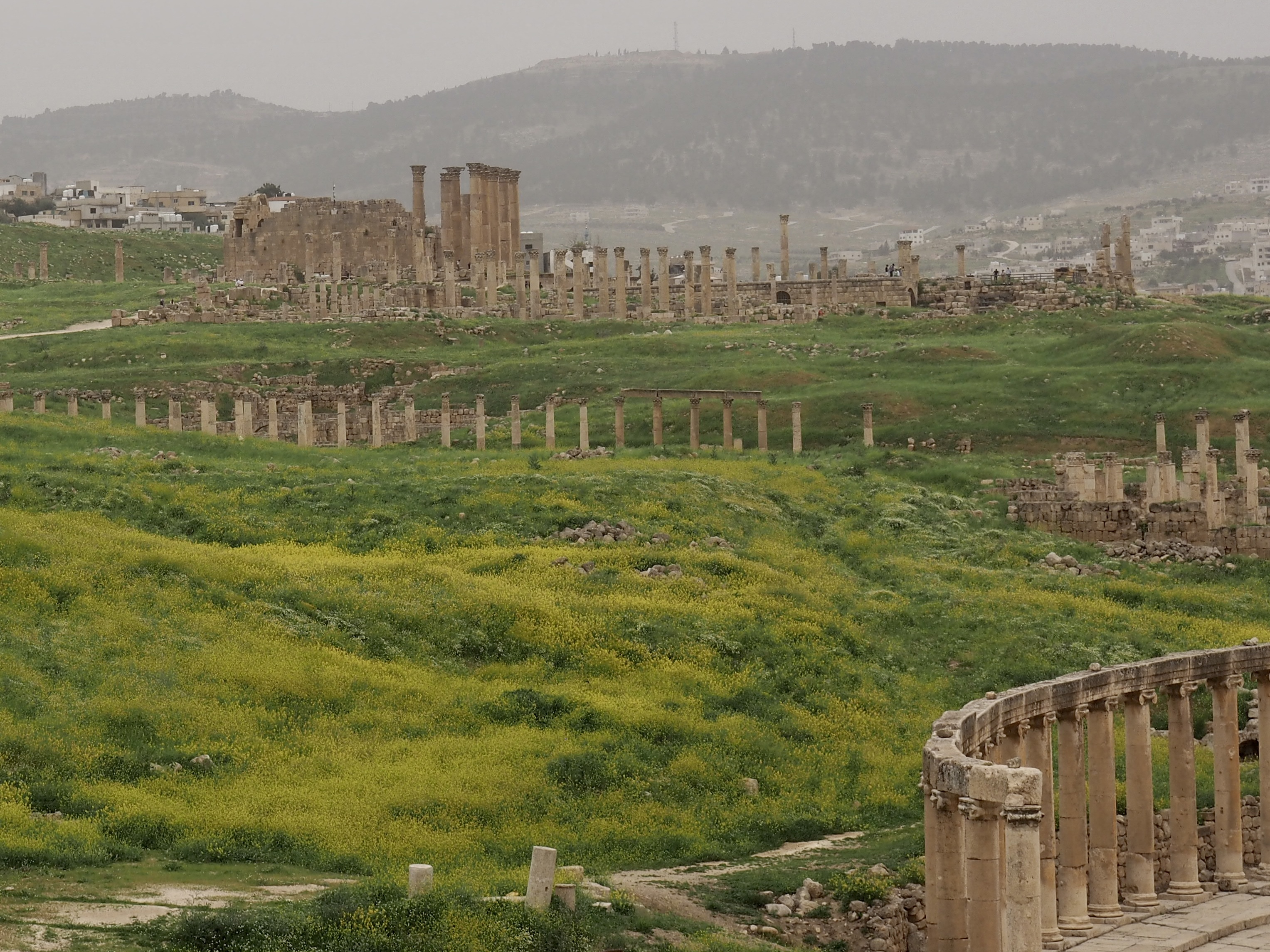
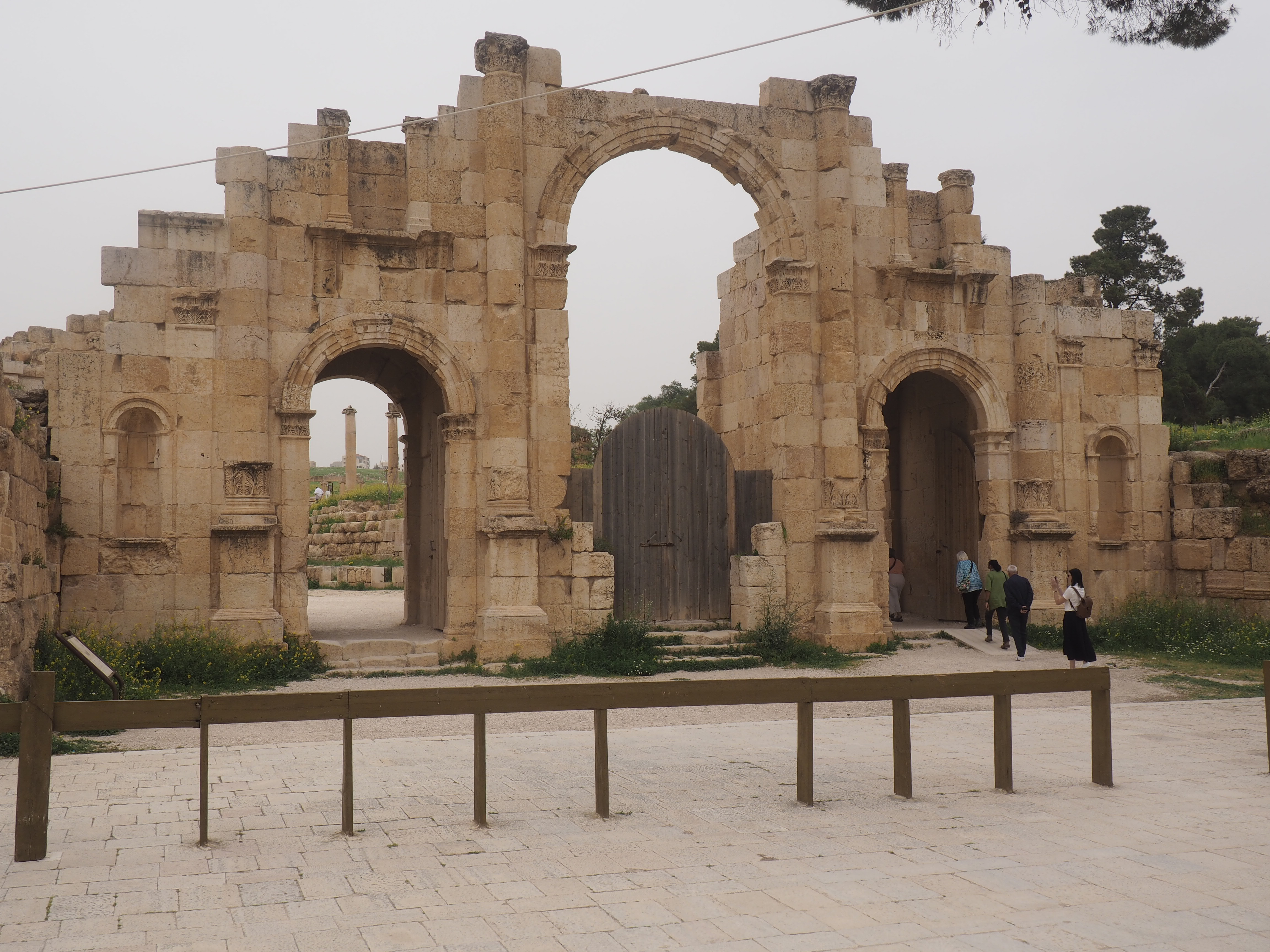
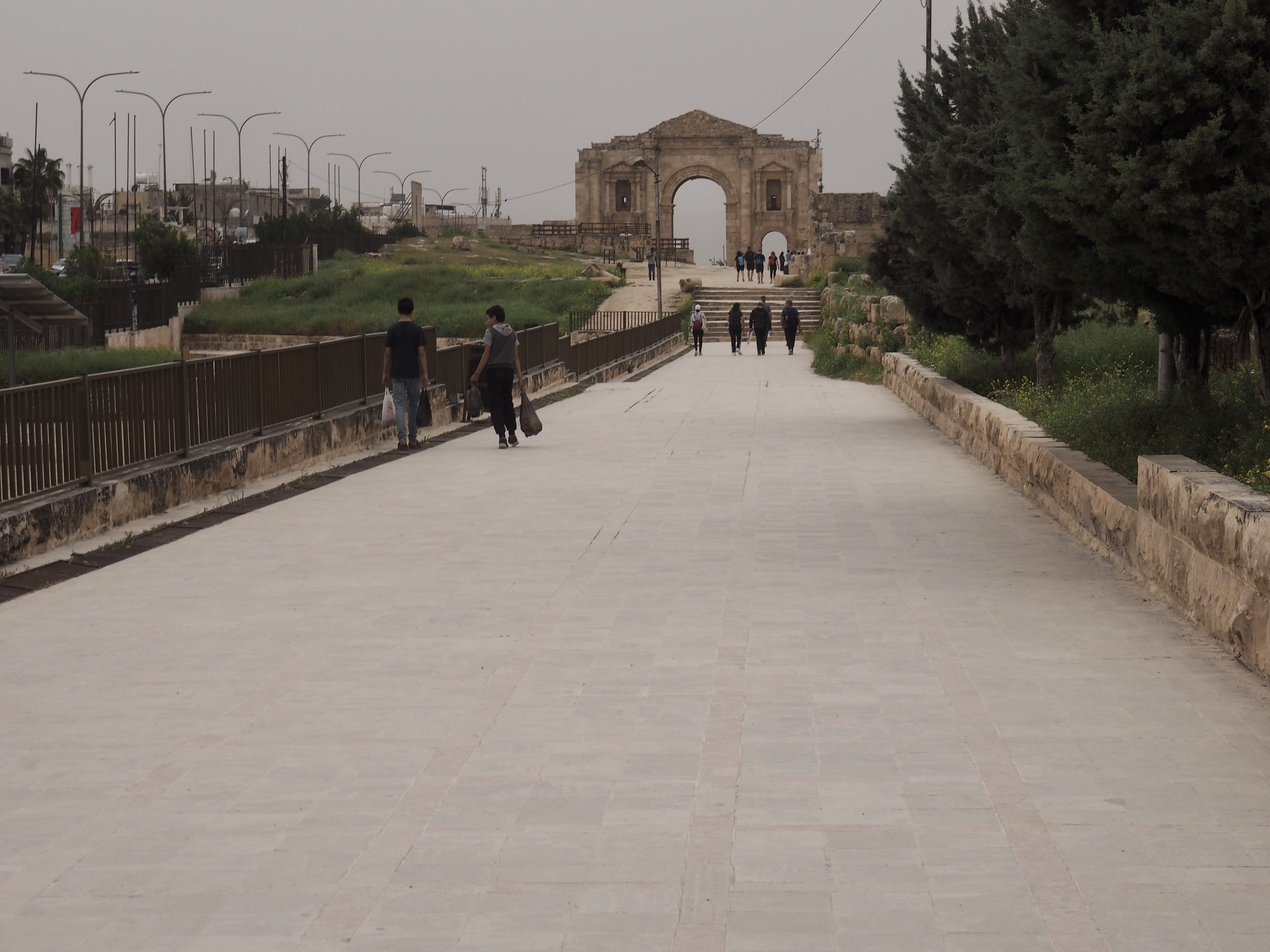
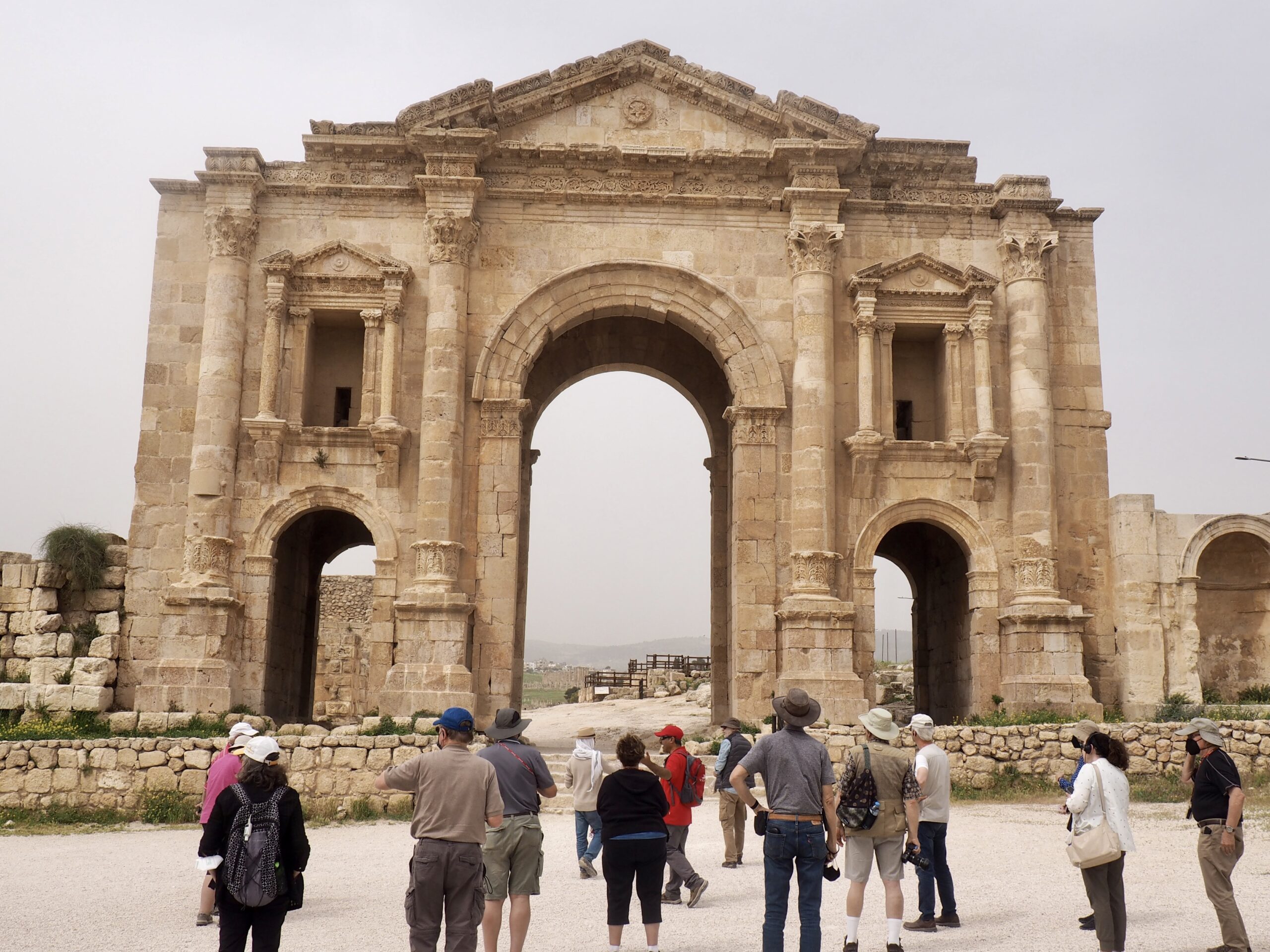
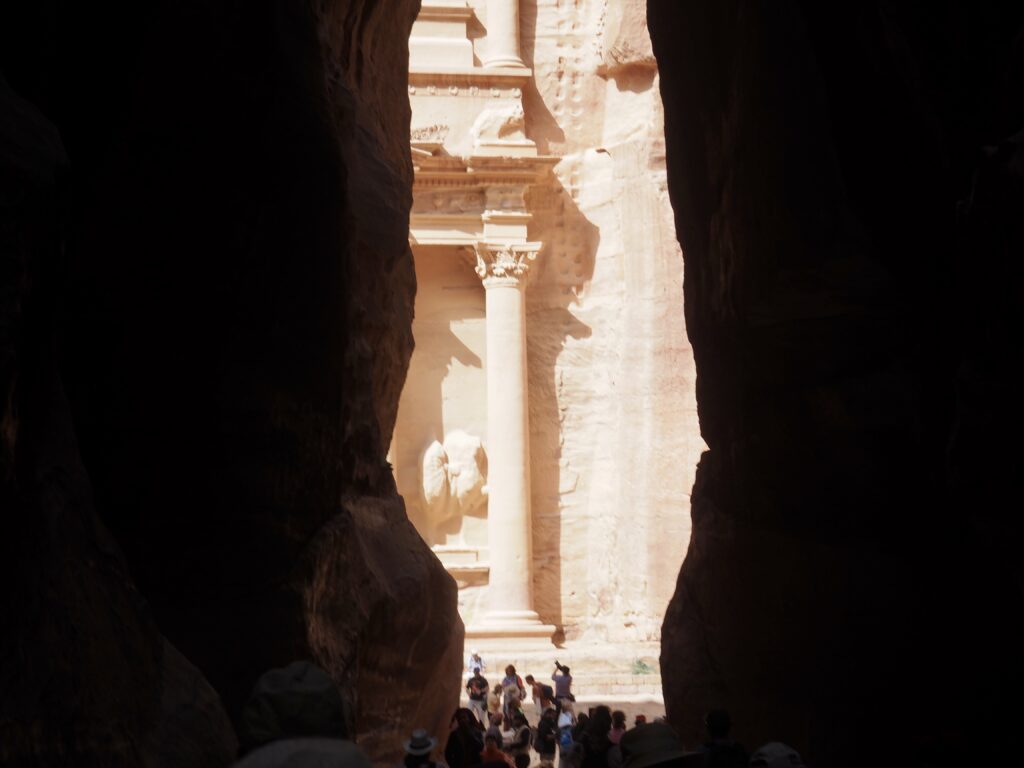
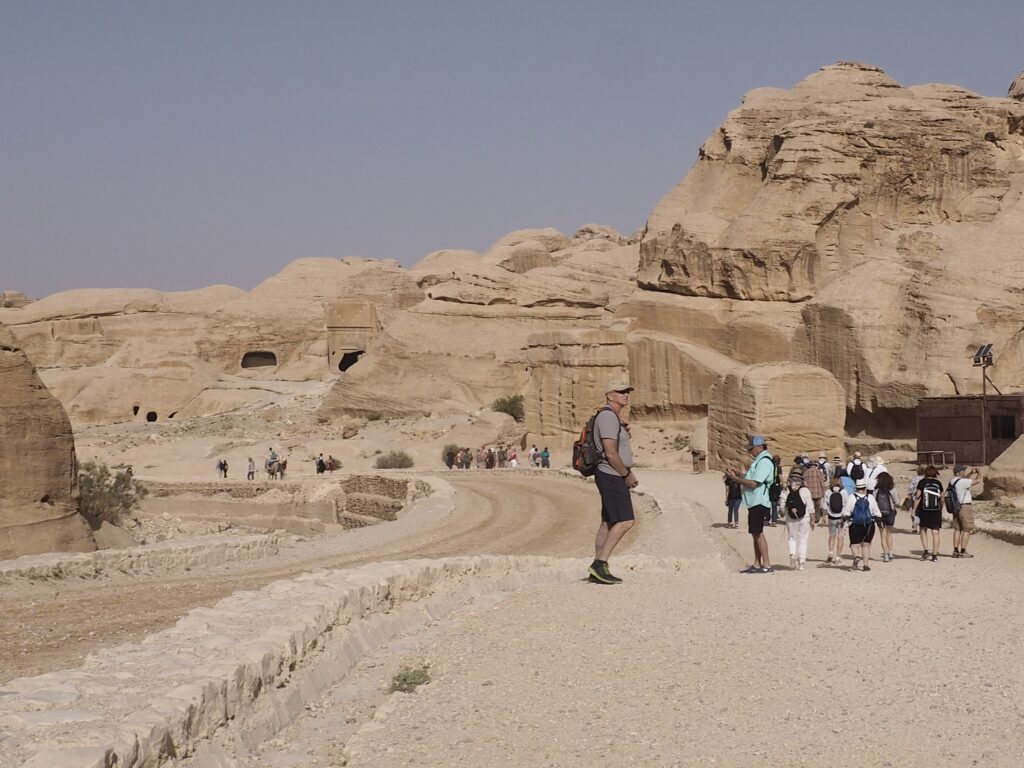
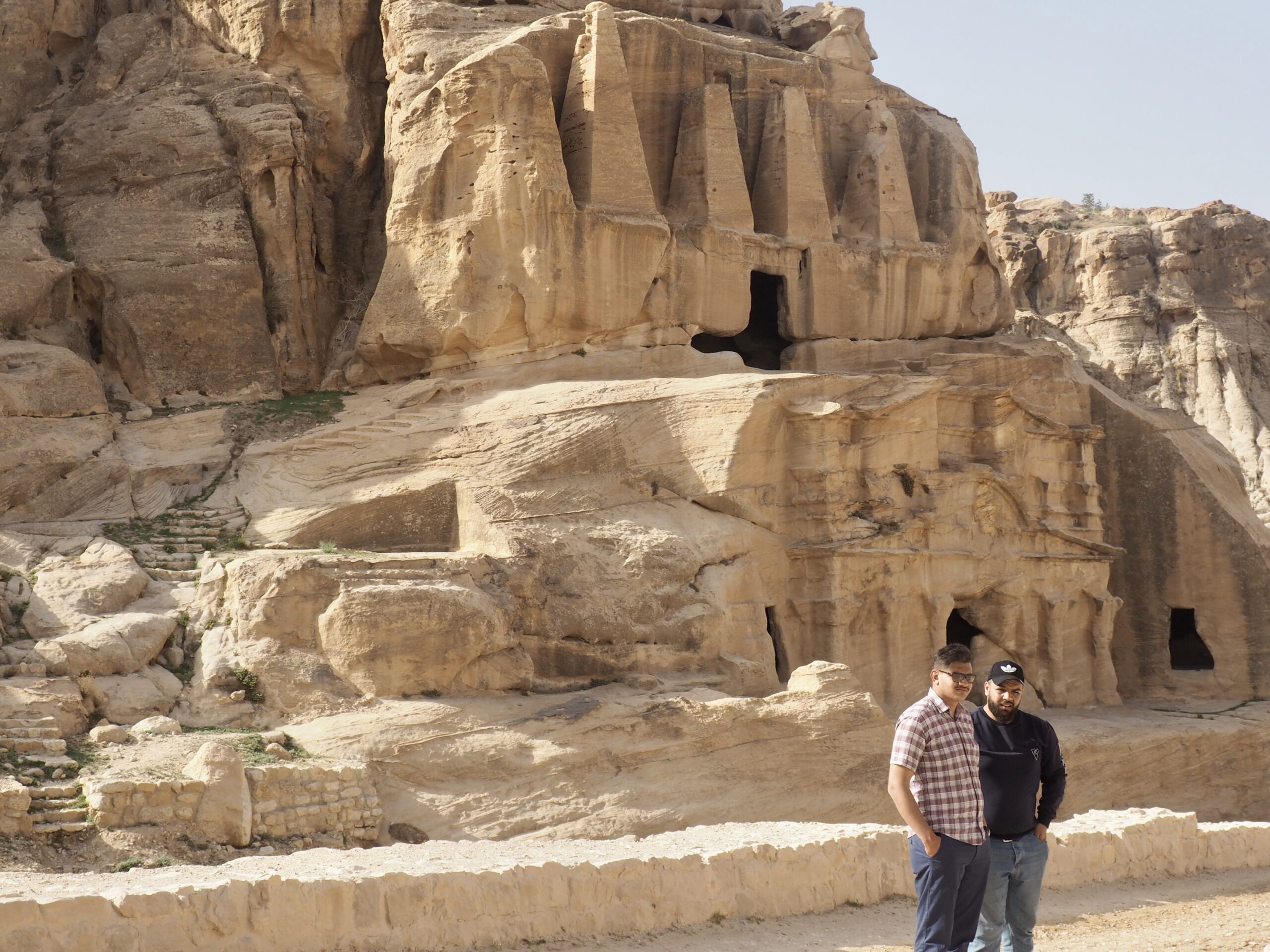
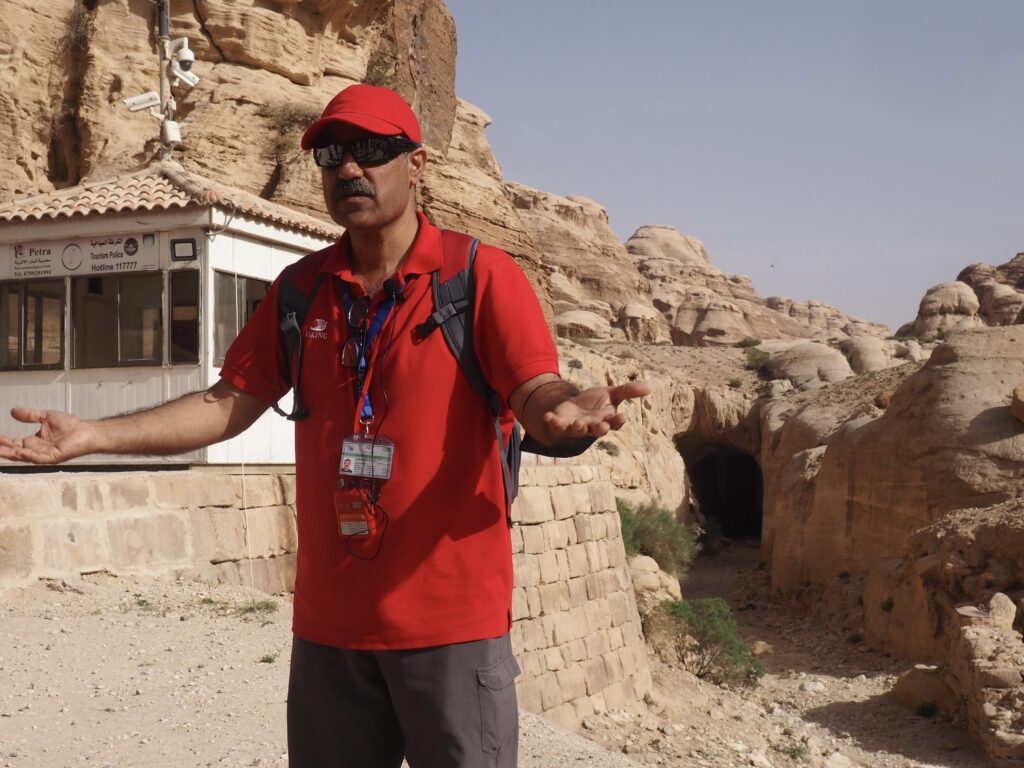
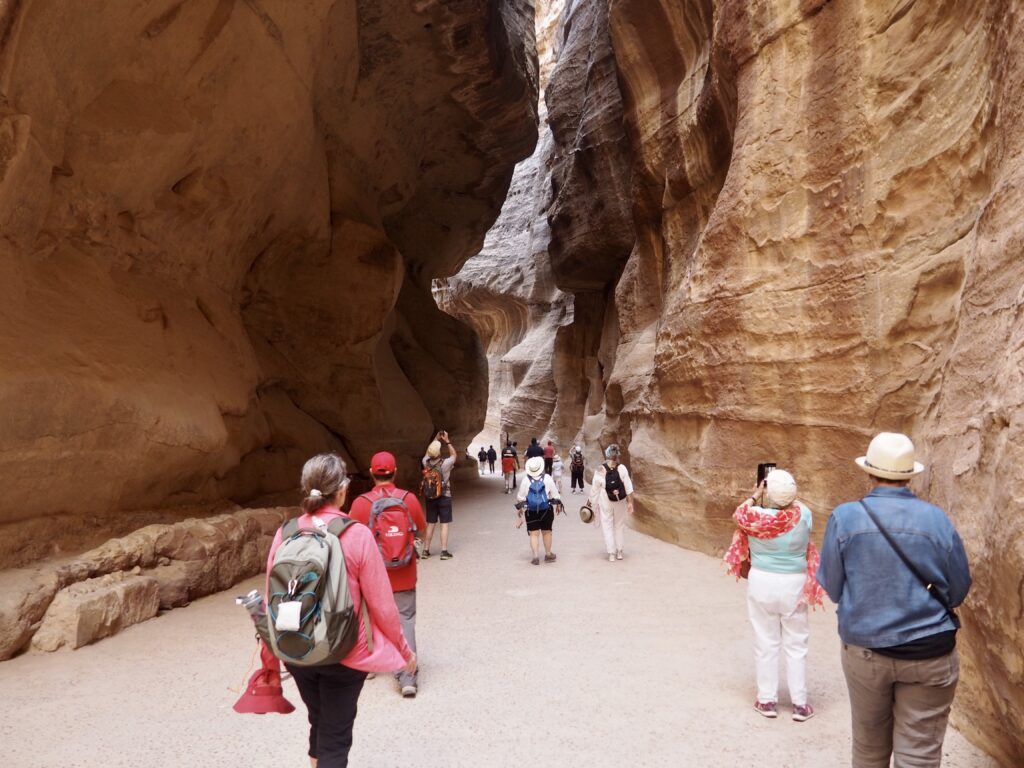
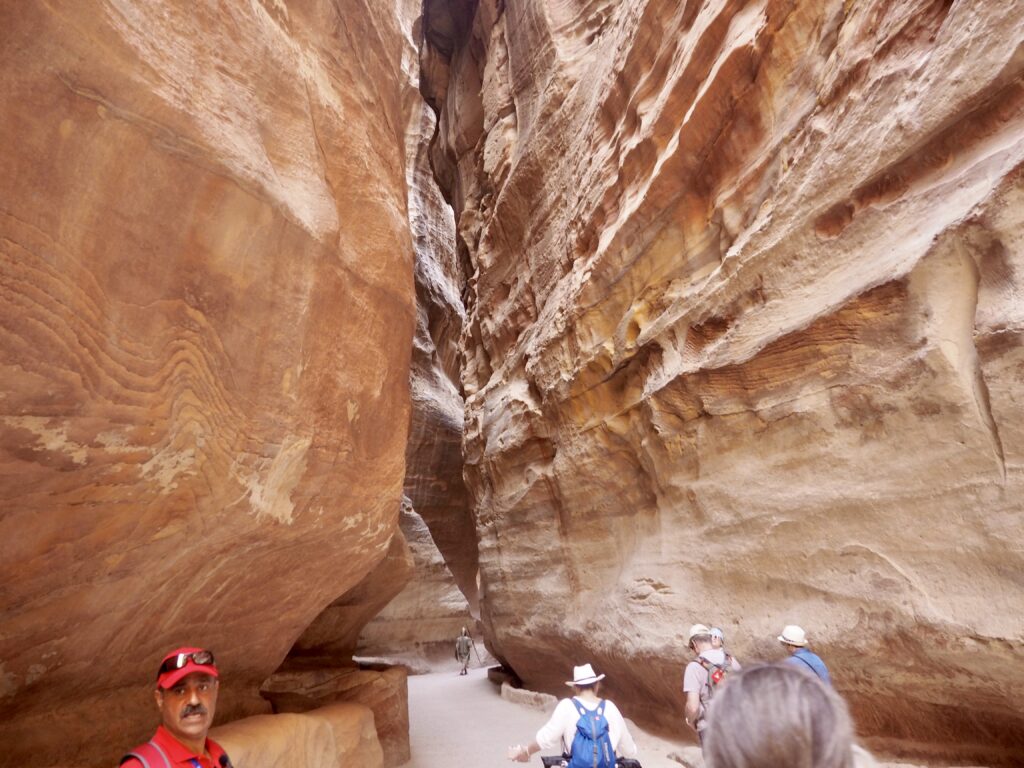
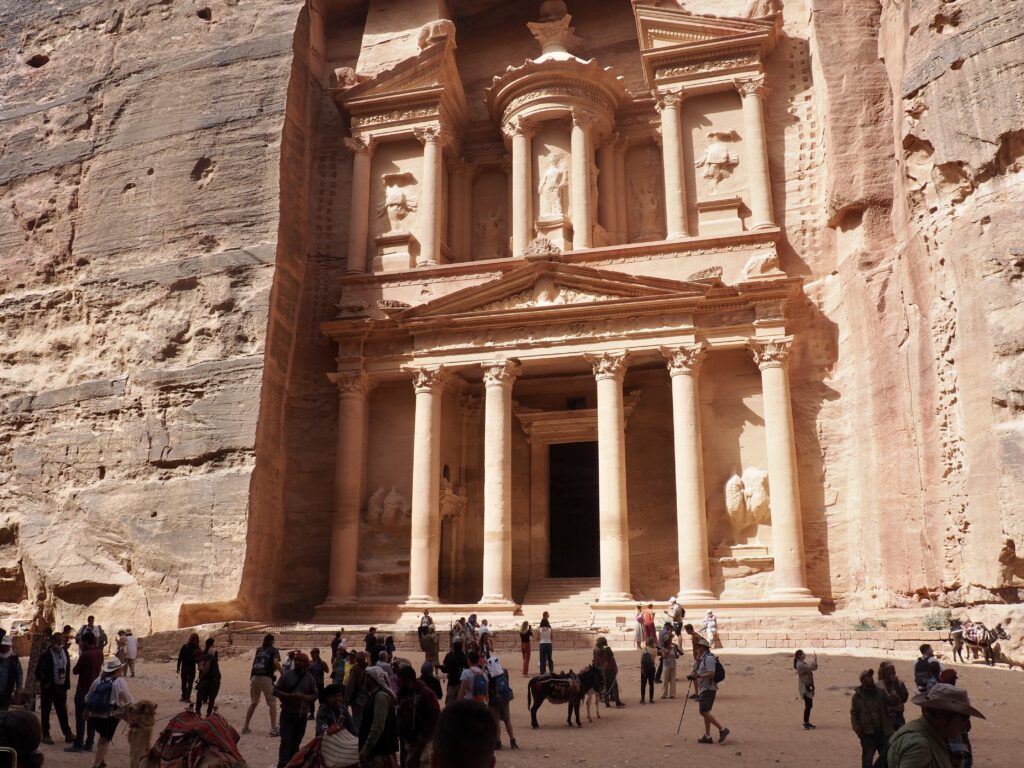
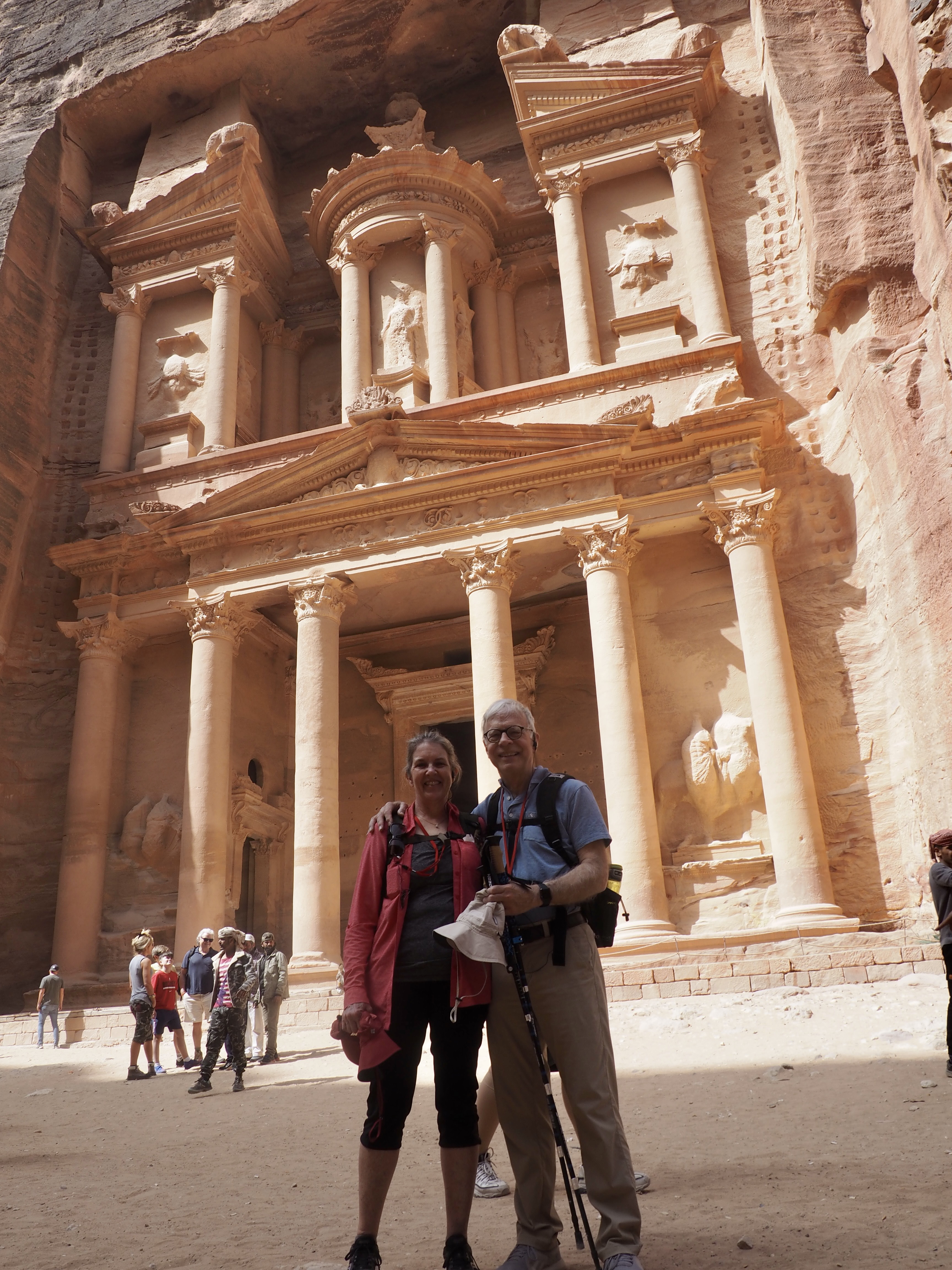
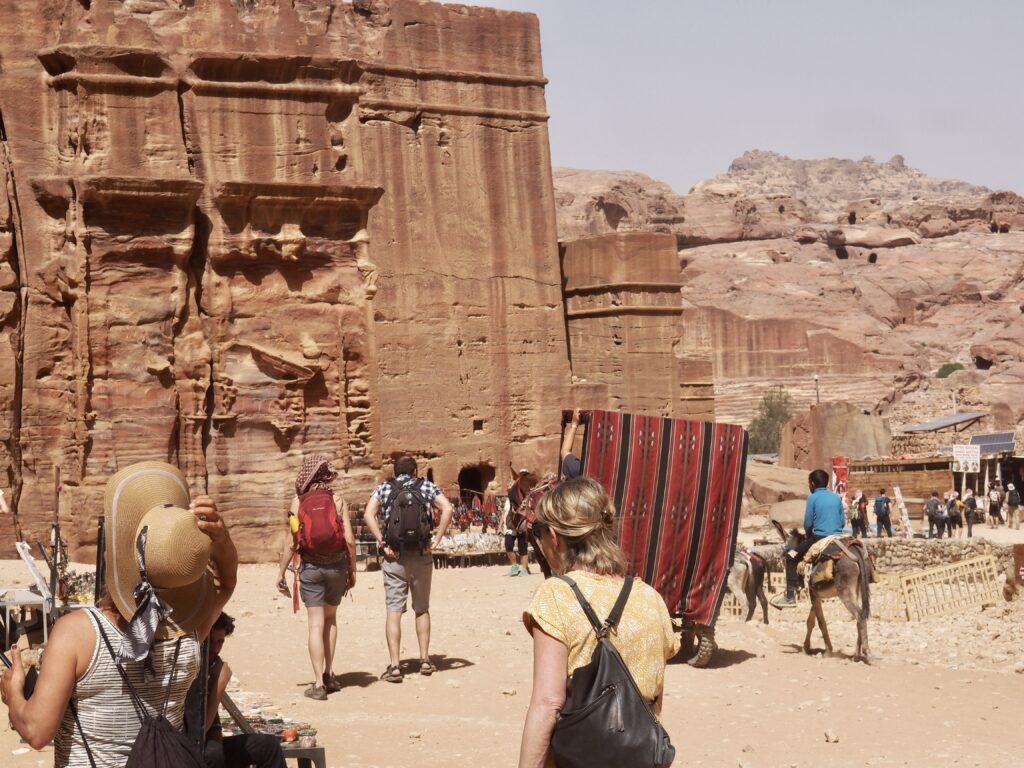
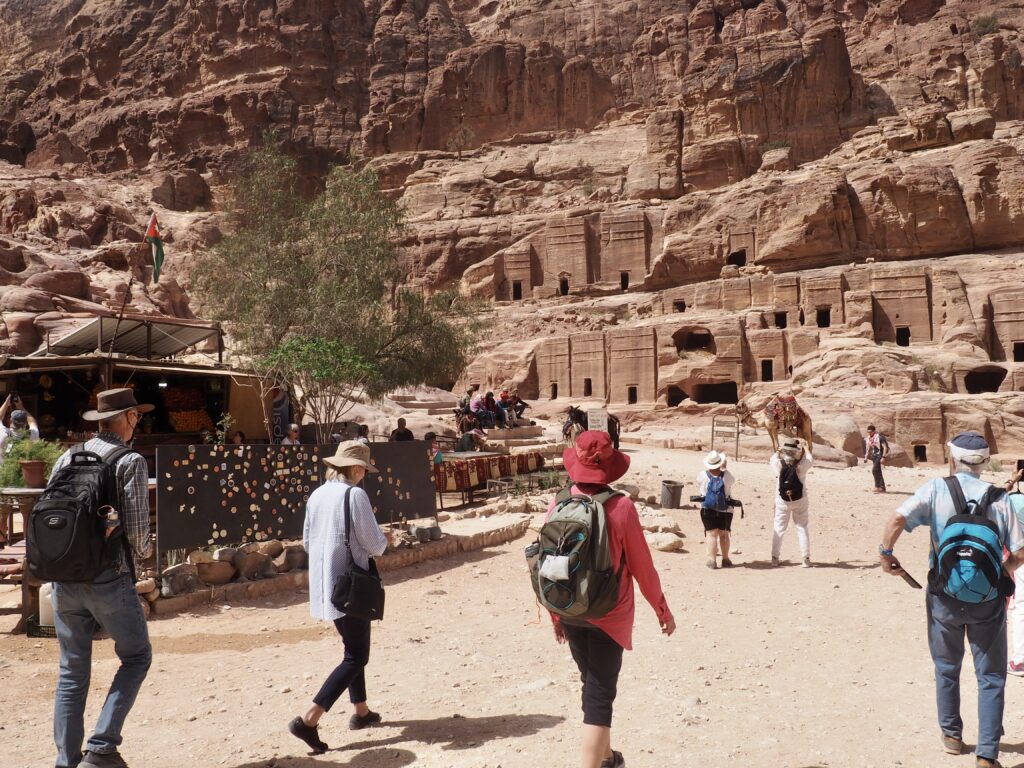
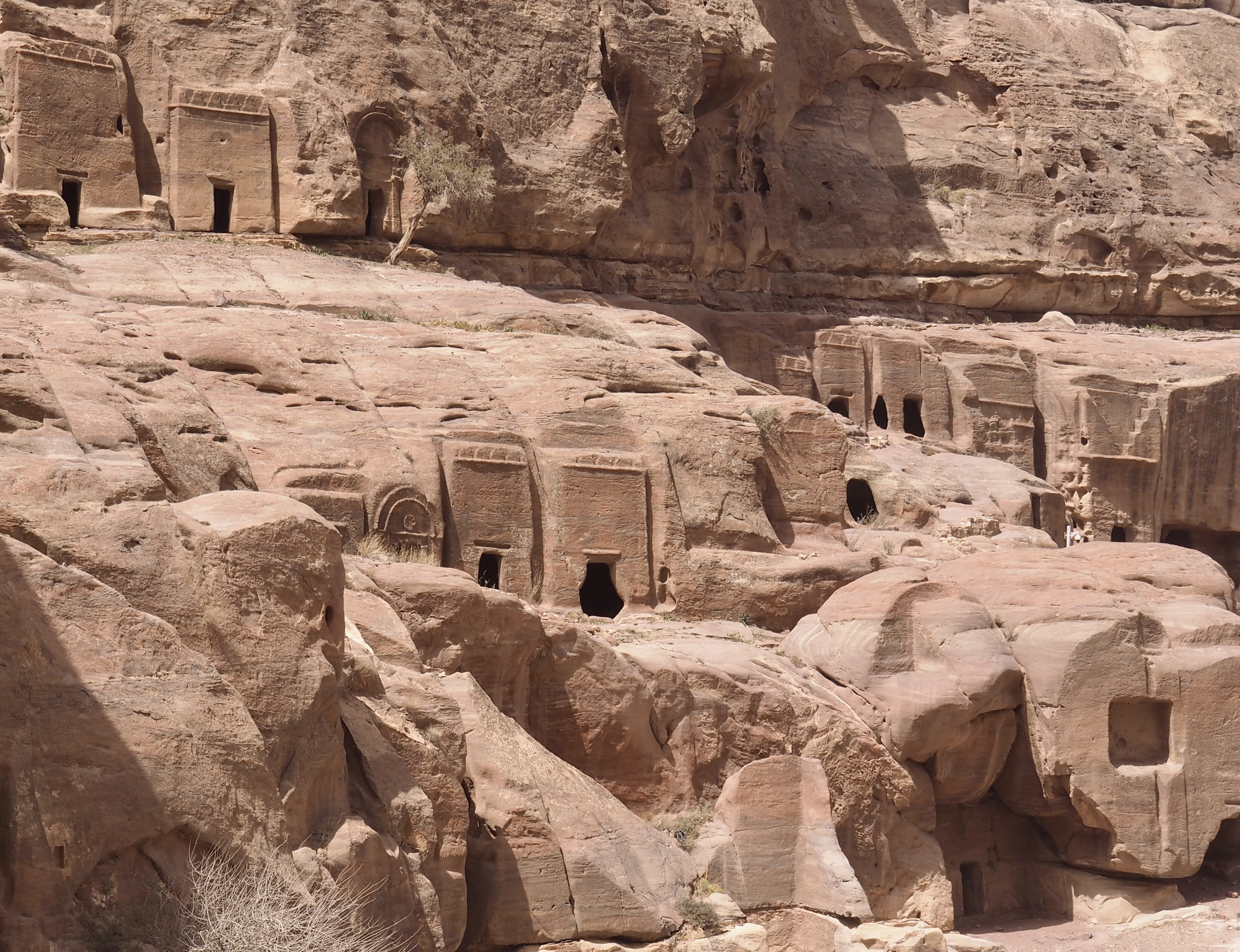
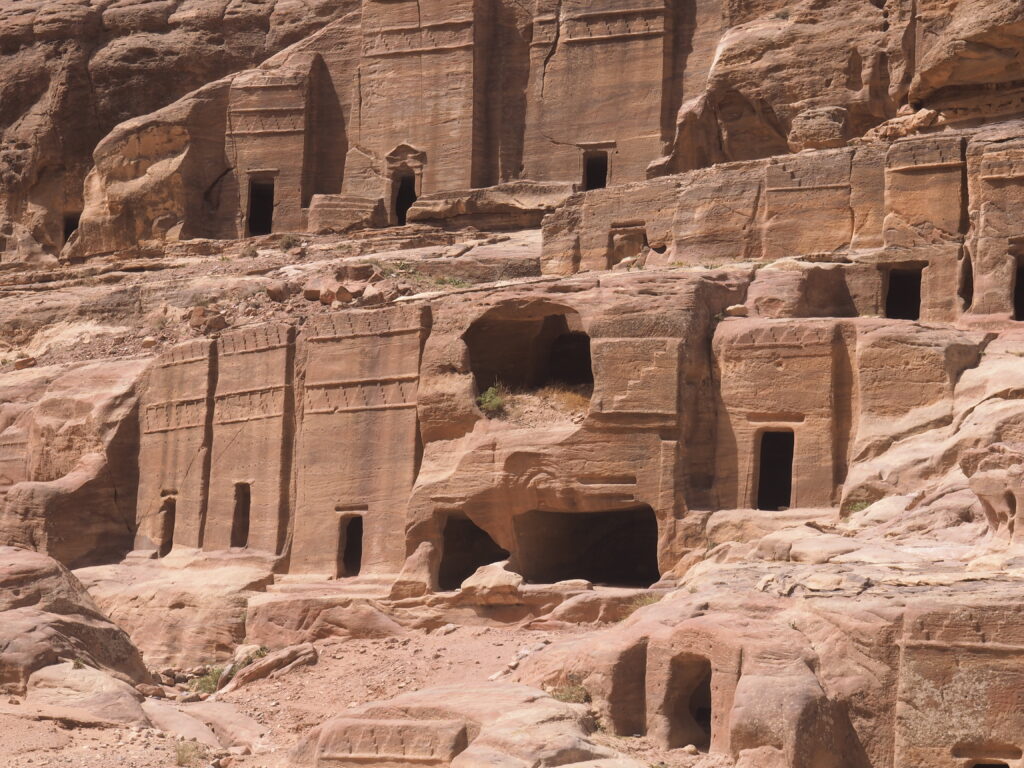
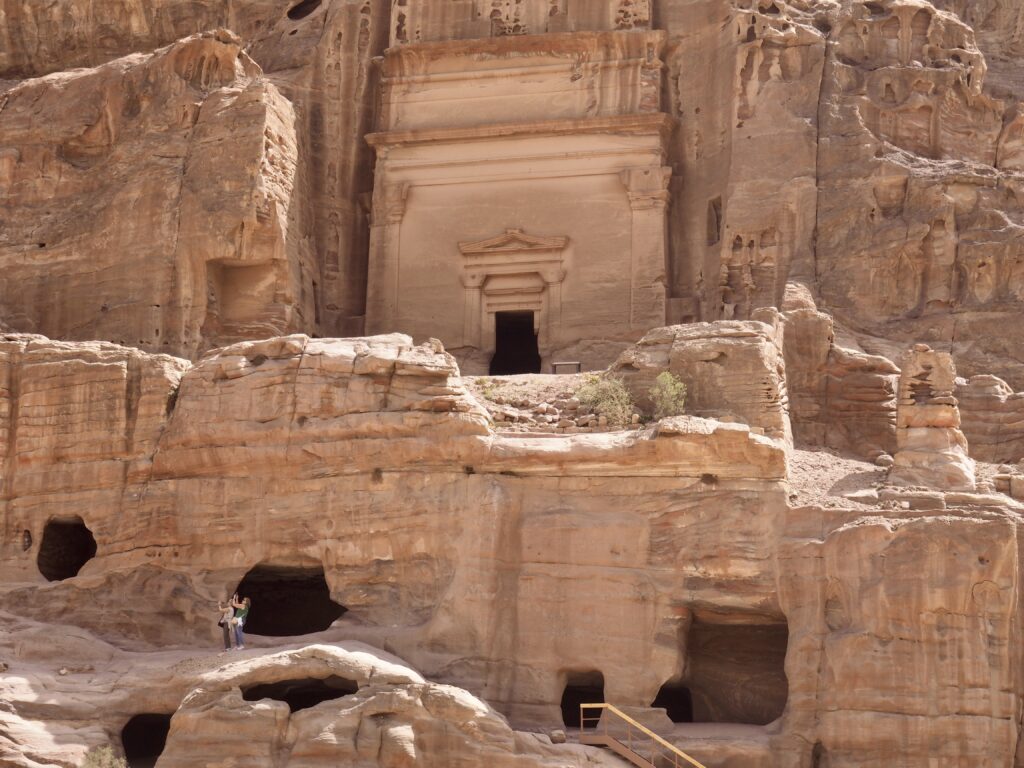
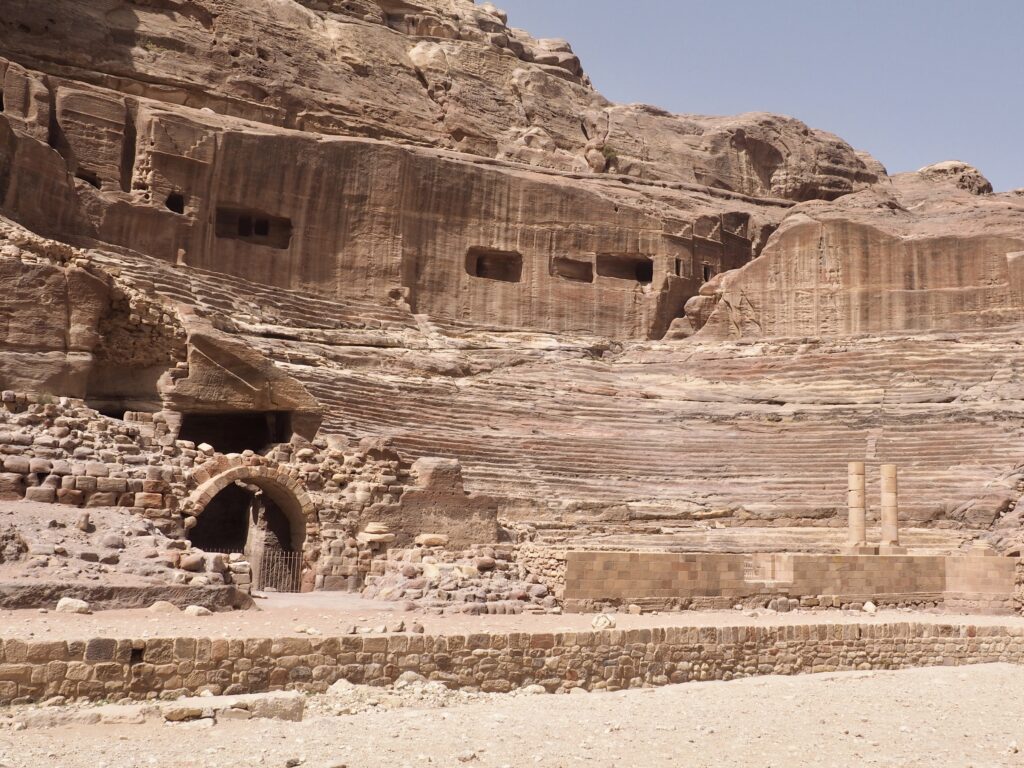
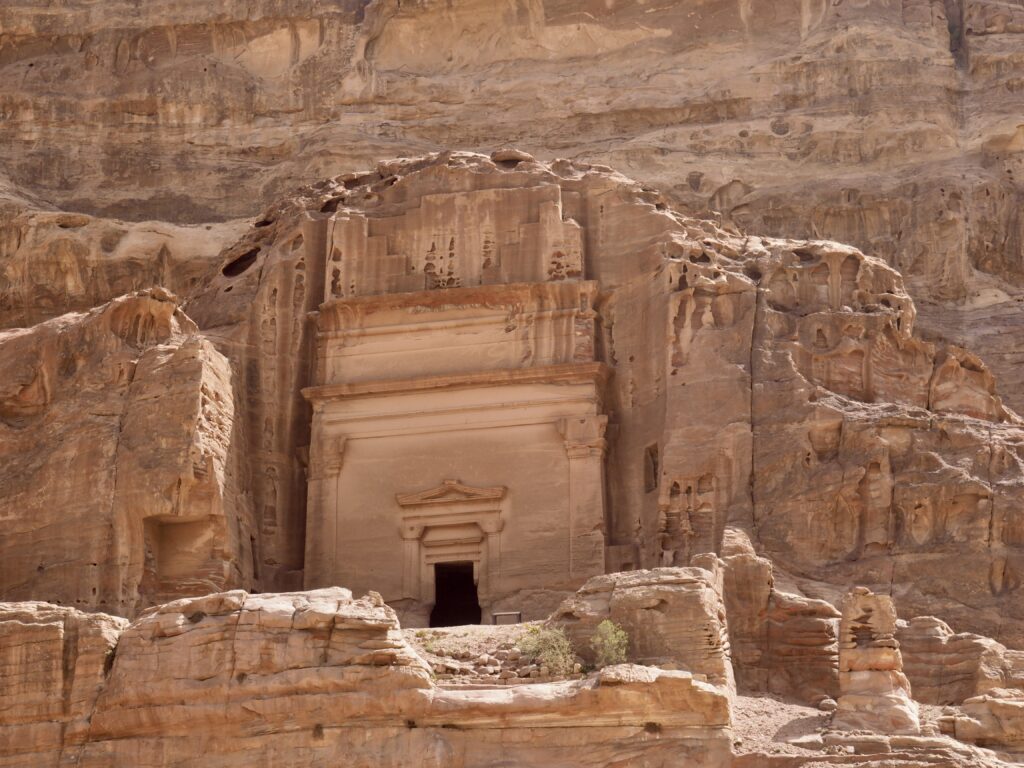
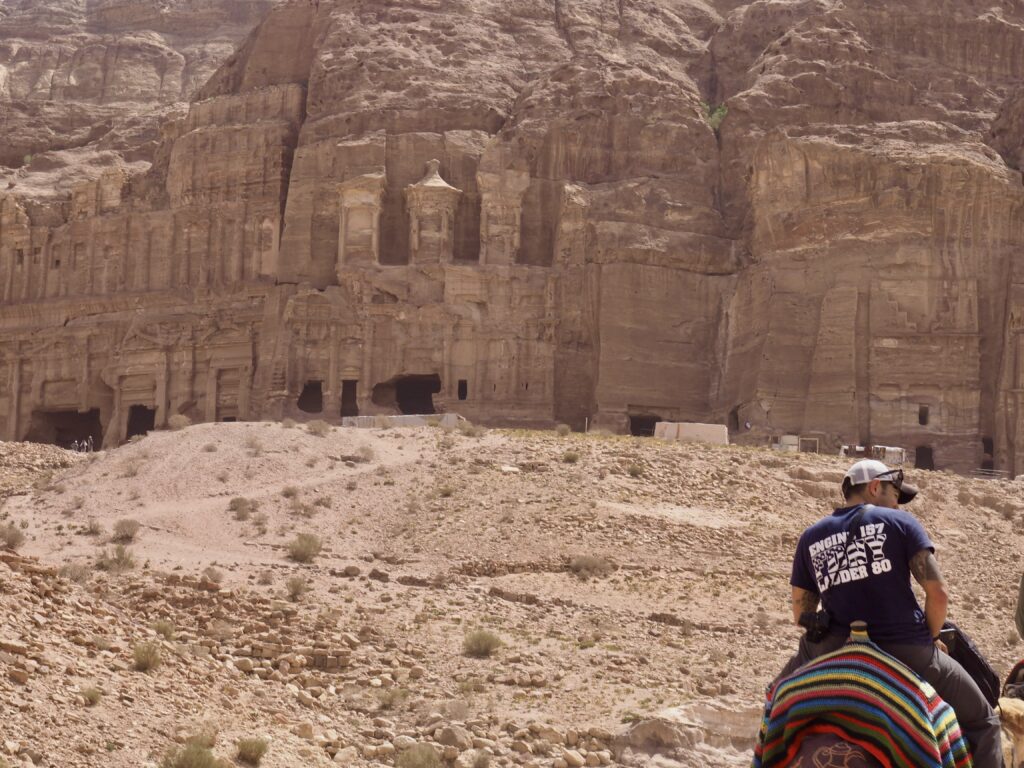
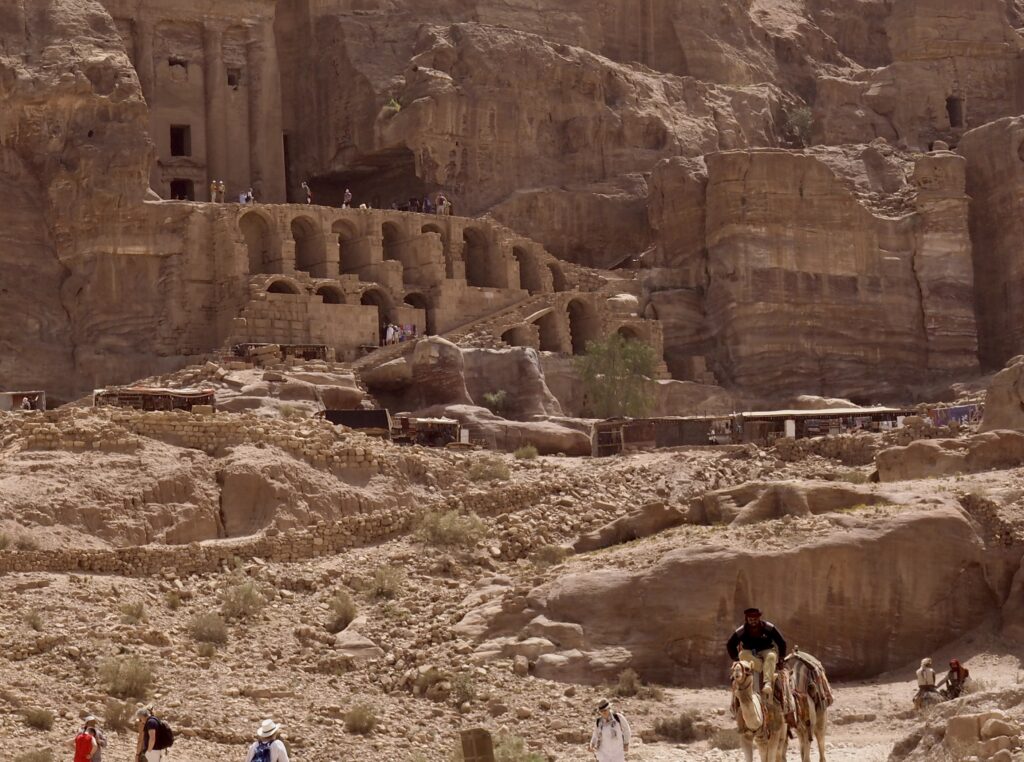
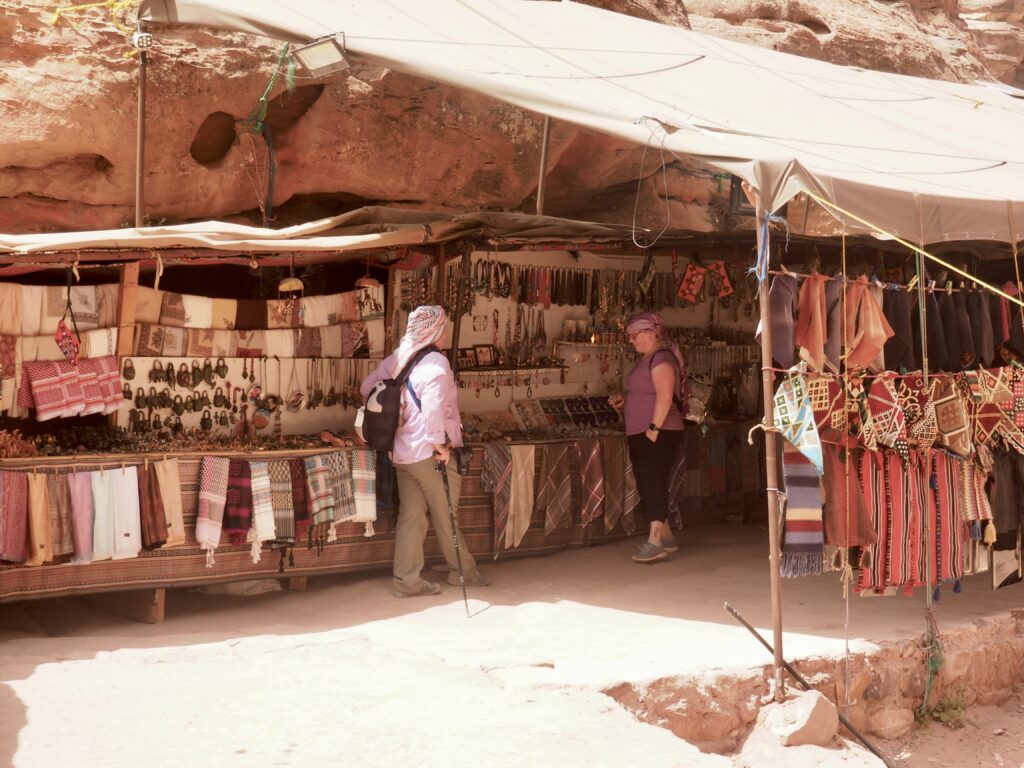
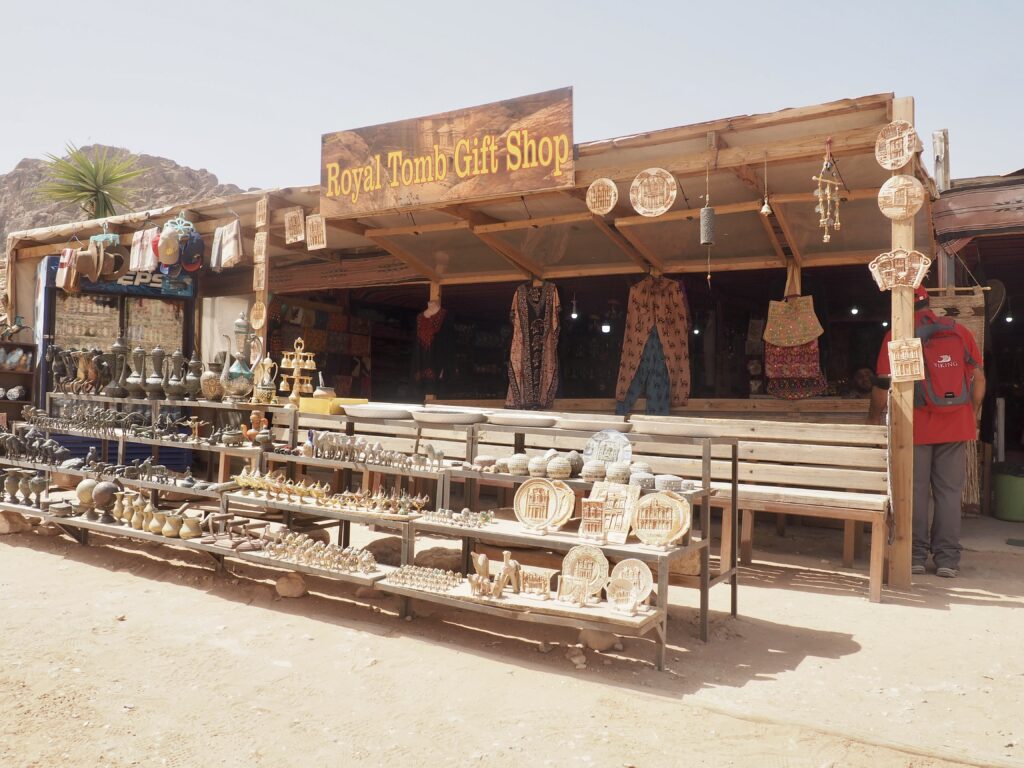
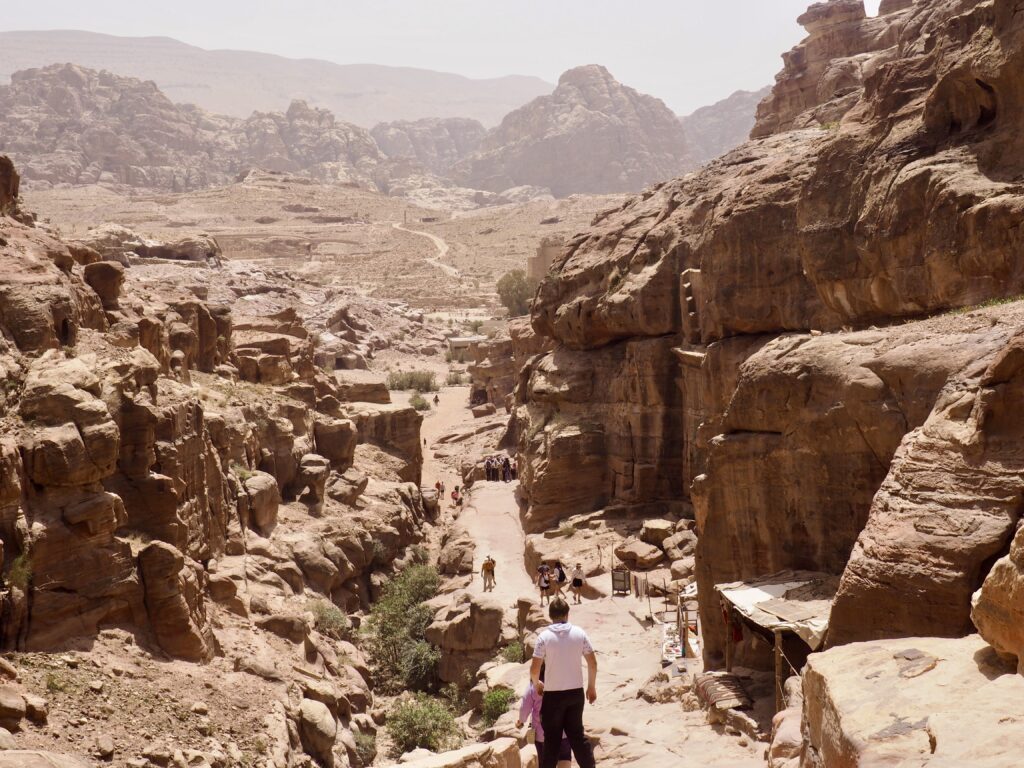
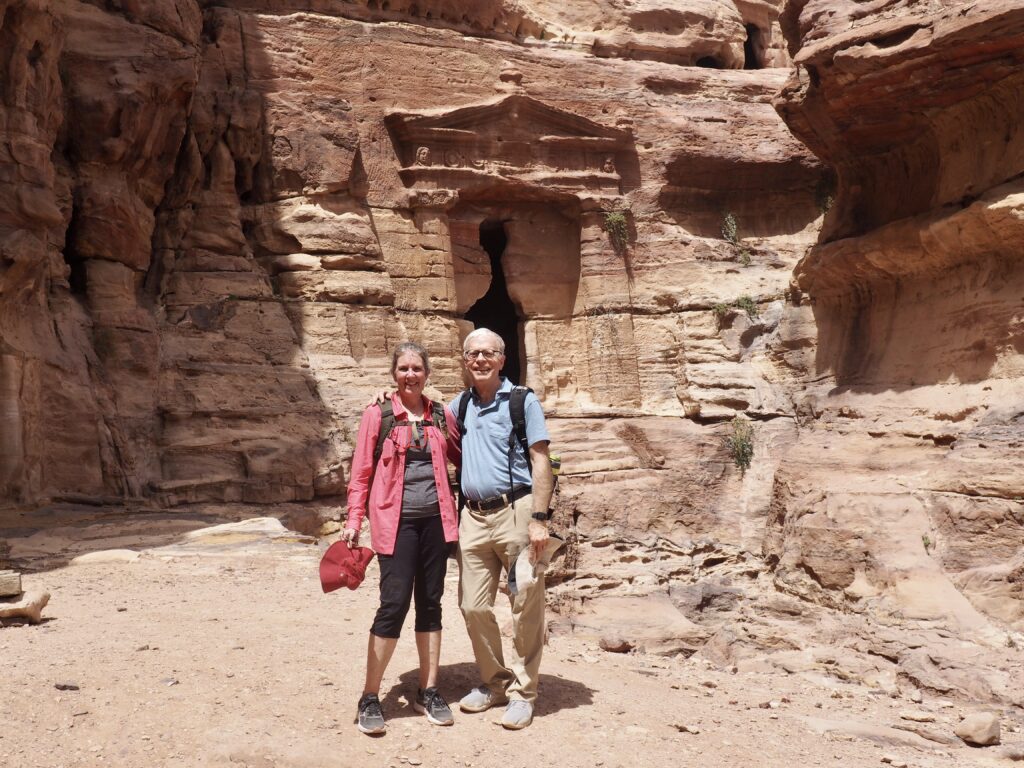
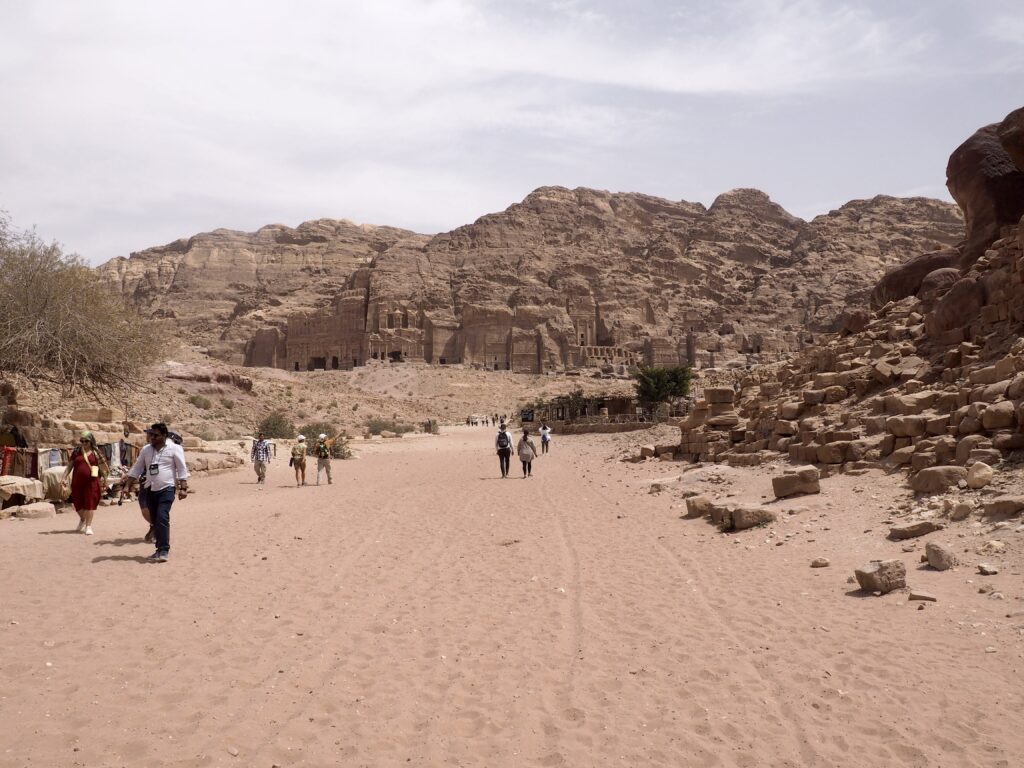
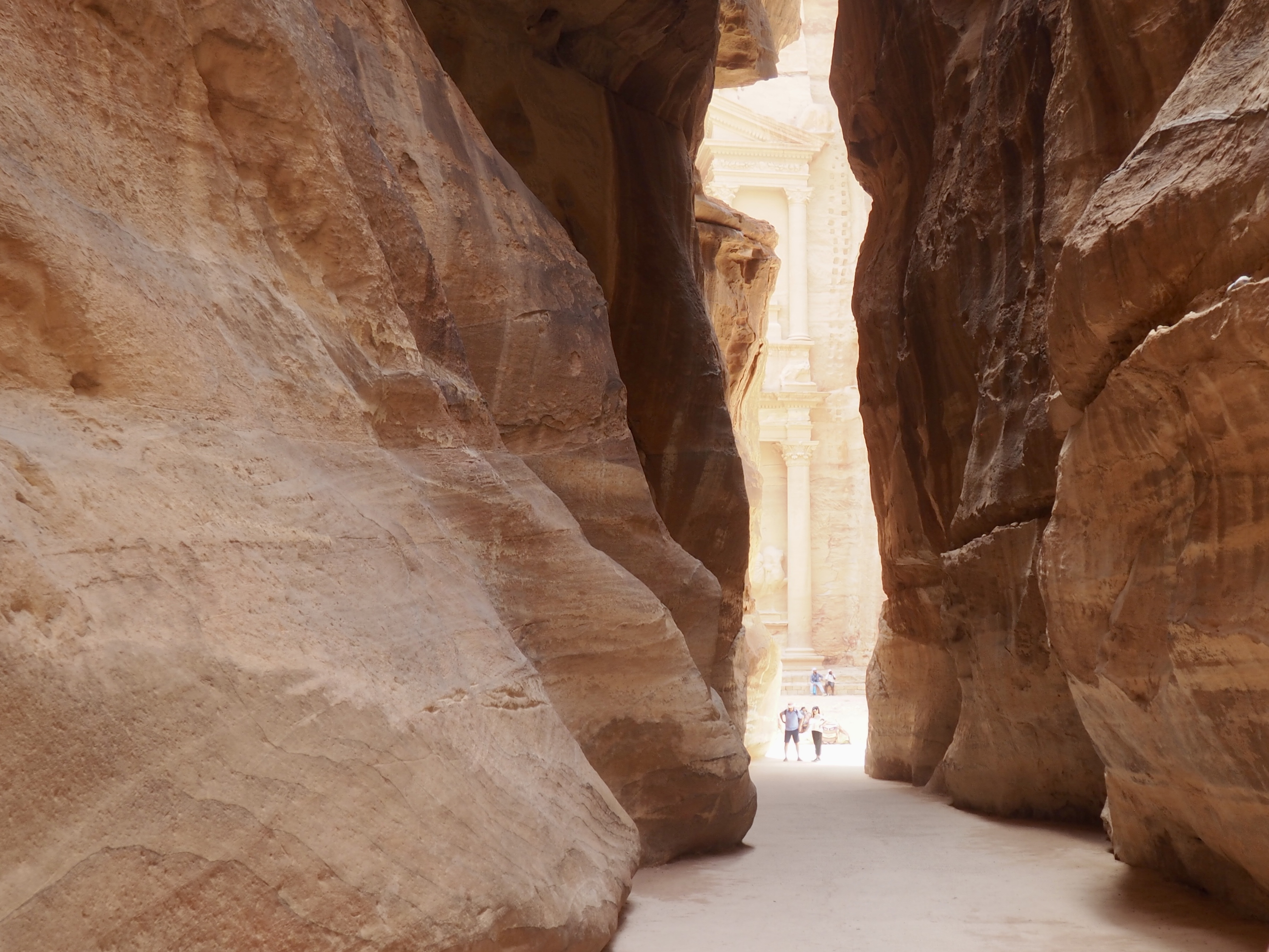
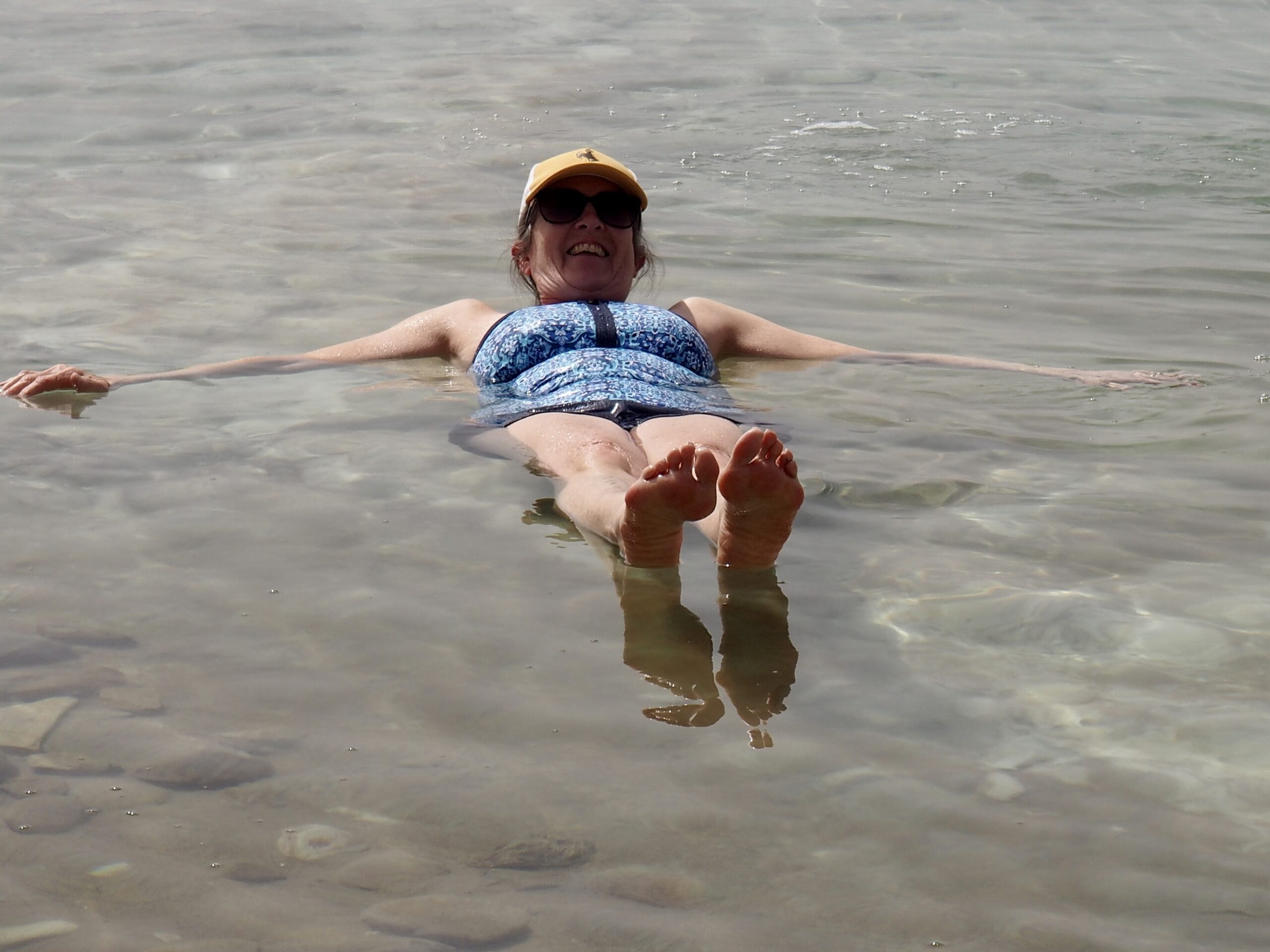
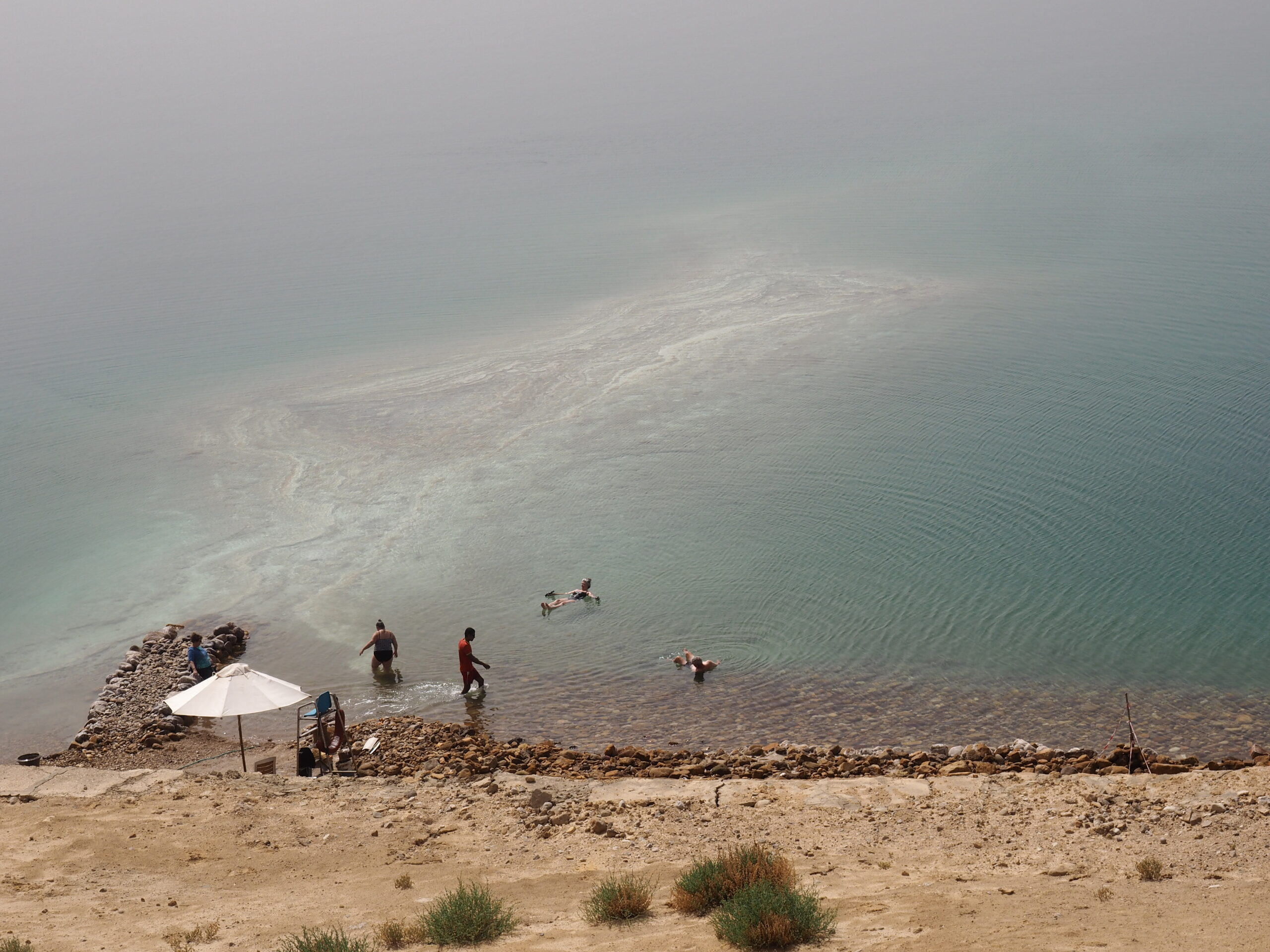
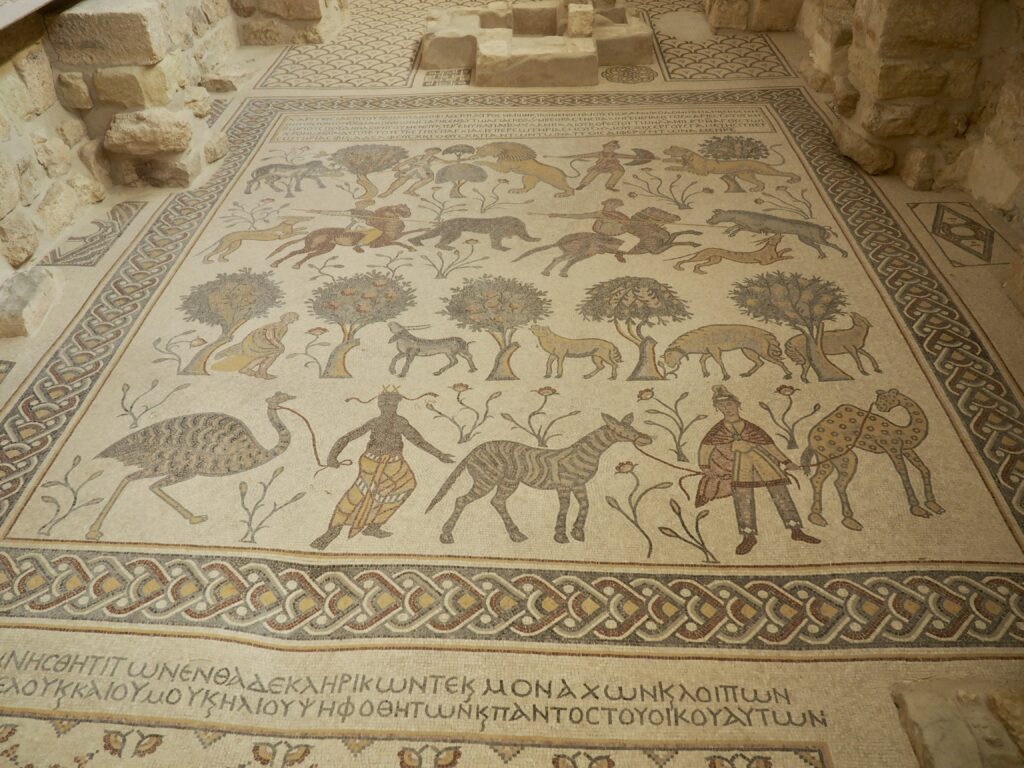
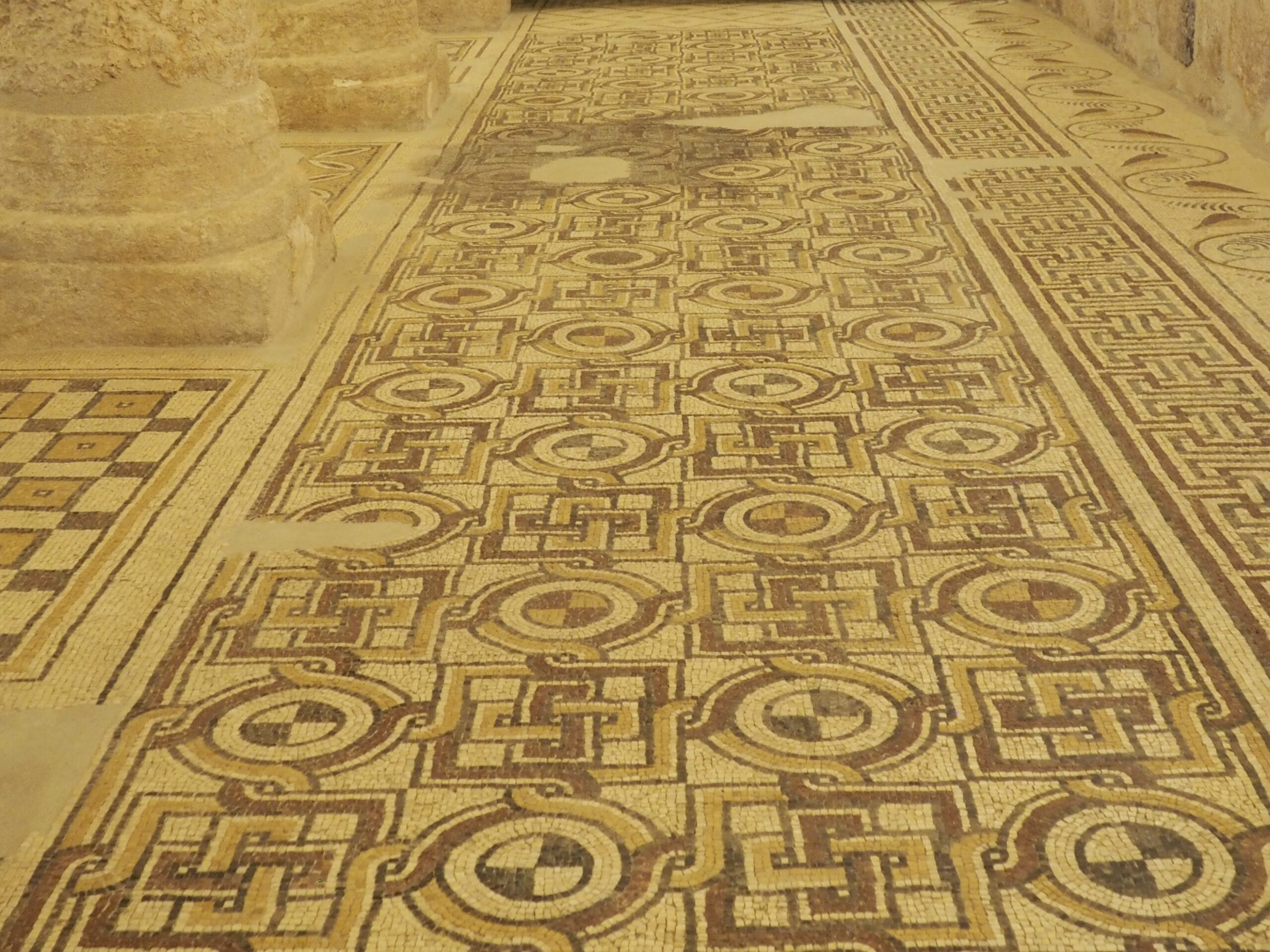
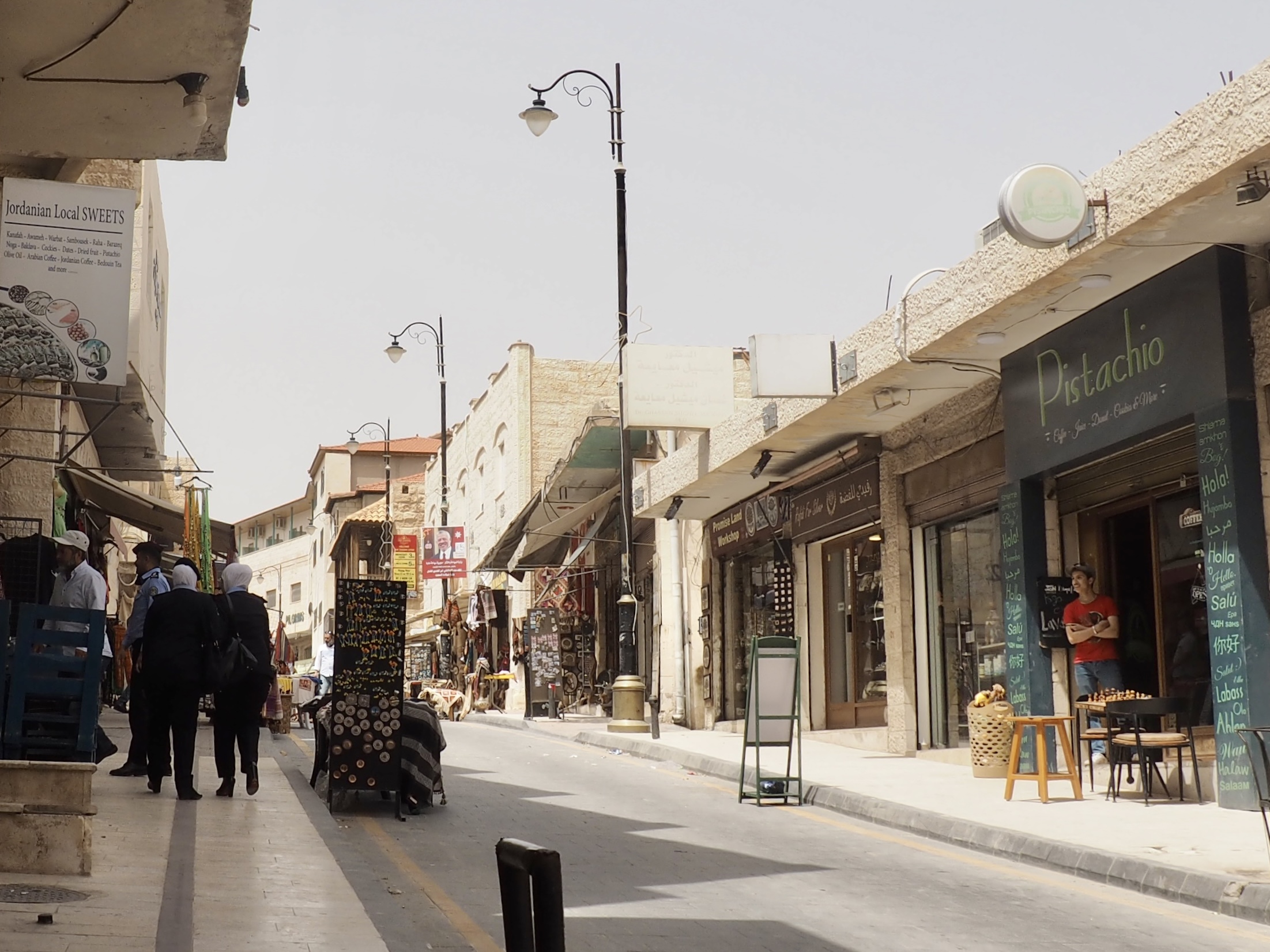
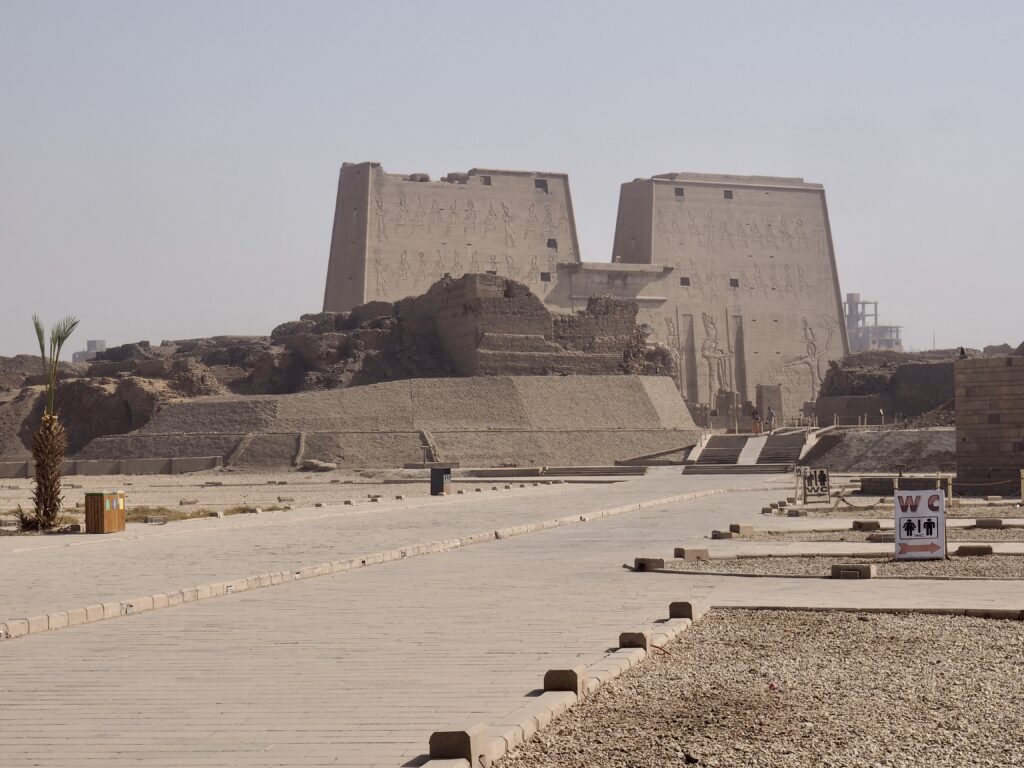
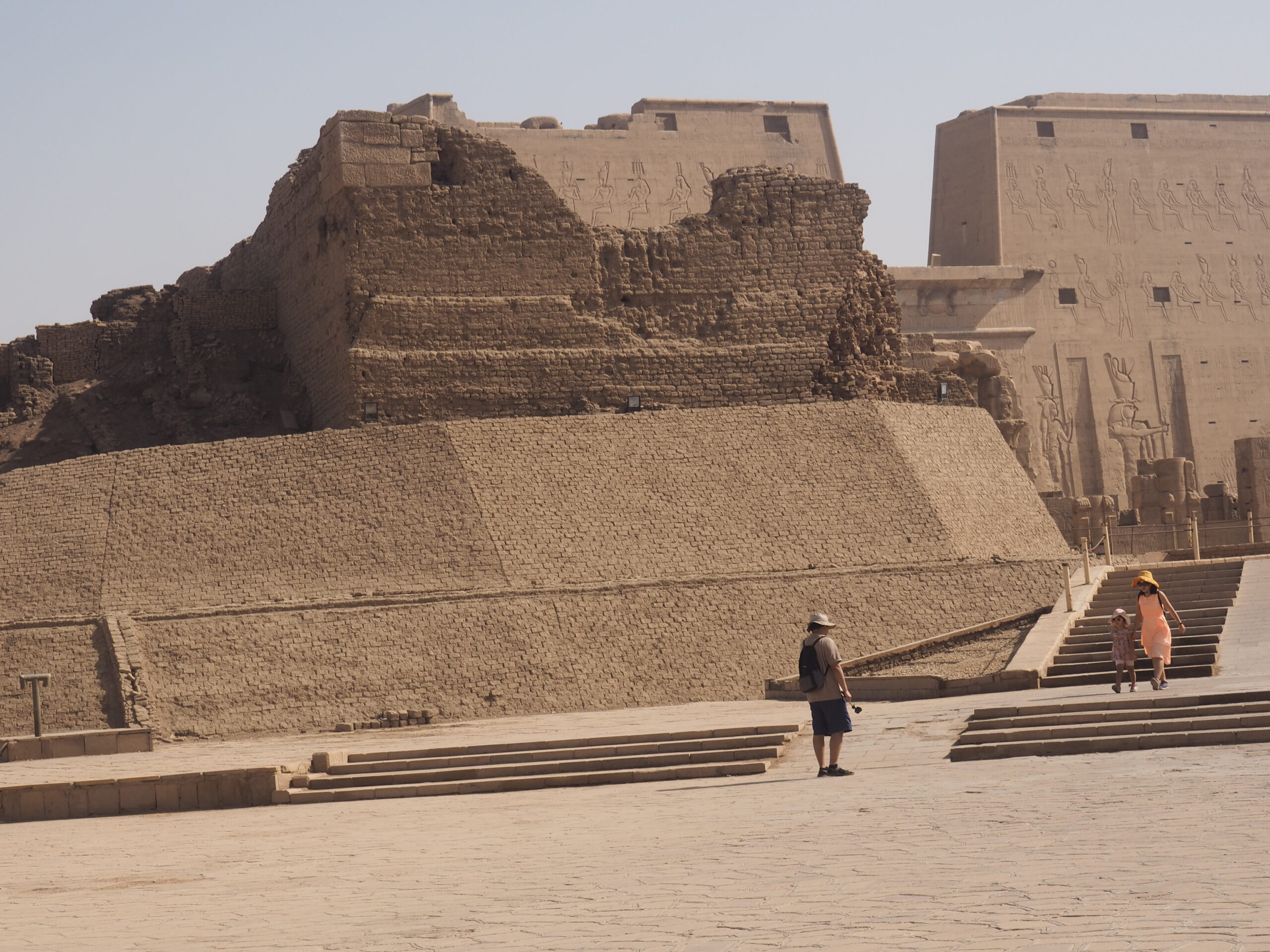
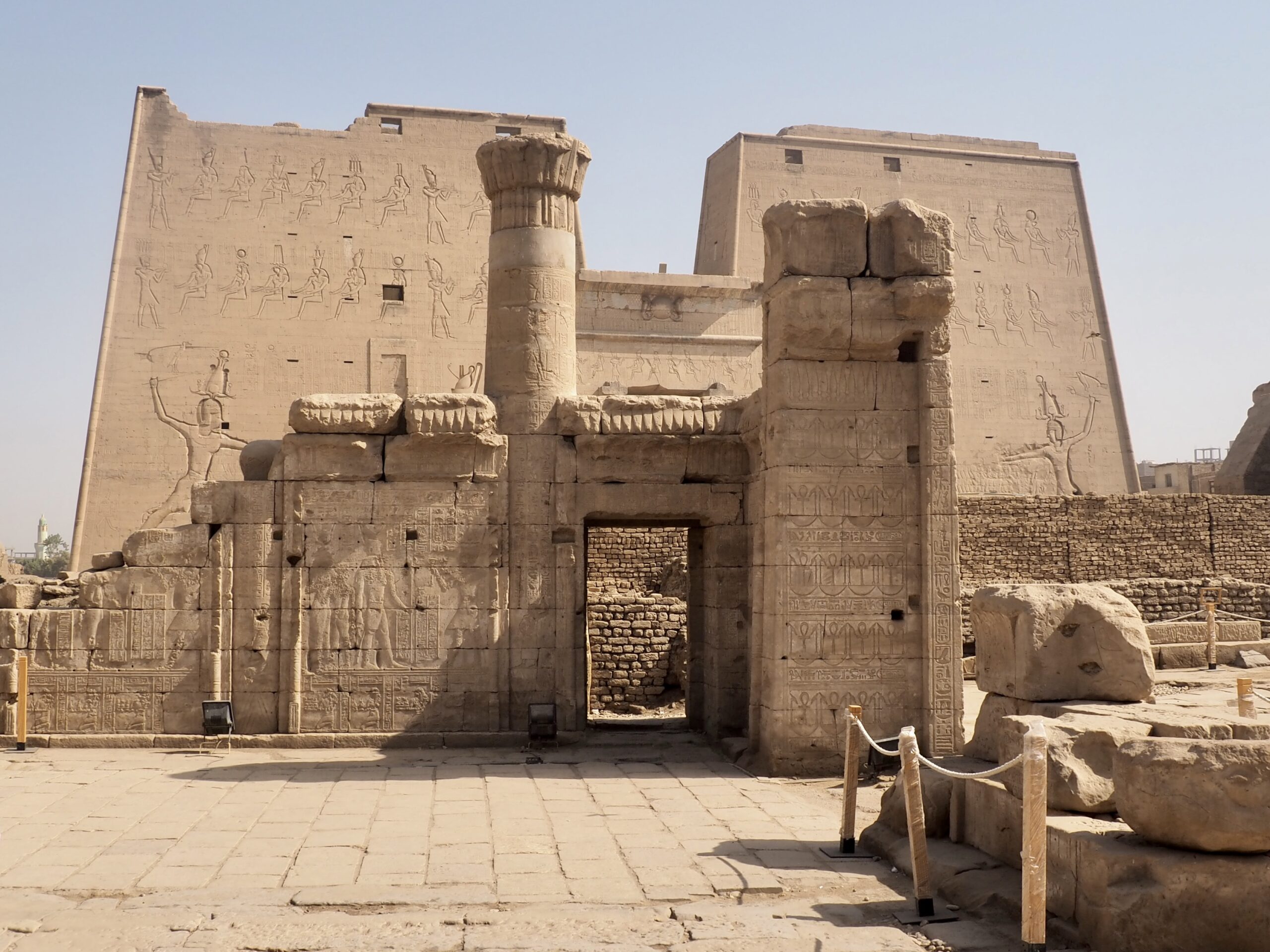
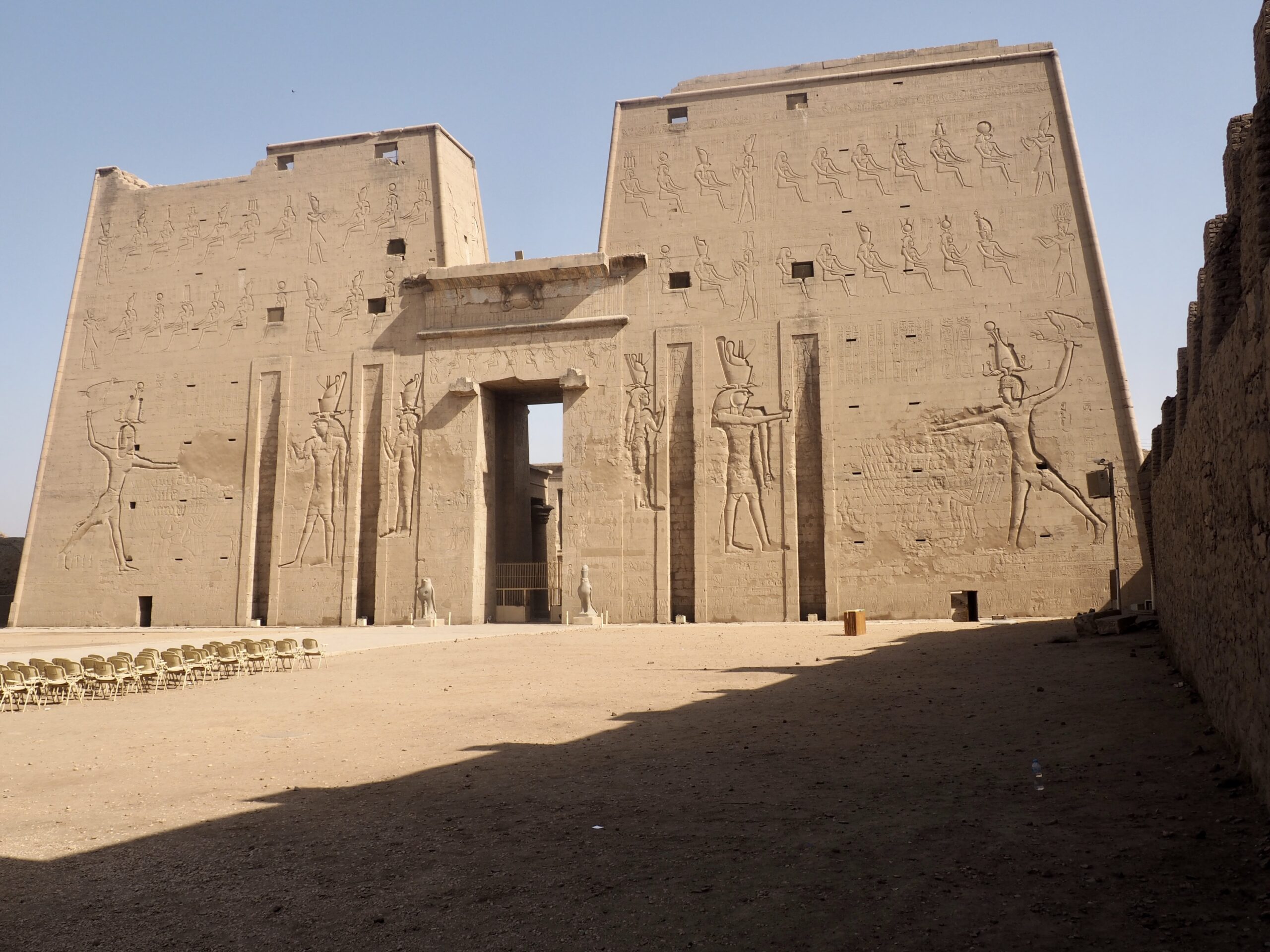
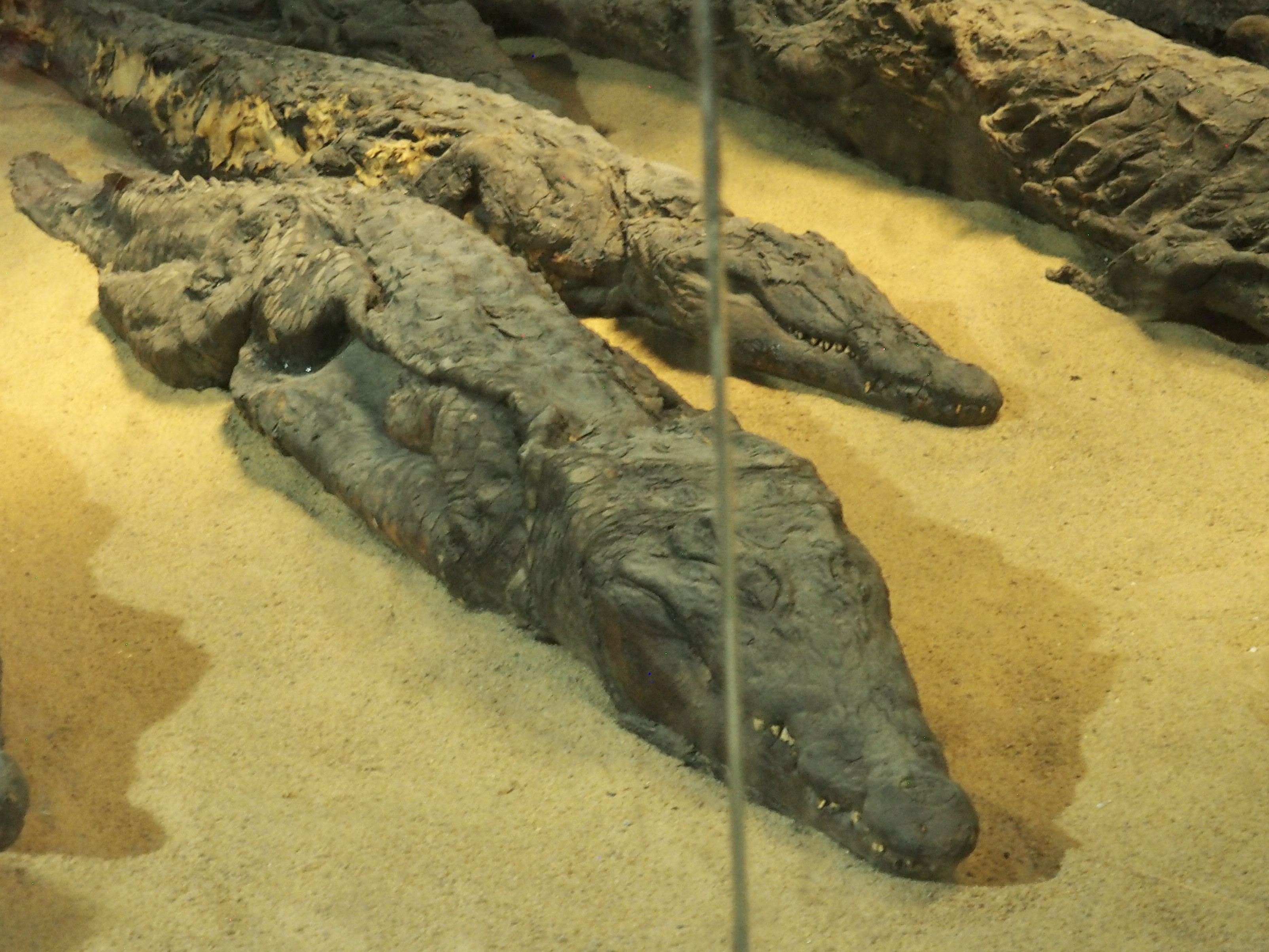
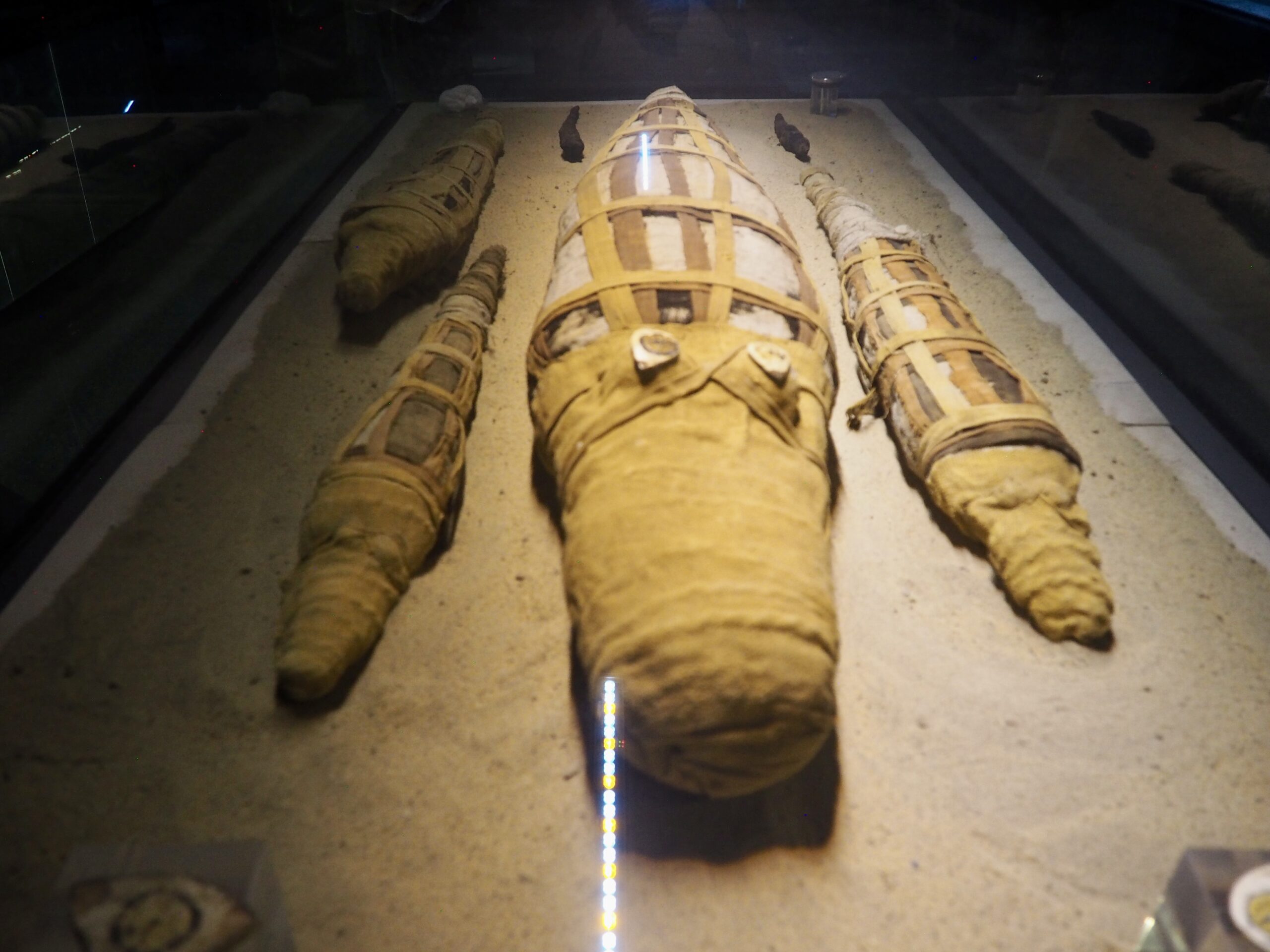
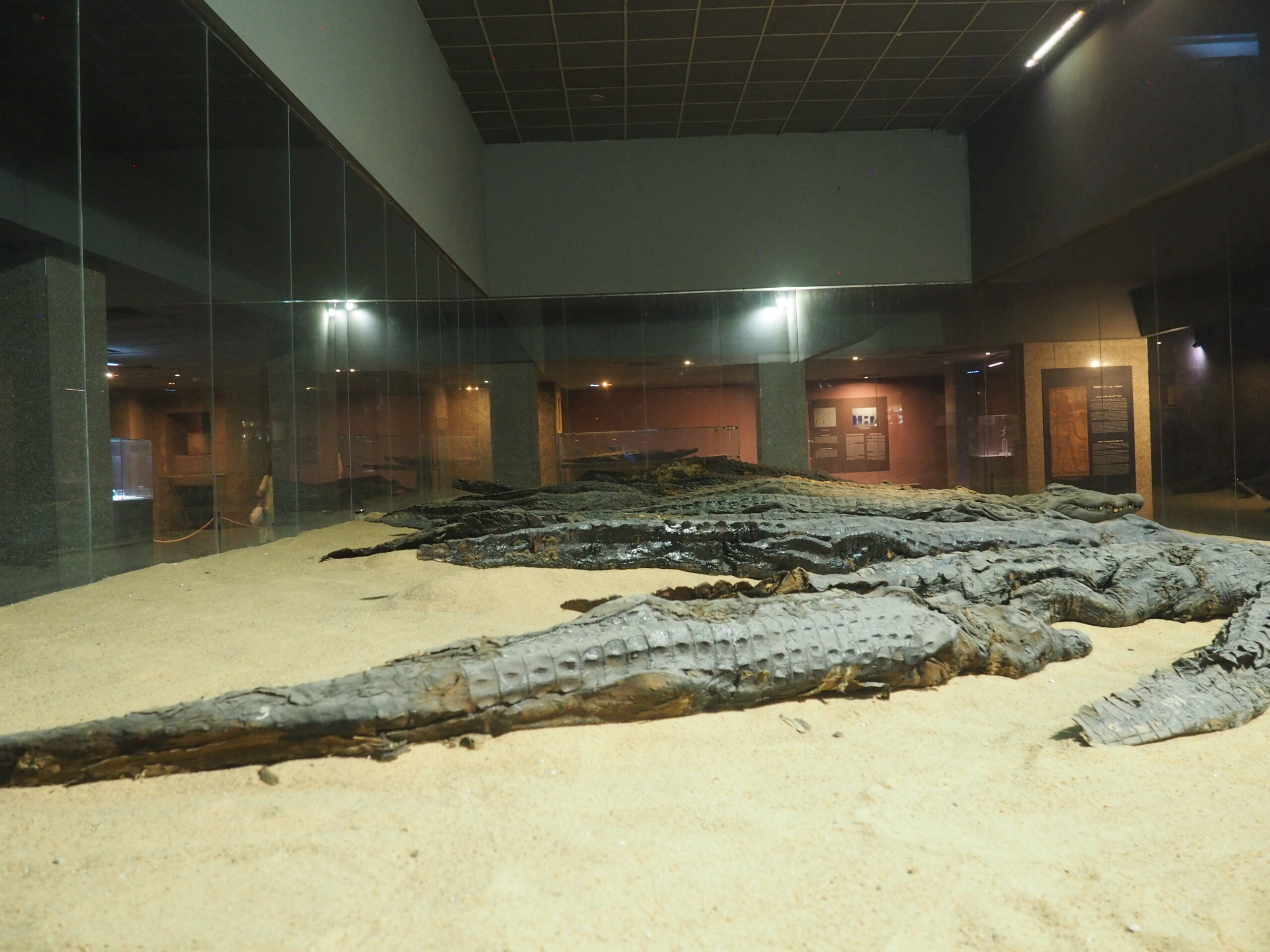
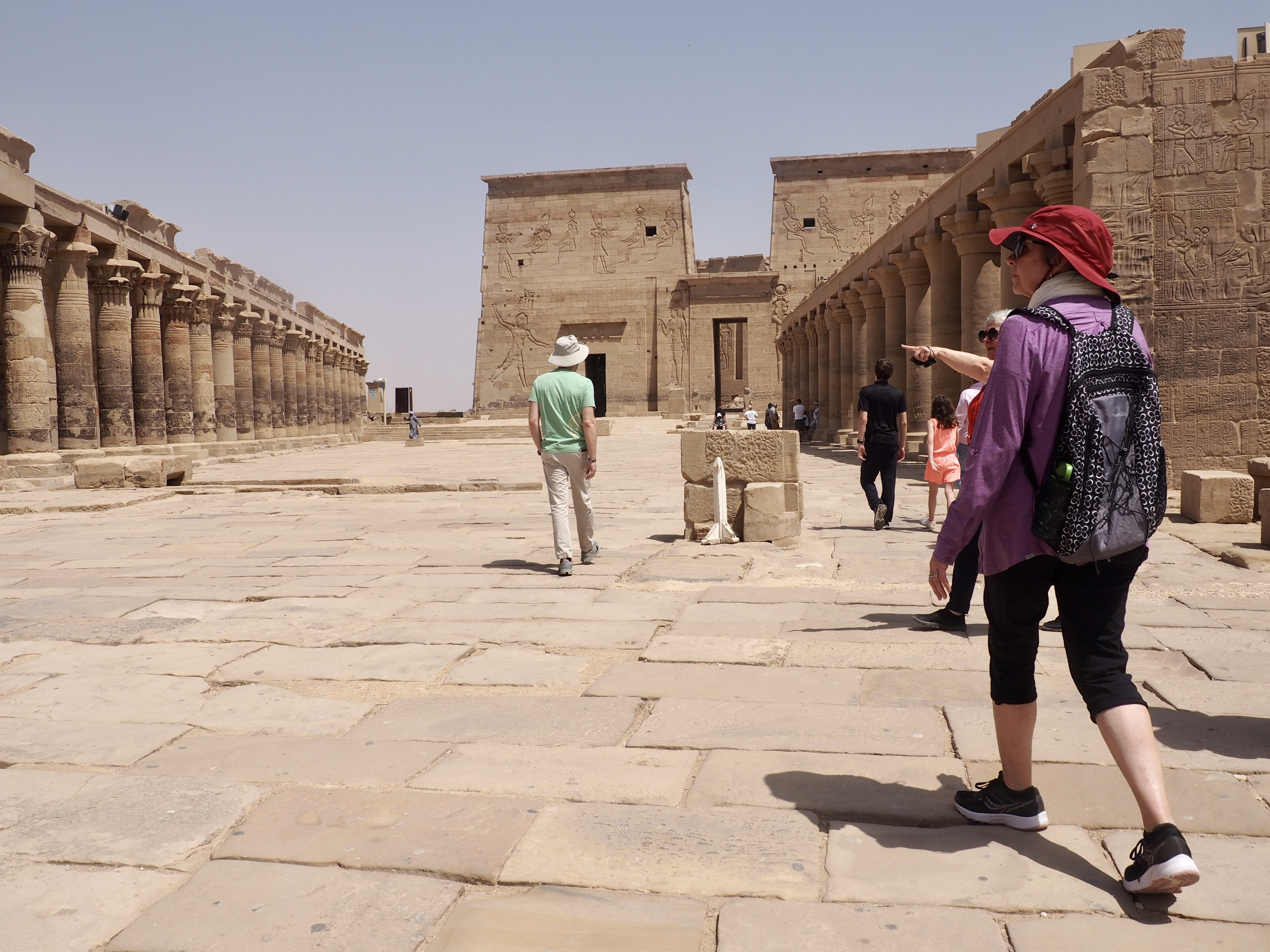
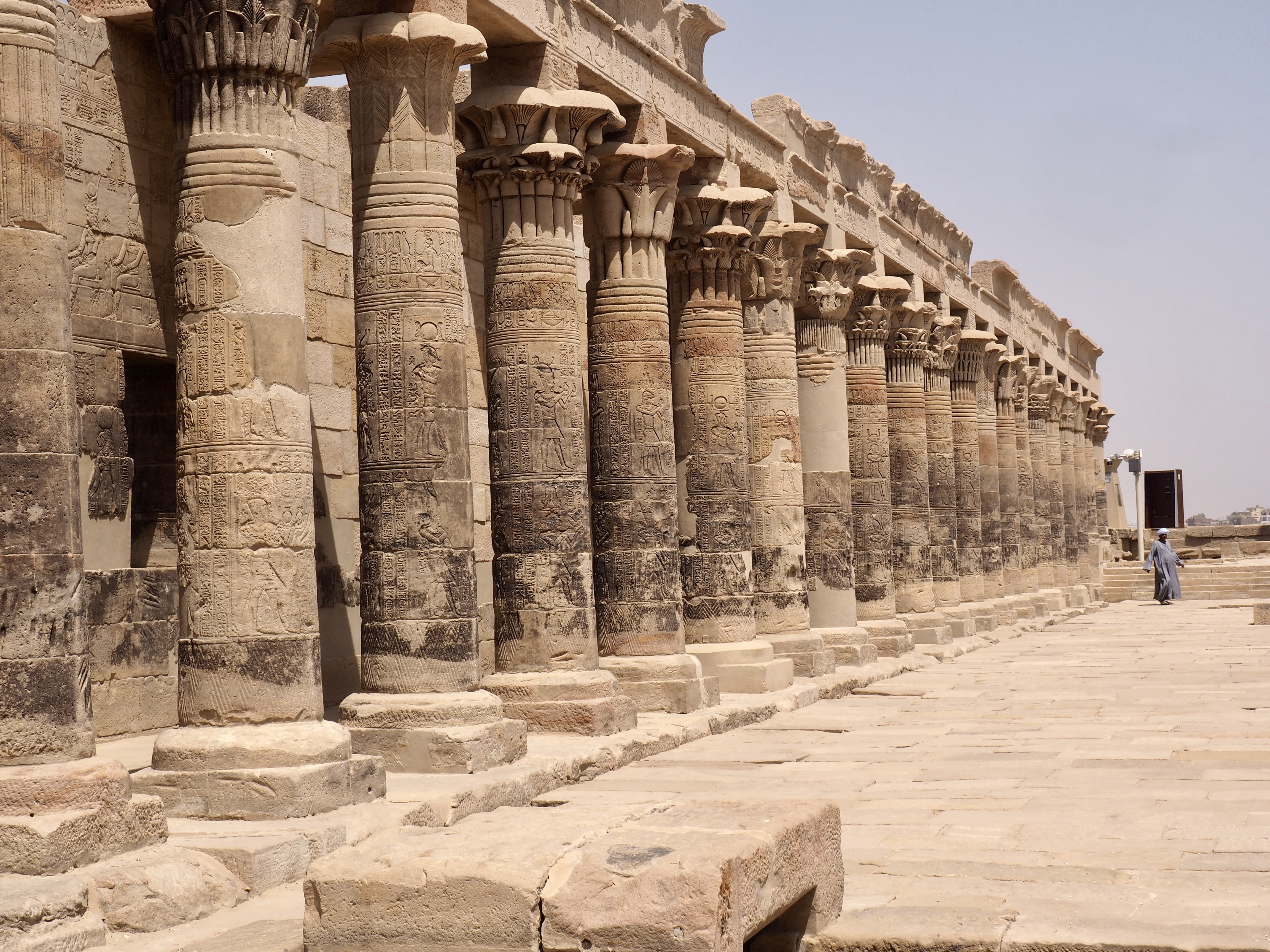
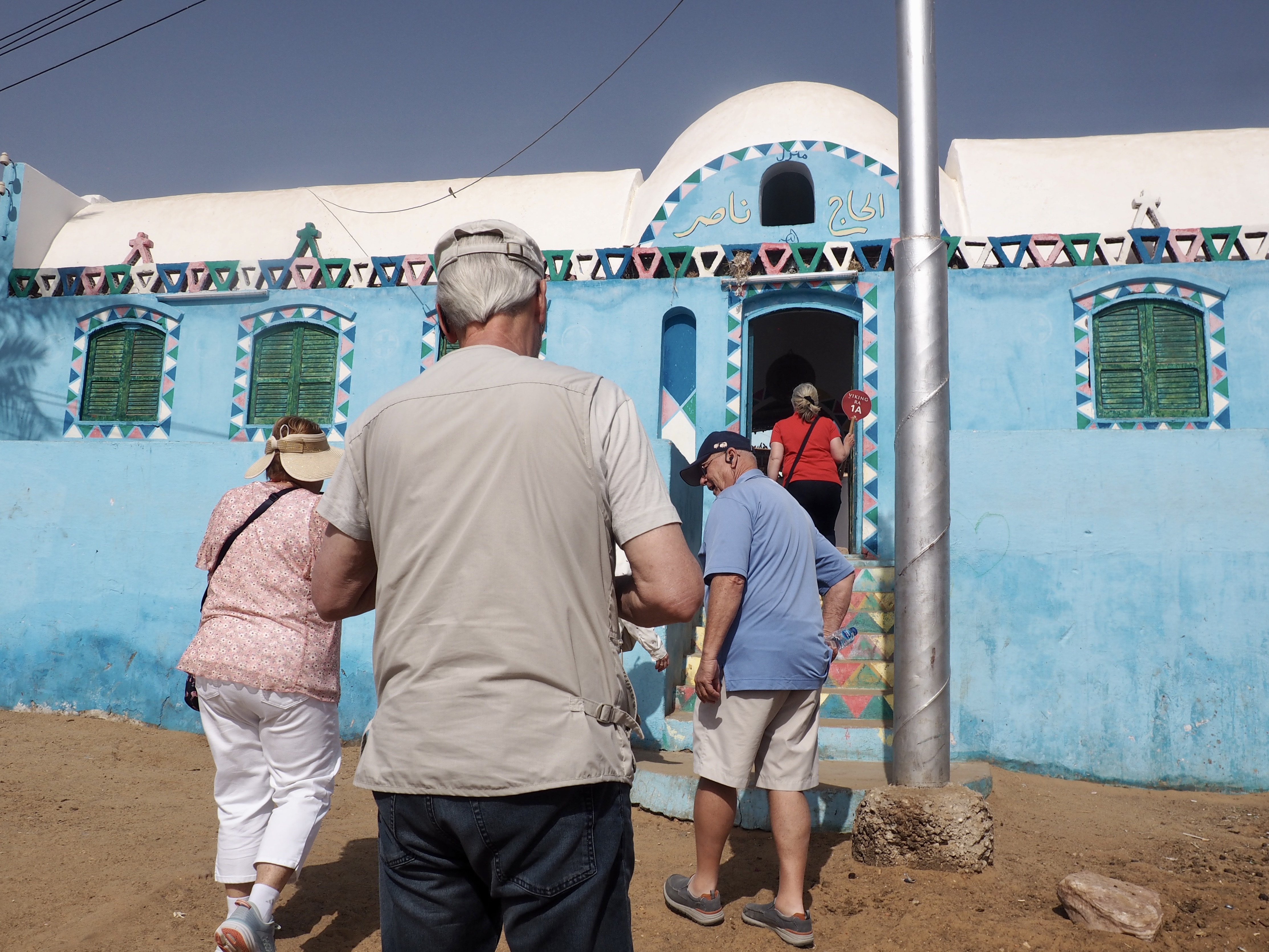
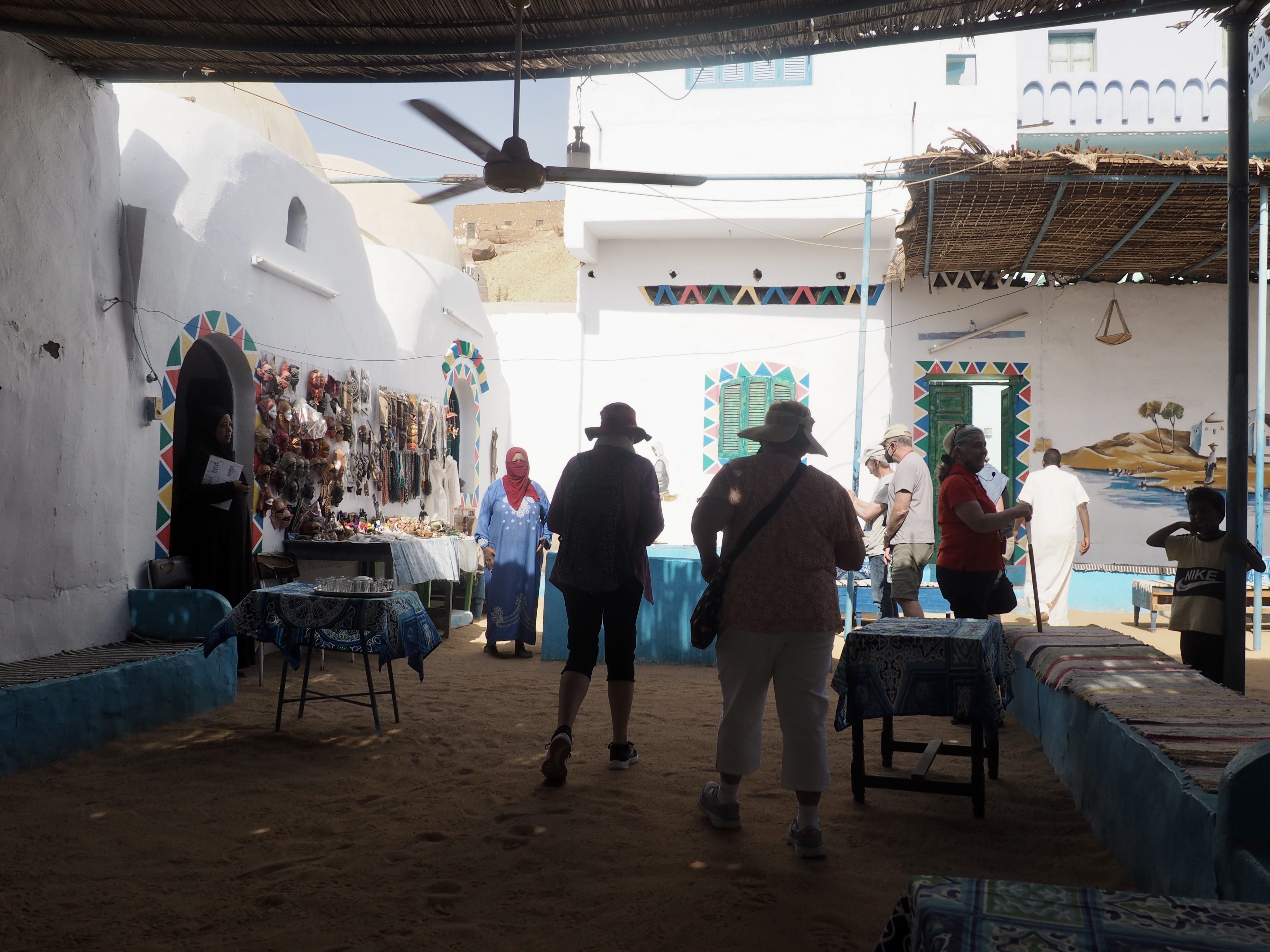
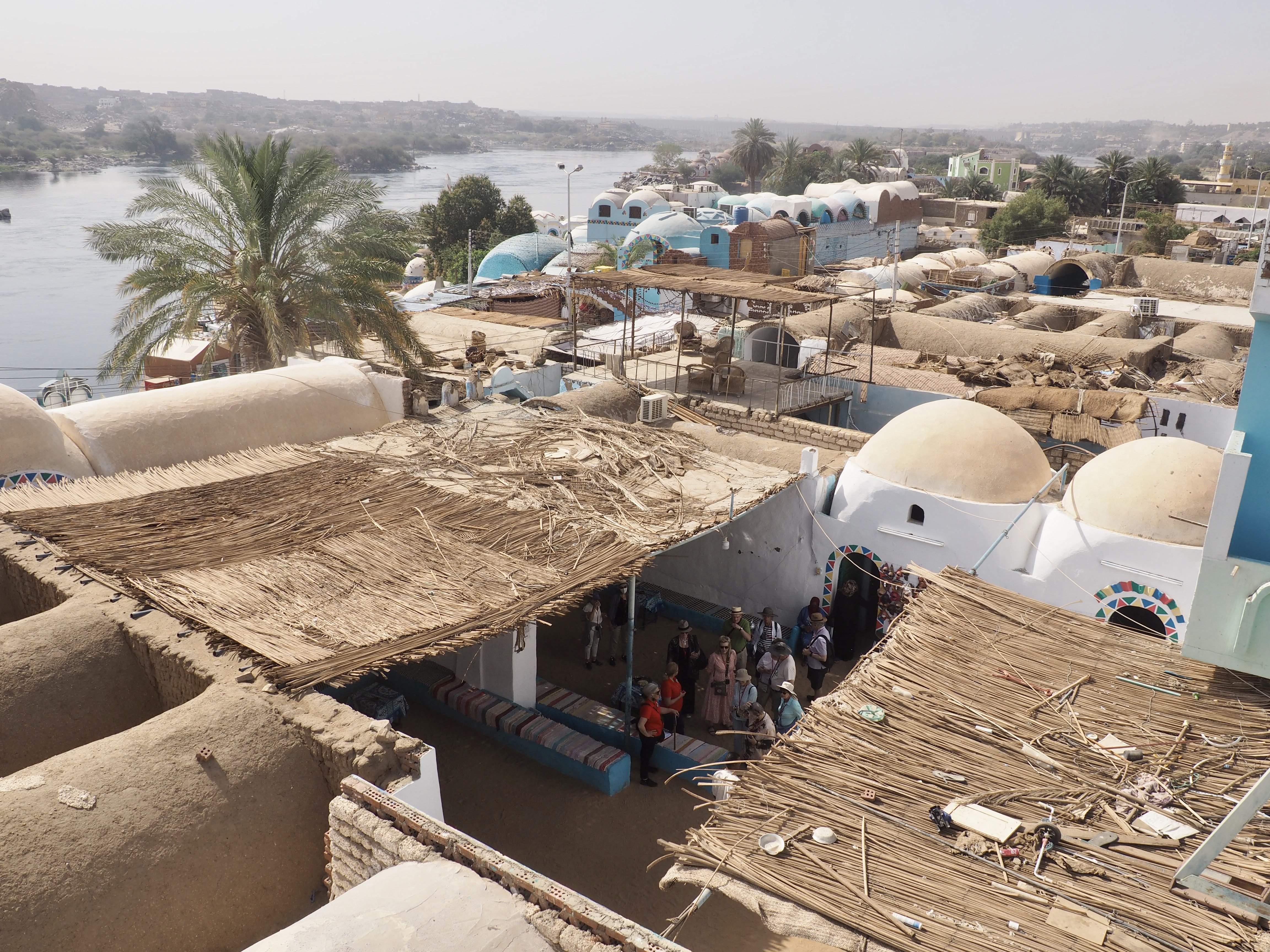
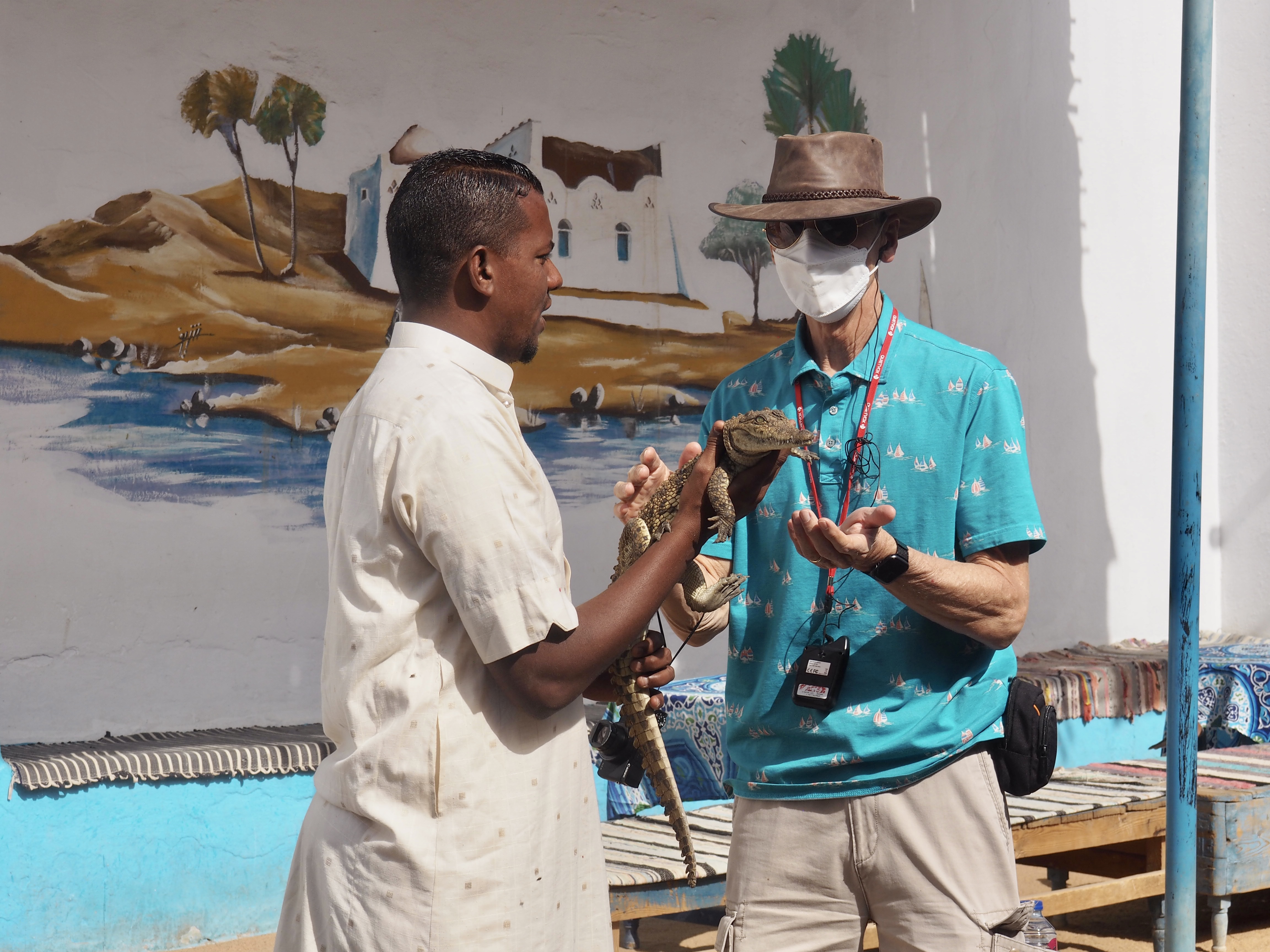
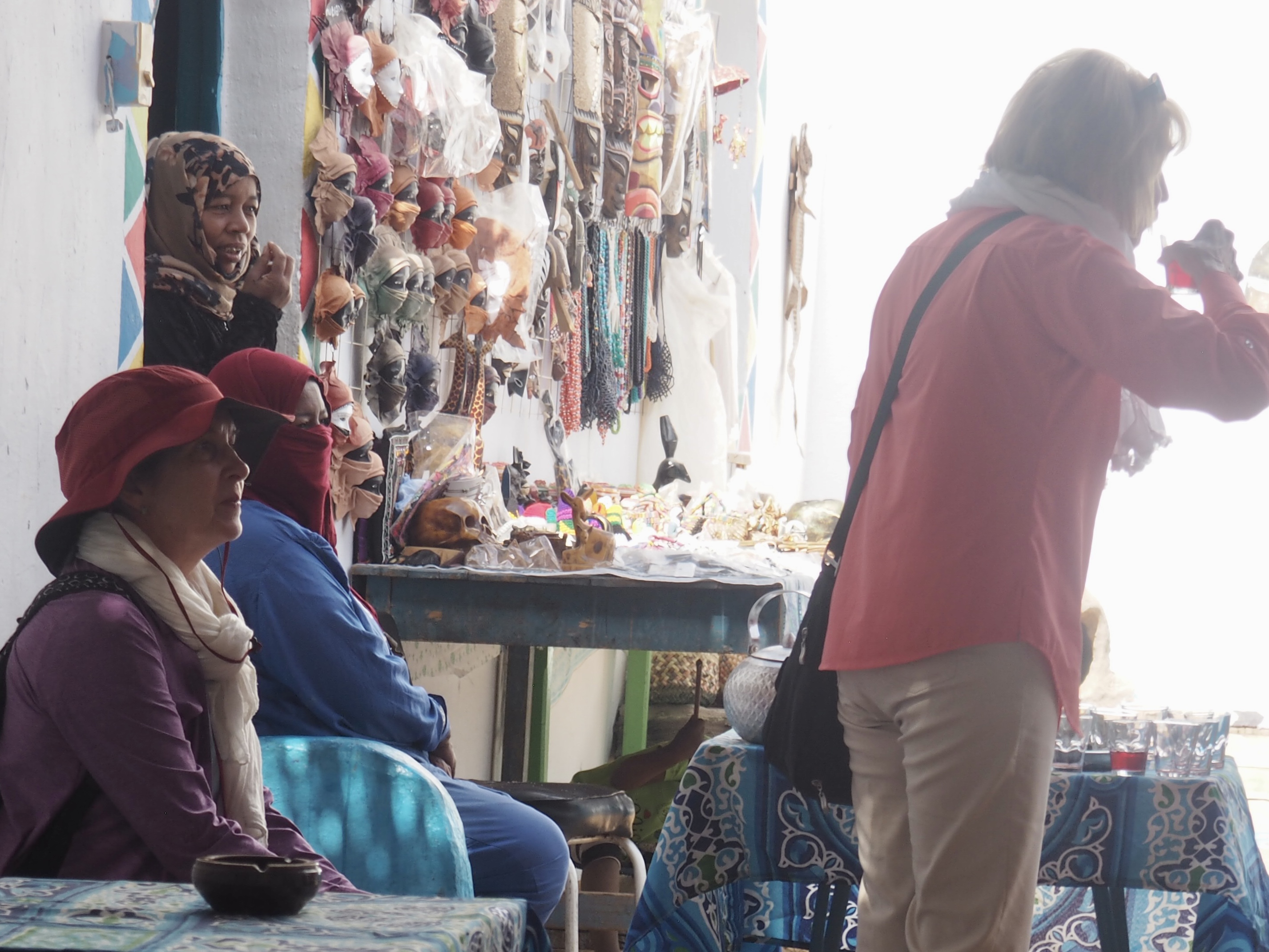
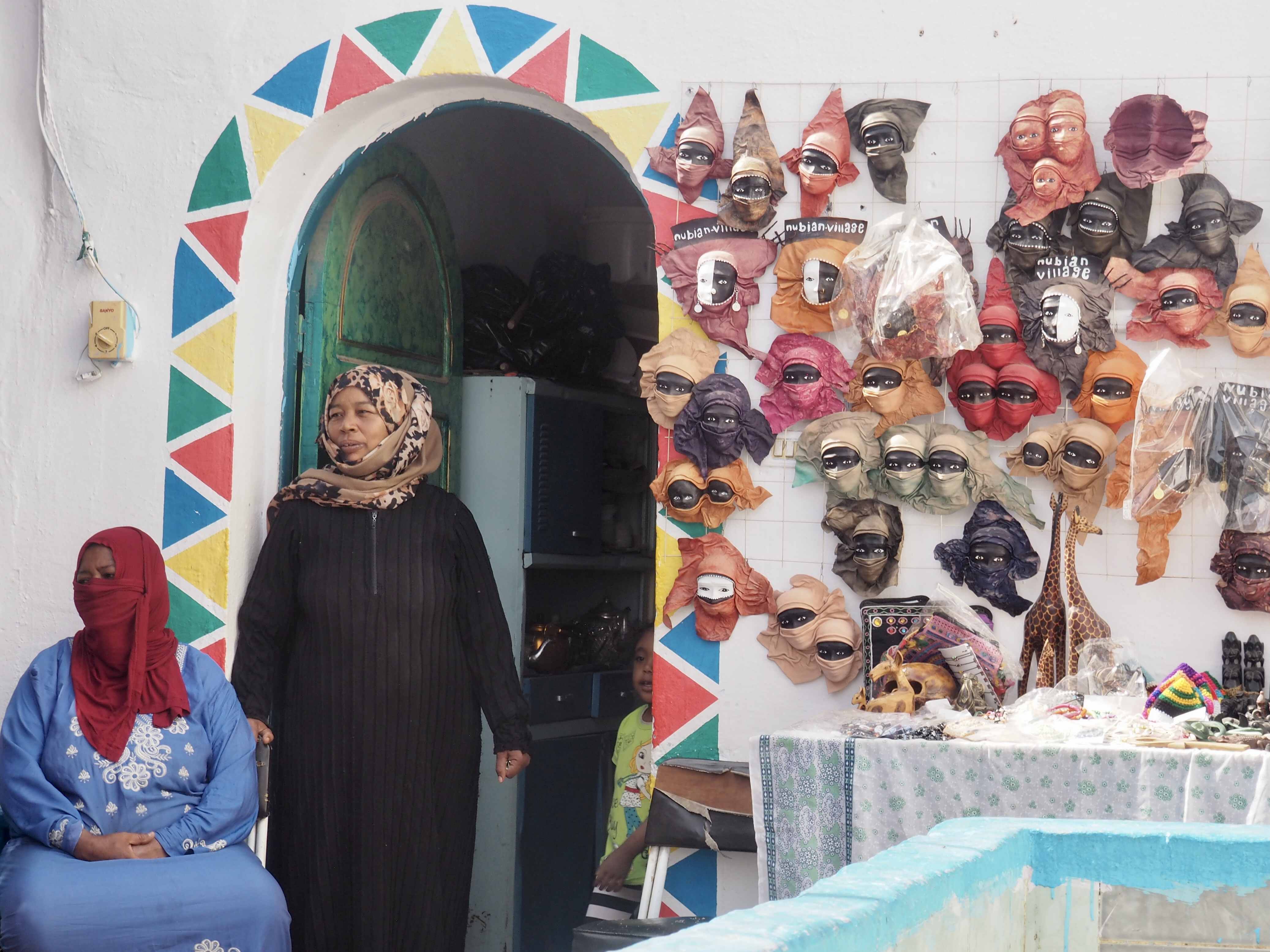
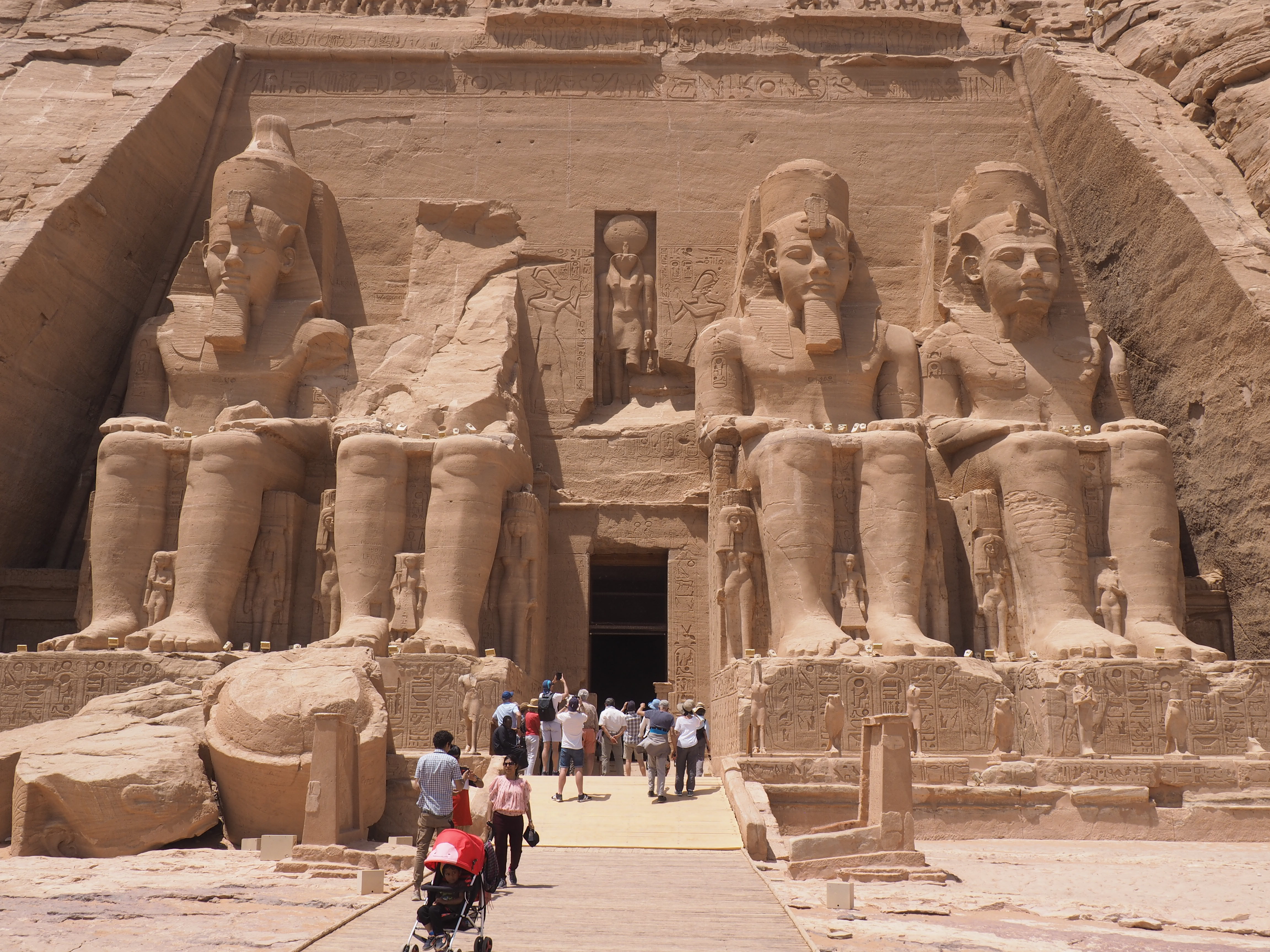
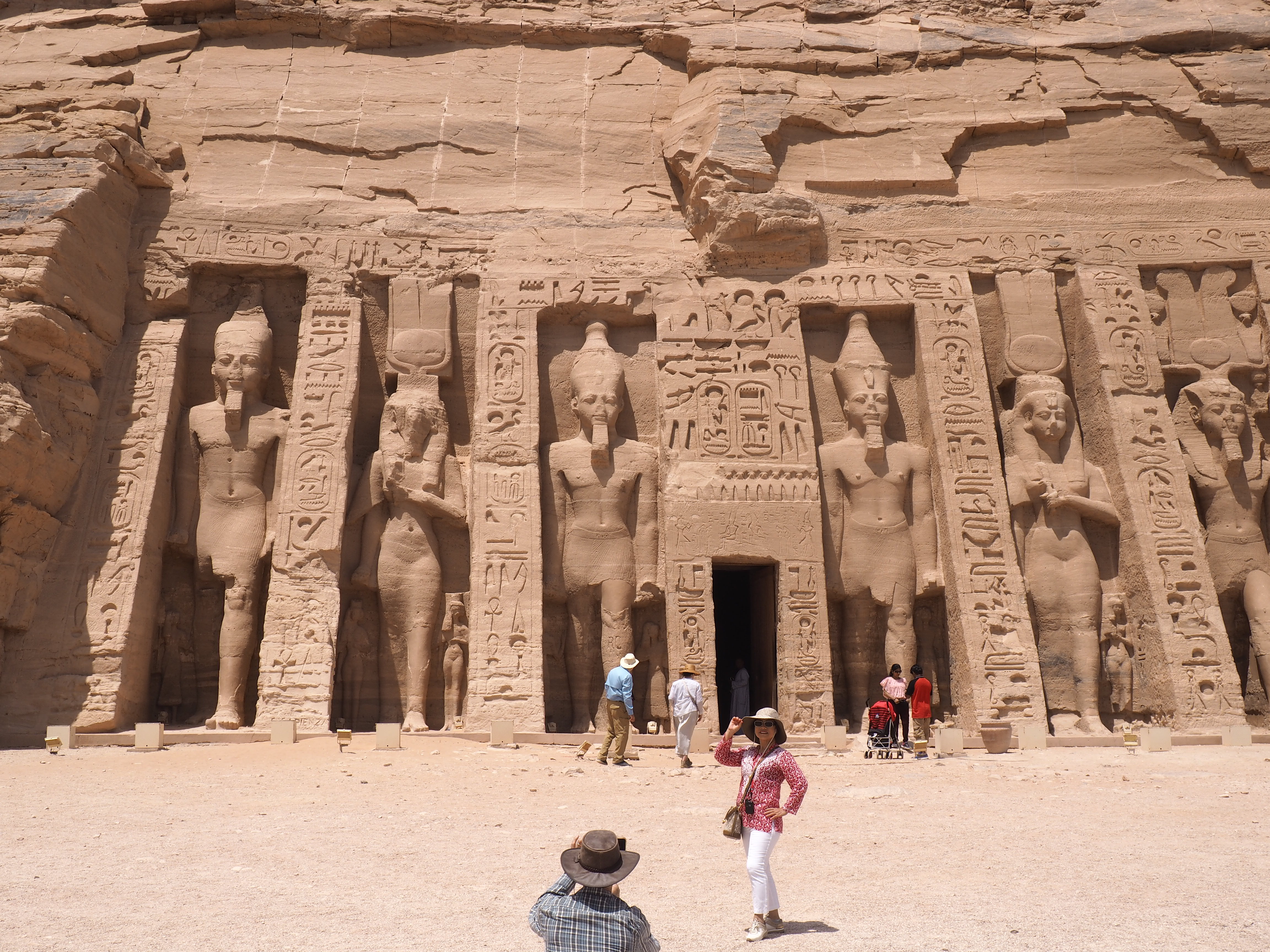
Whenever we travel for pleasure outside of our own country, we have to wonder about ourselves. Are we big game hunters or voyeurs, are we genuinely trying to engage with another place, another culture and people, or are we simply trying to satisfy the insatiable human need for stories? Even if we feel welcomed by ordinary pandemic weary people (like the locals cheering us as we rode by on a bus in one Egyptian town), sometimes we feel we have to get out of the way and just observe (watching our toes). So, here are some photos and random thoughts on little things we’ve seen.
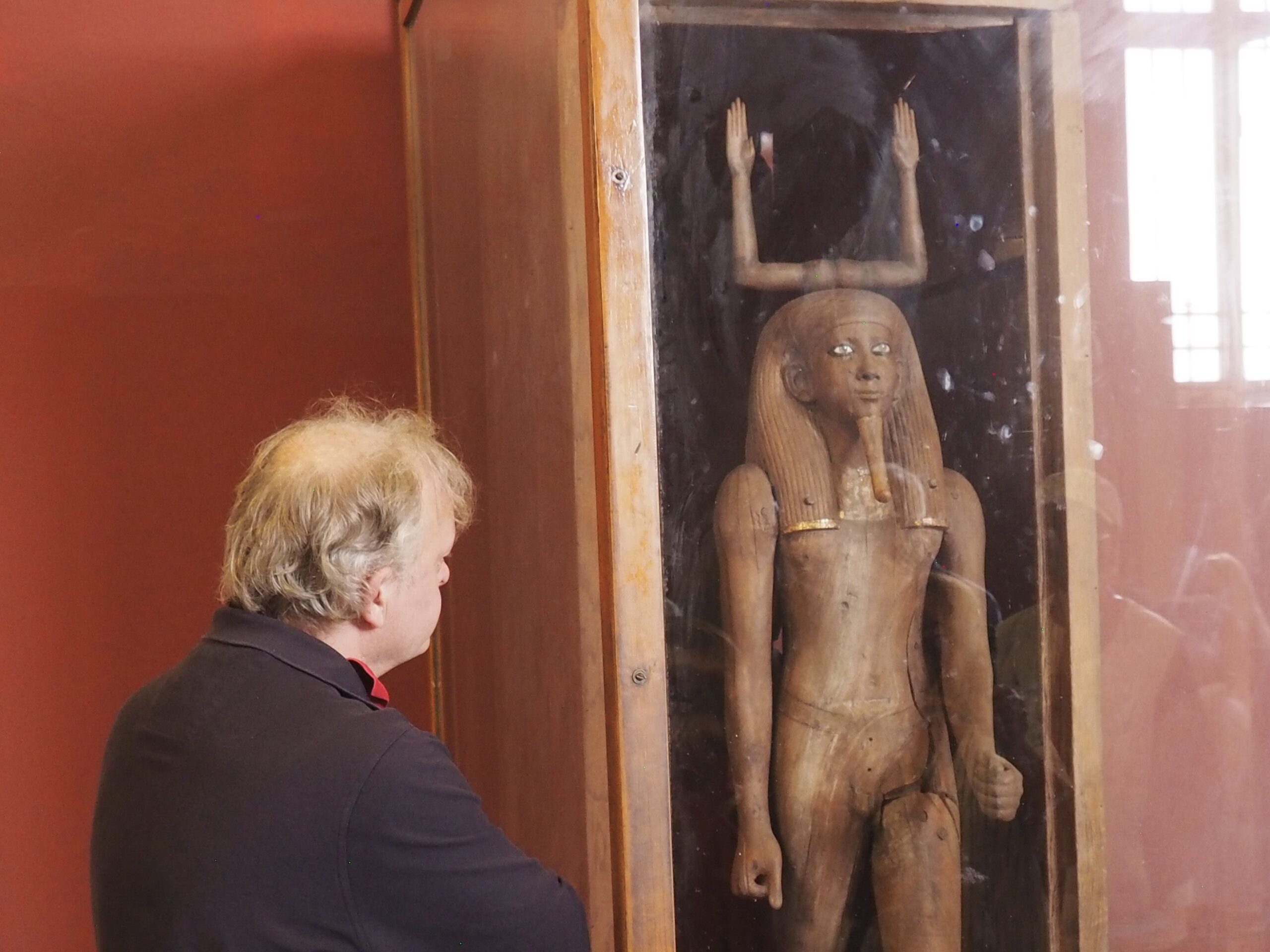

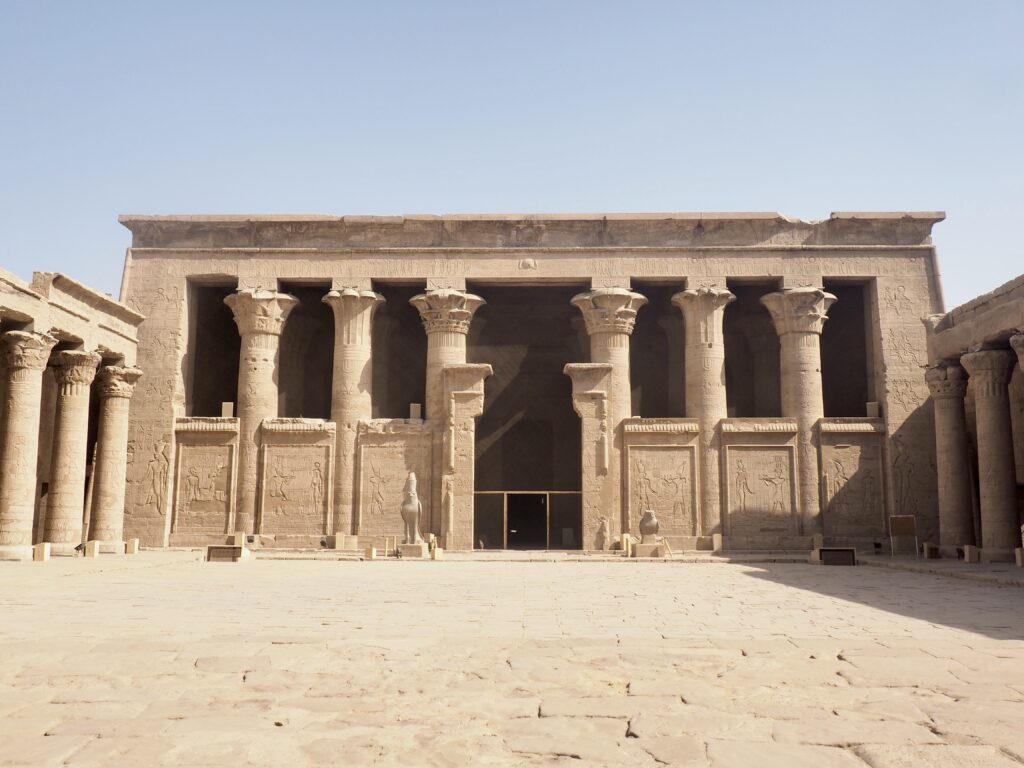
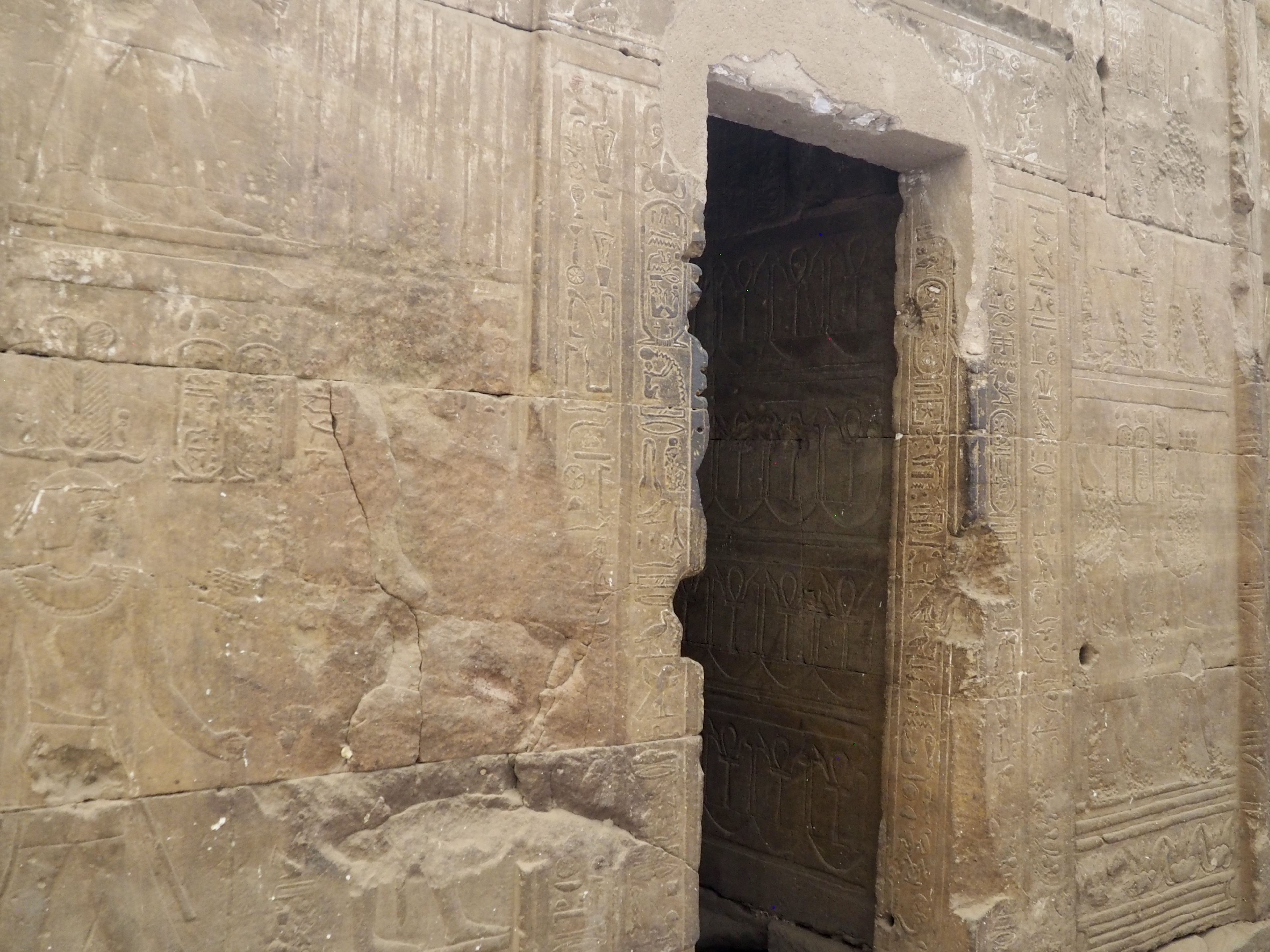
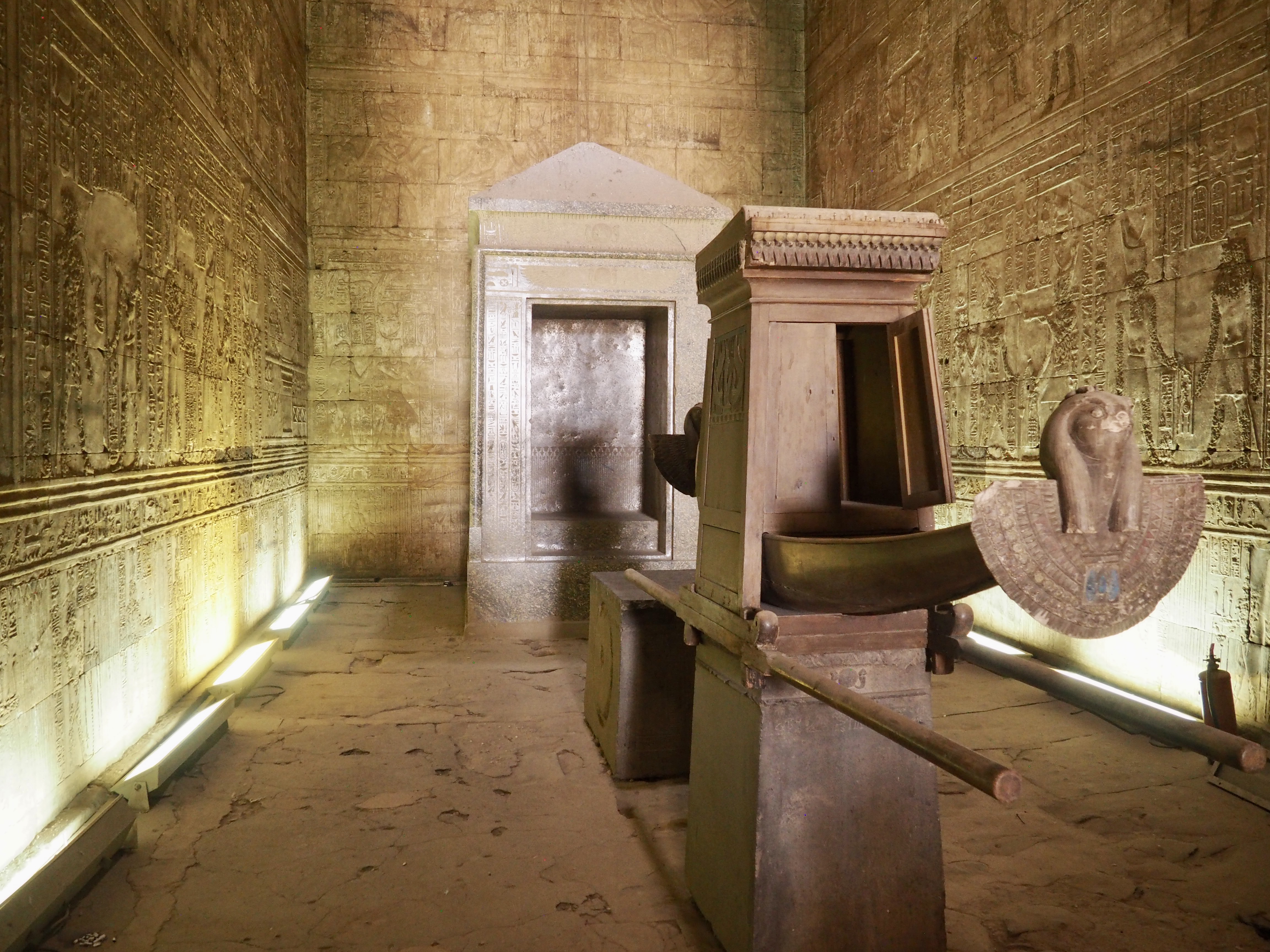
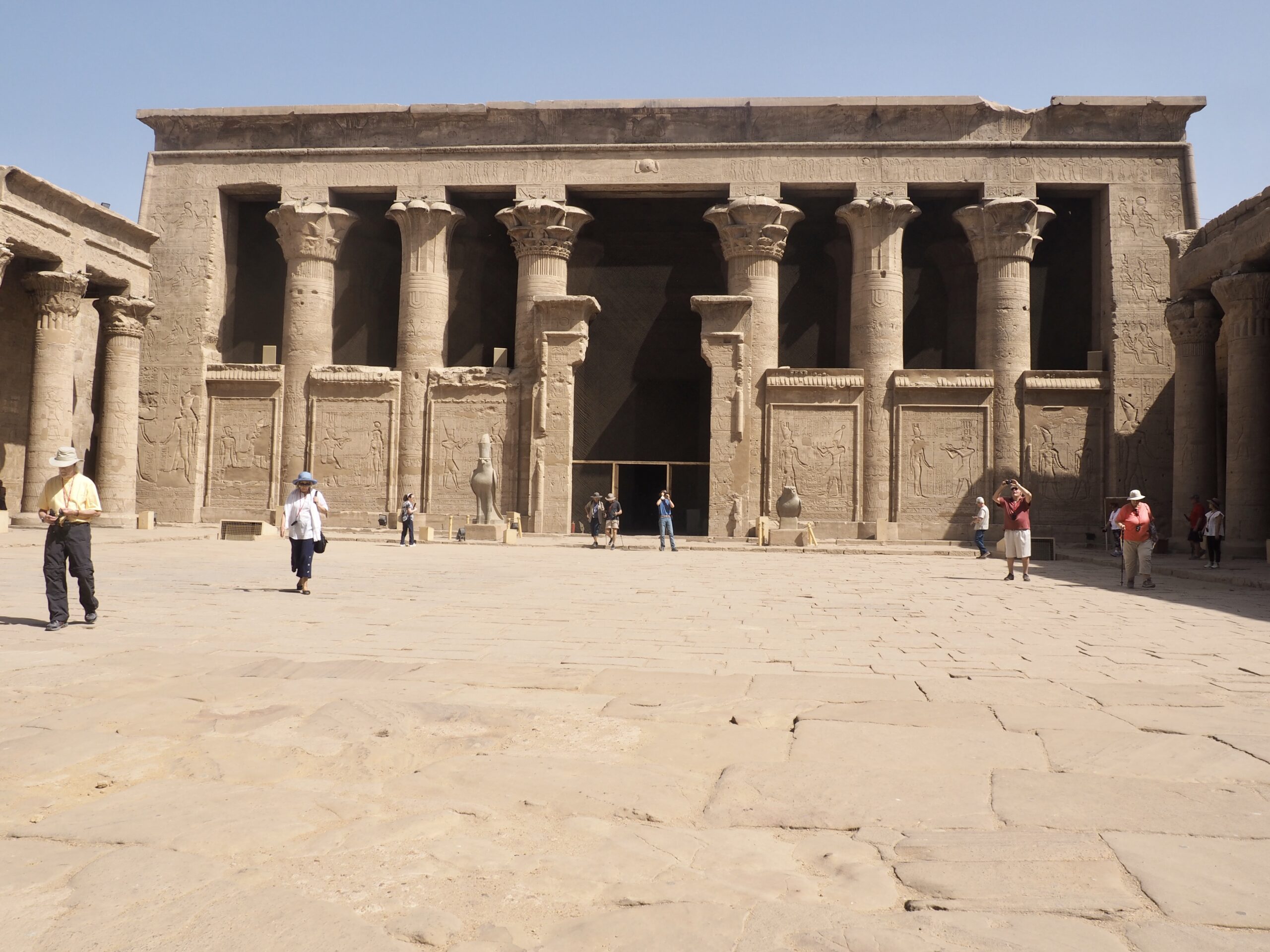
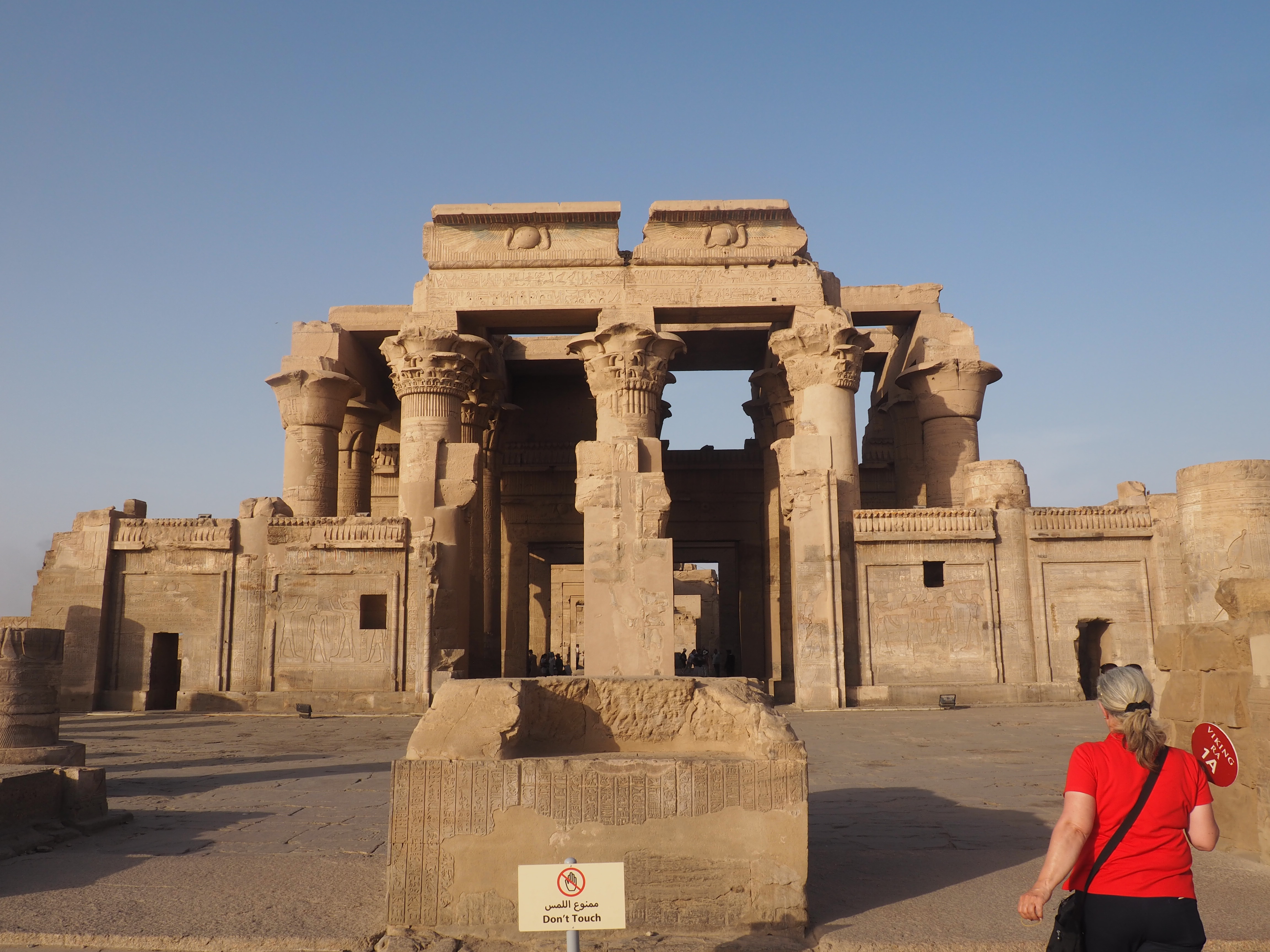
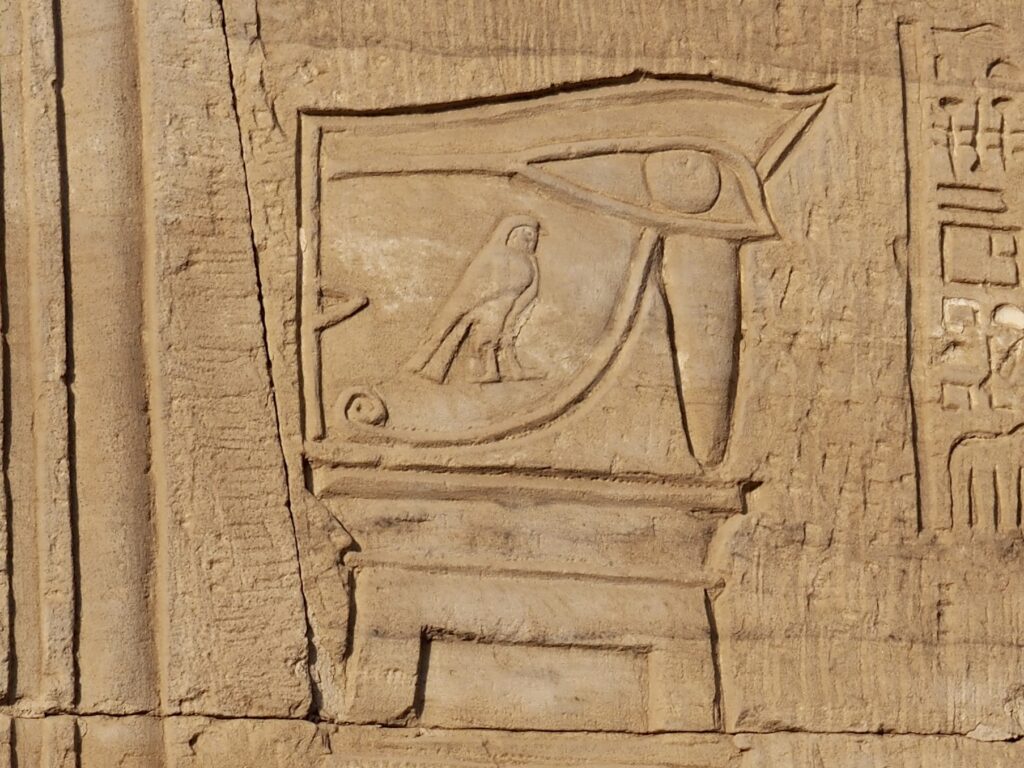
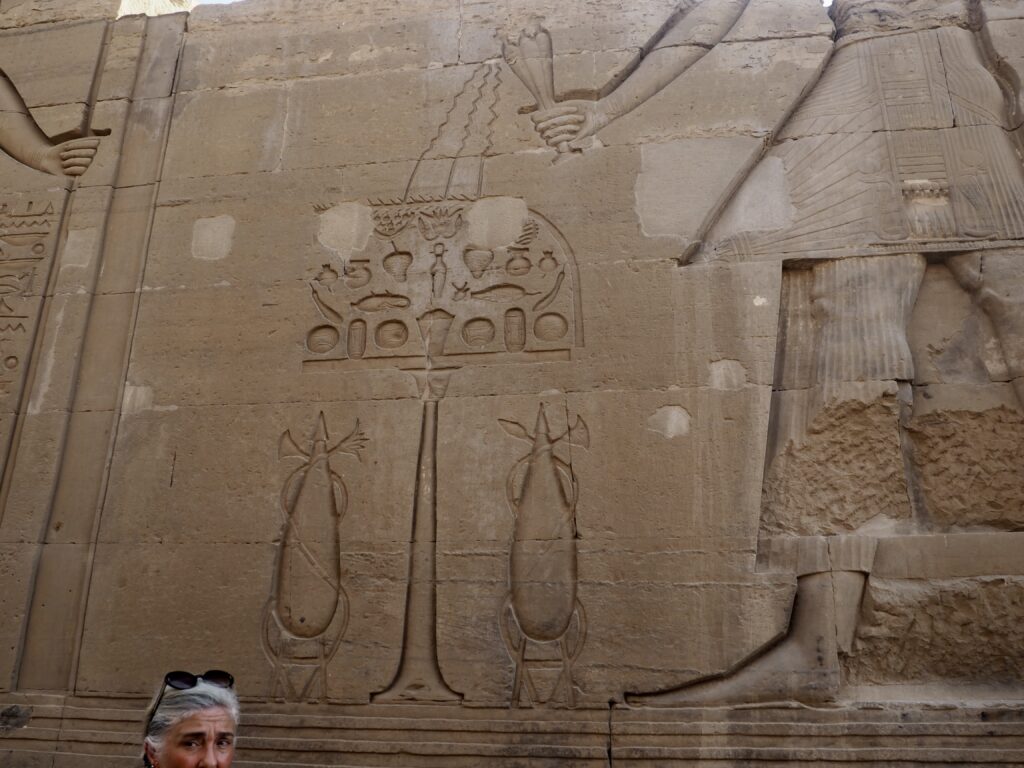
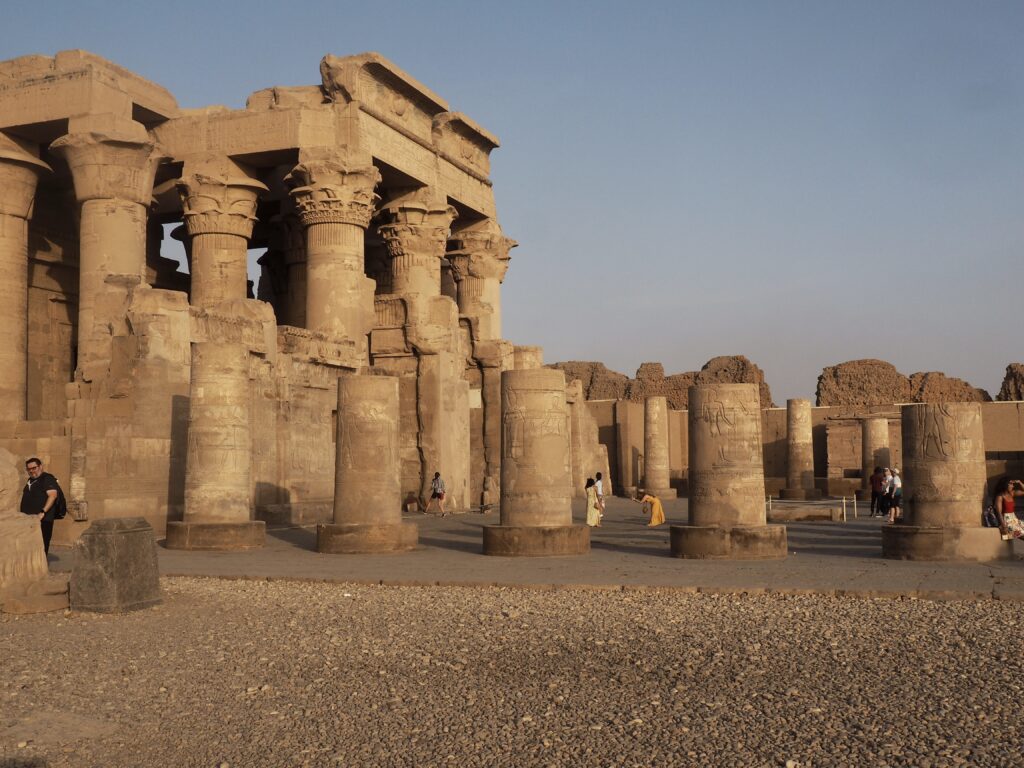
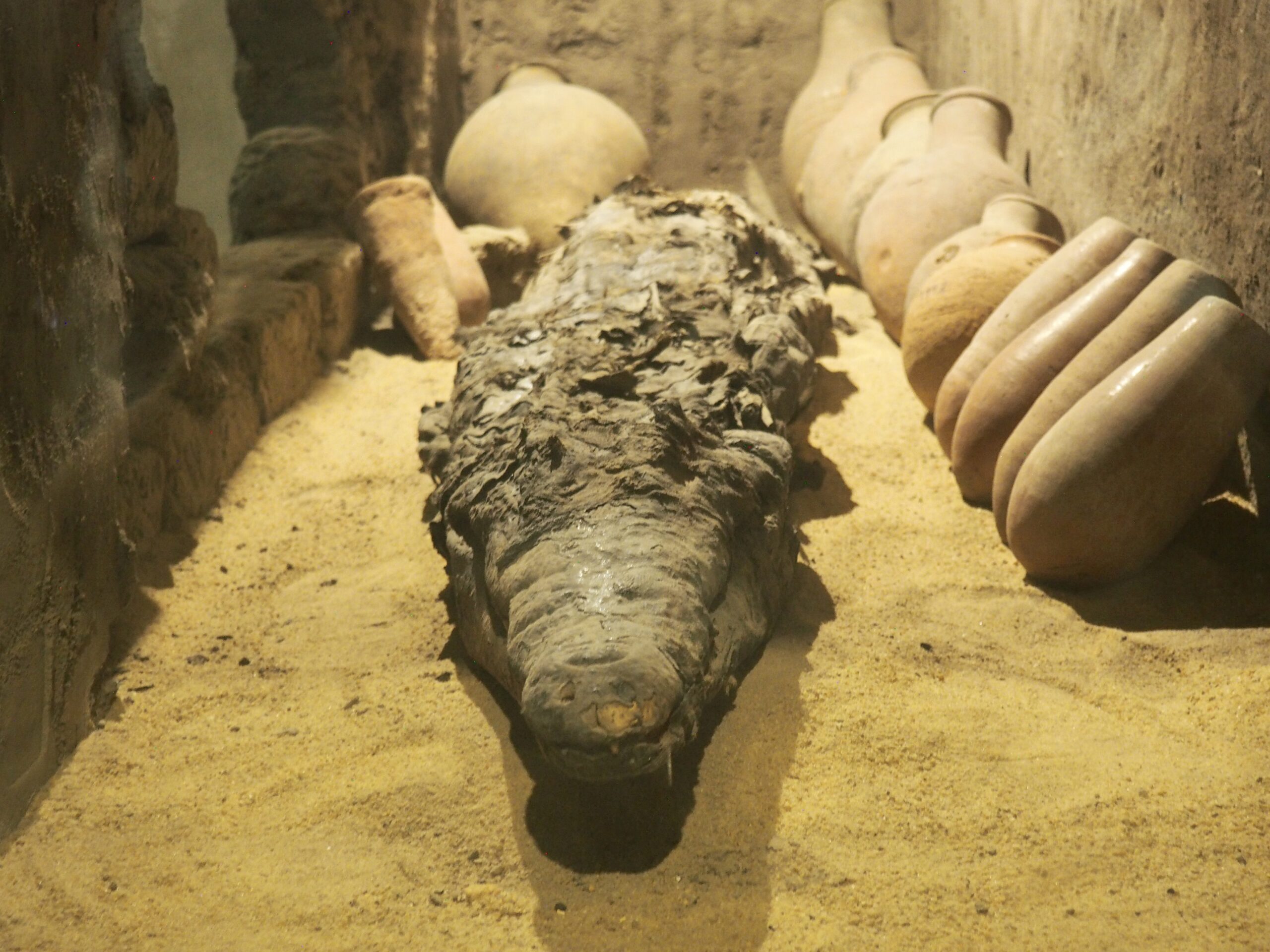
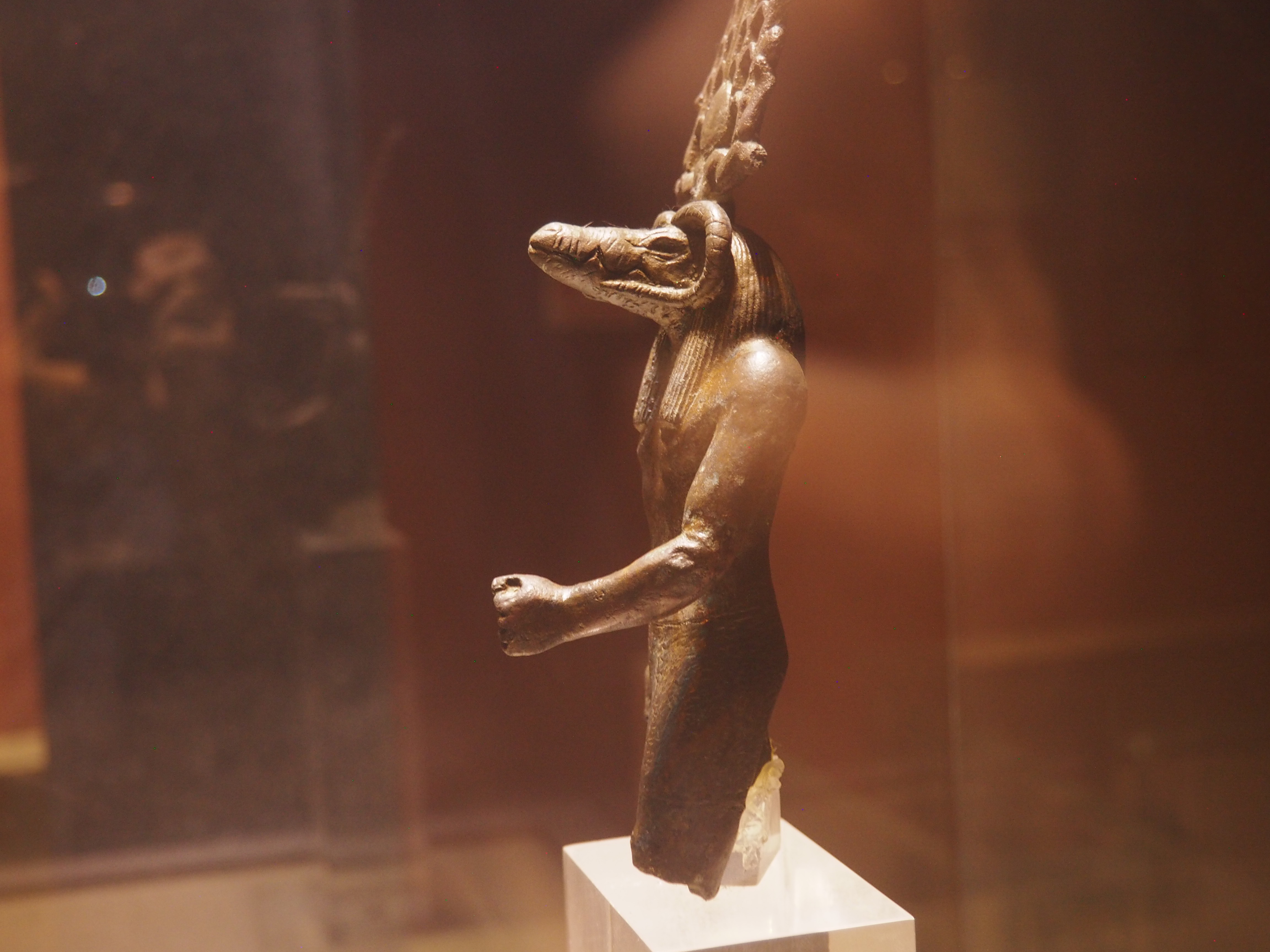
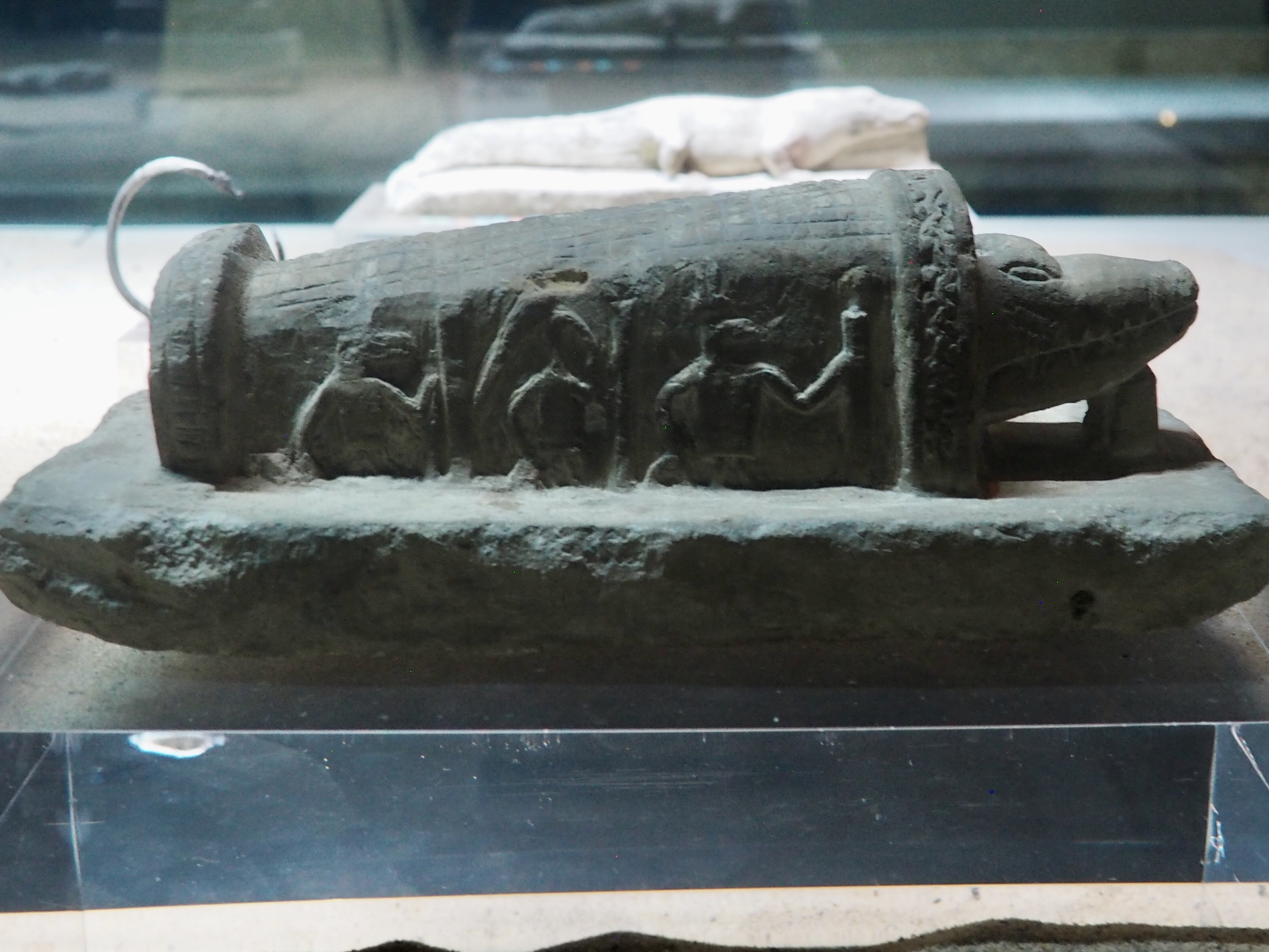
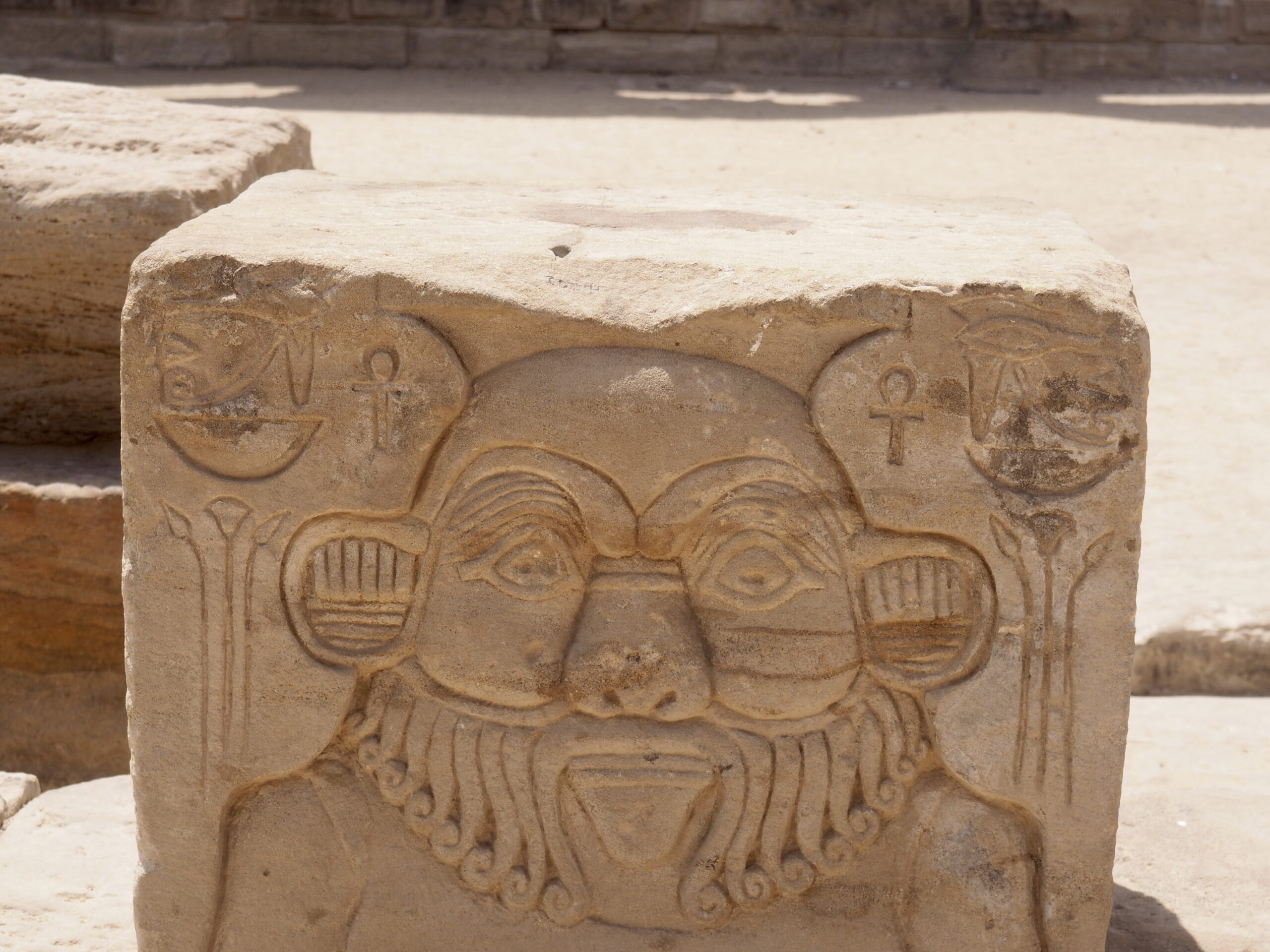
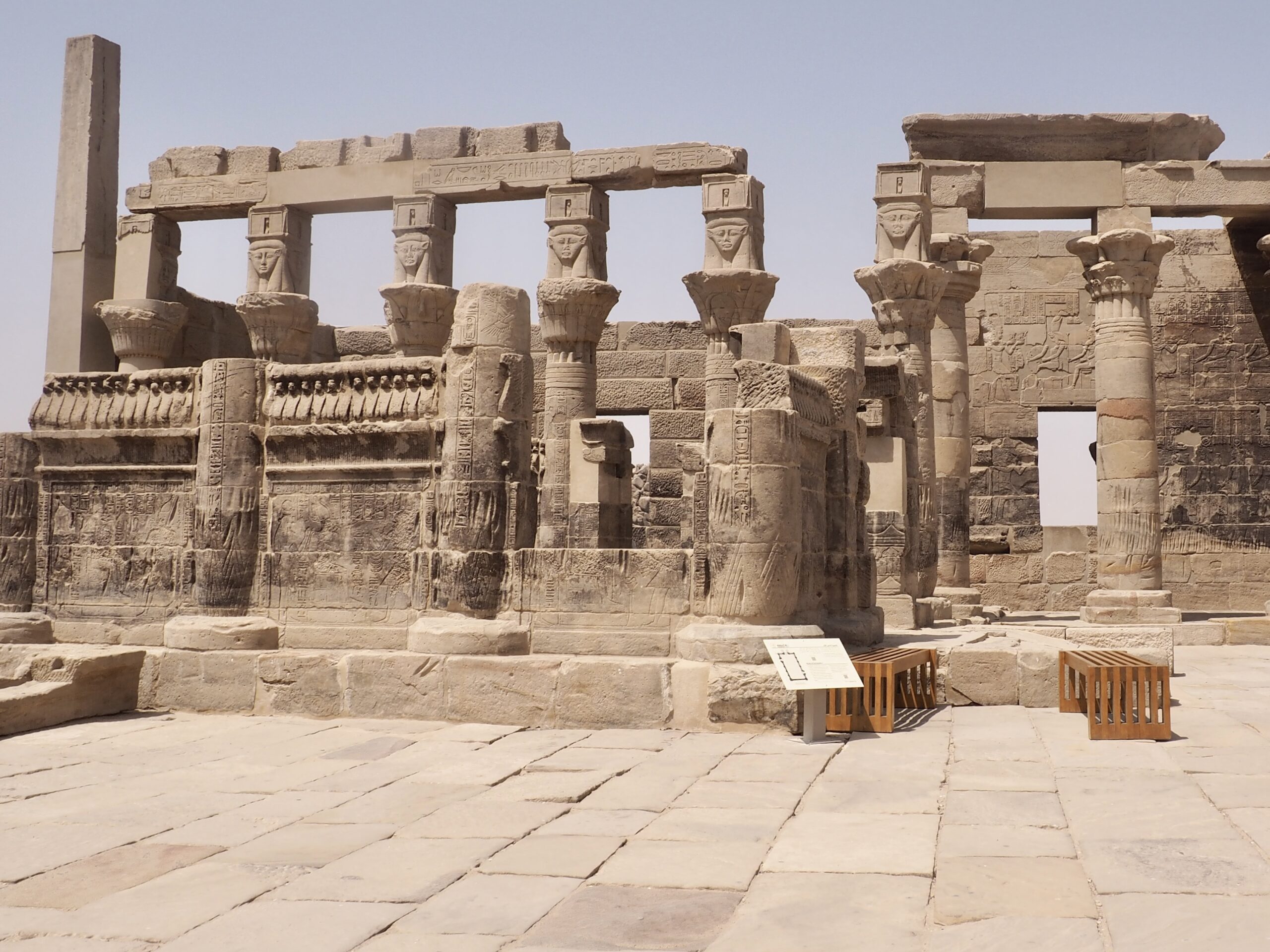
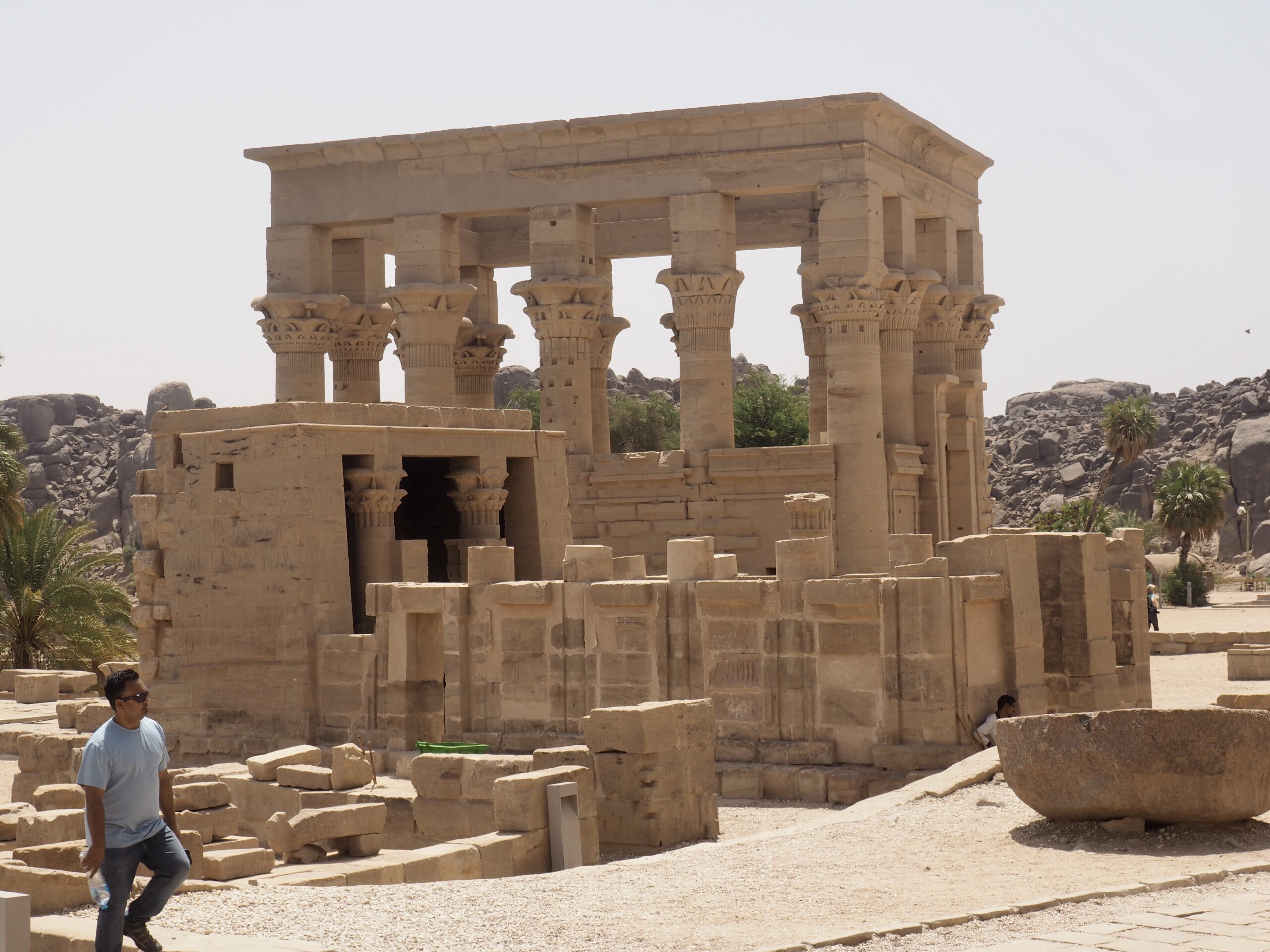
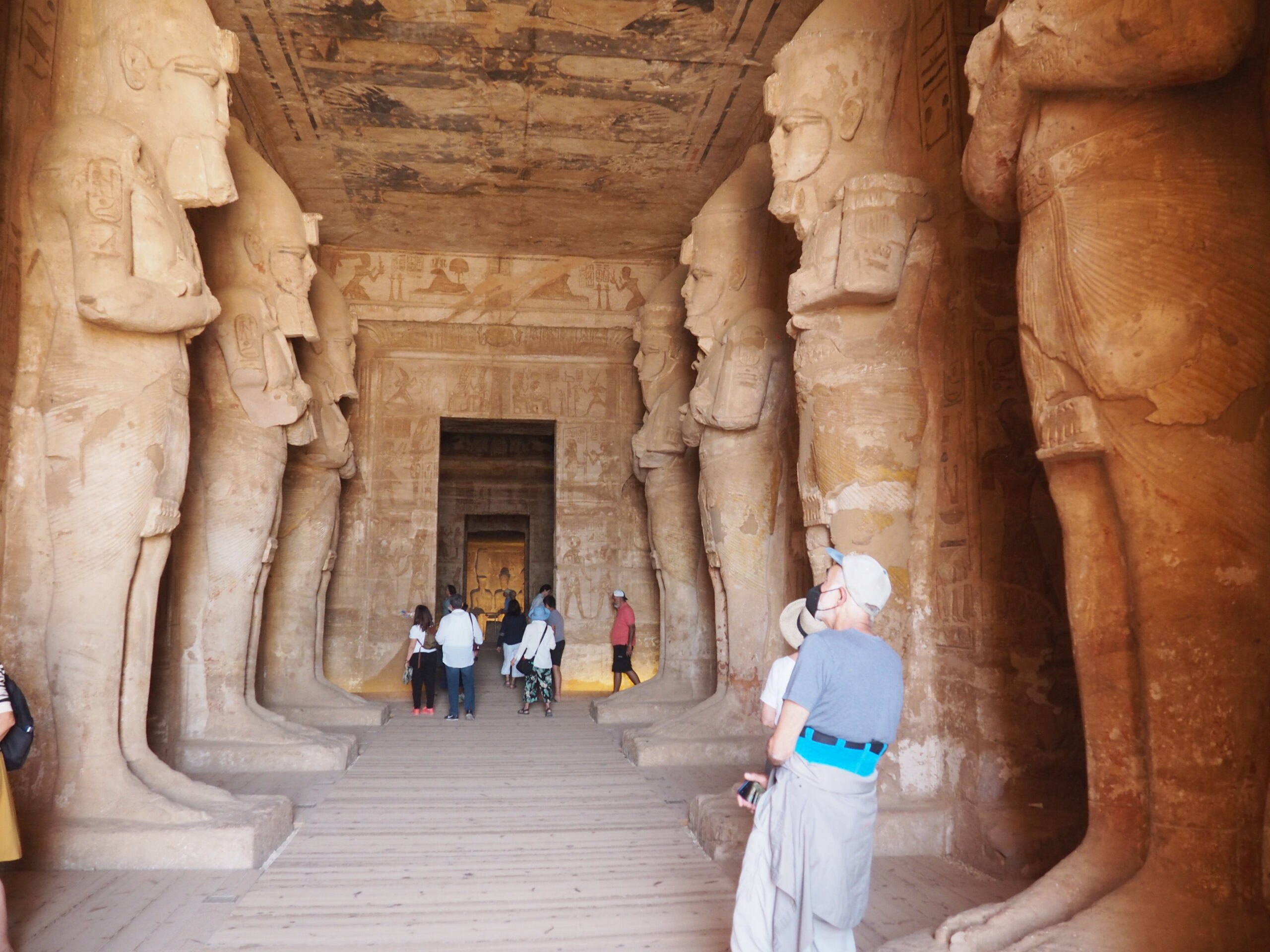
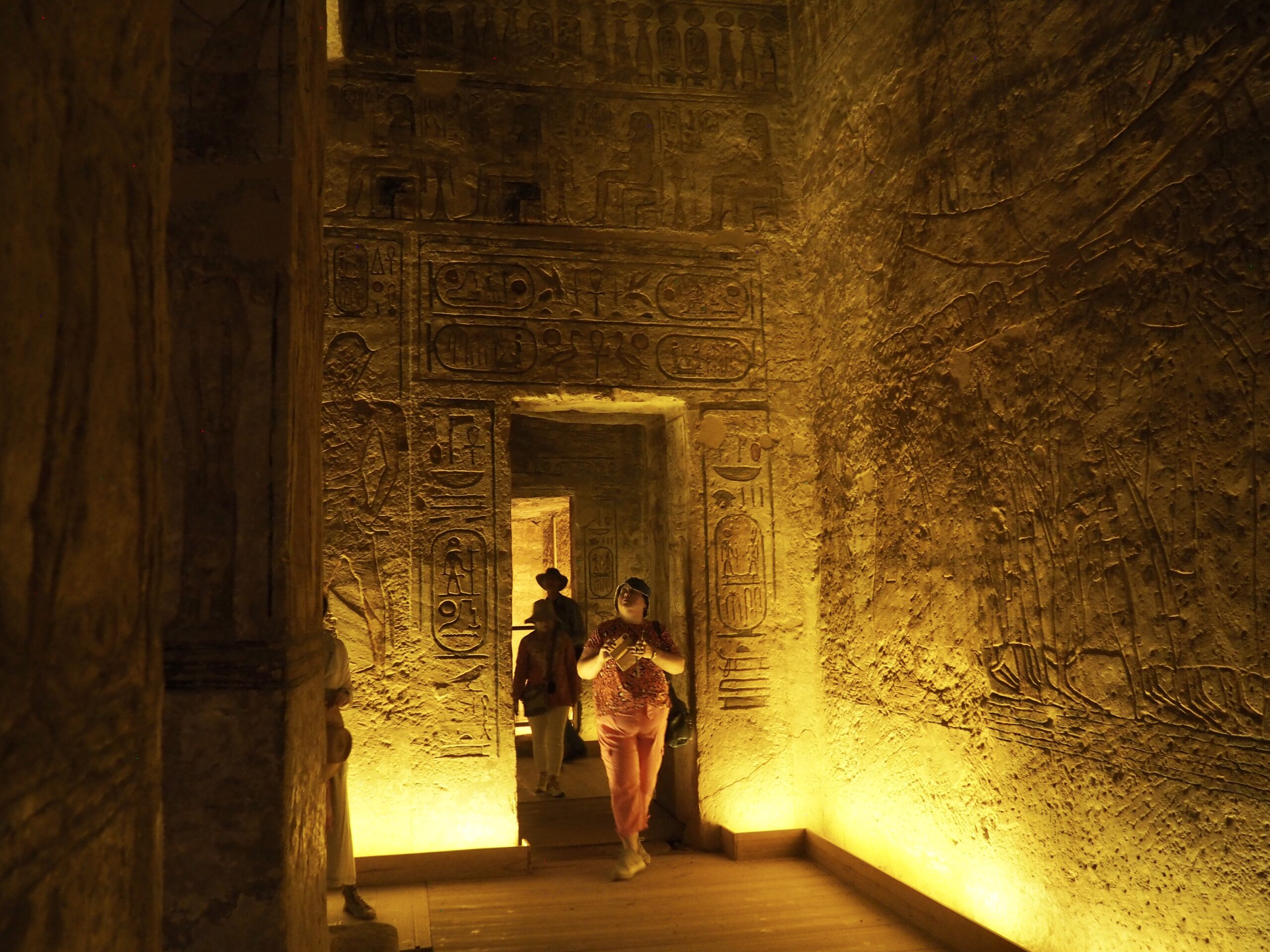
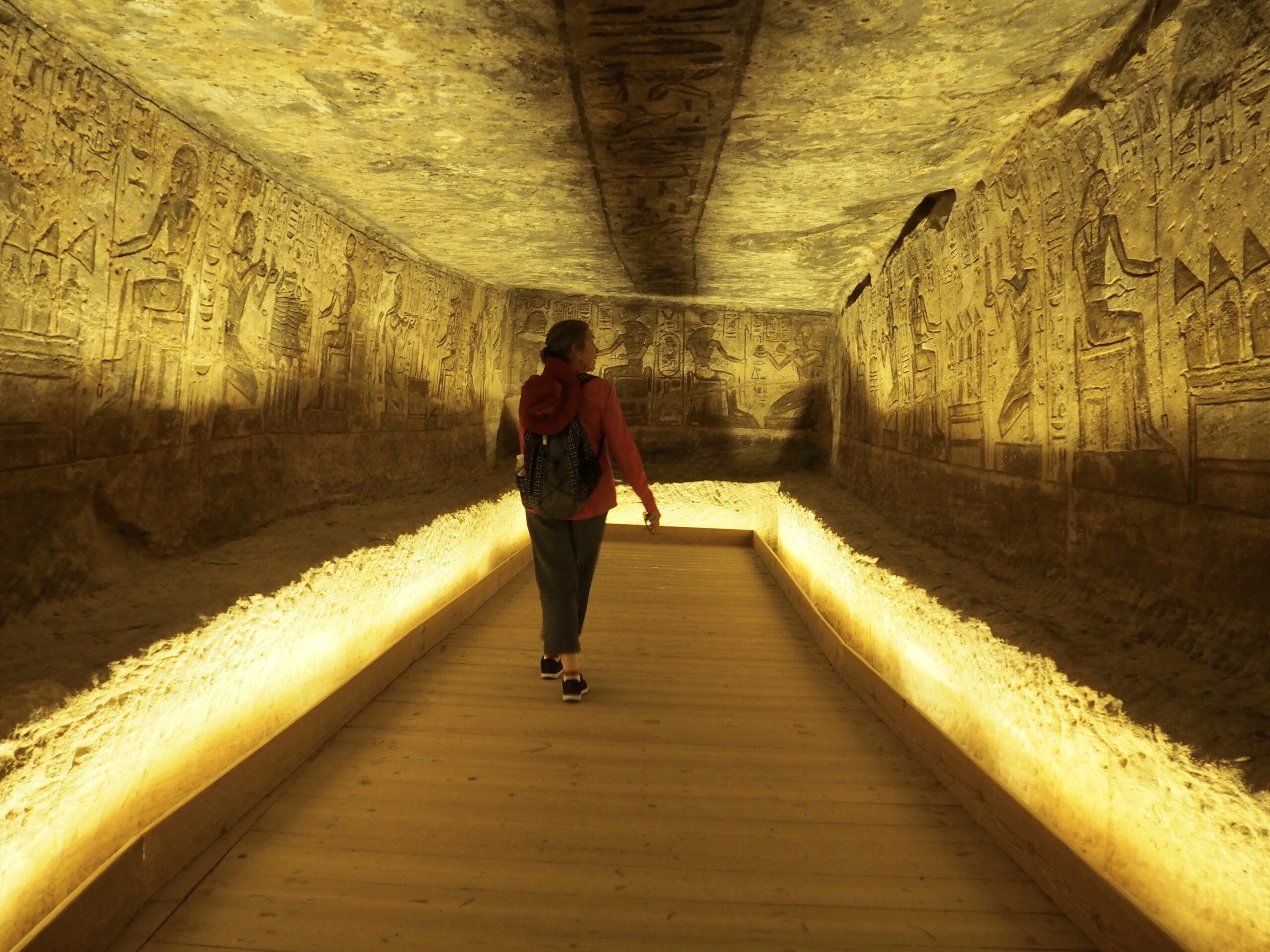
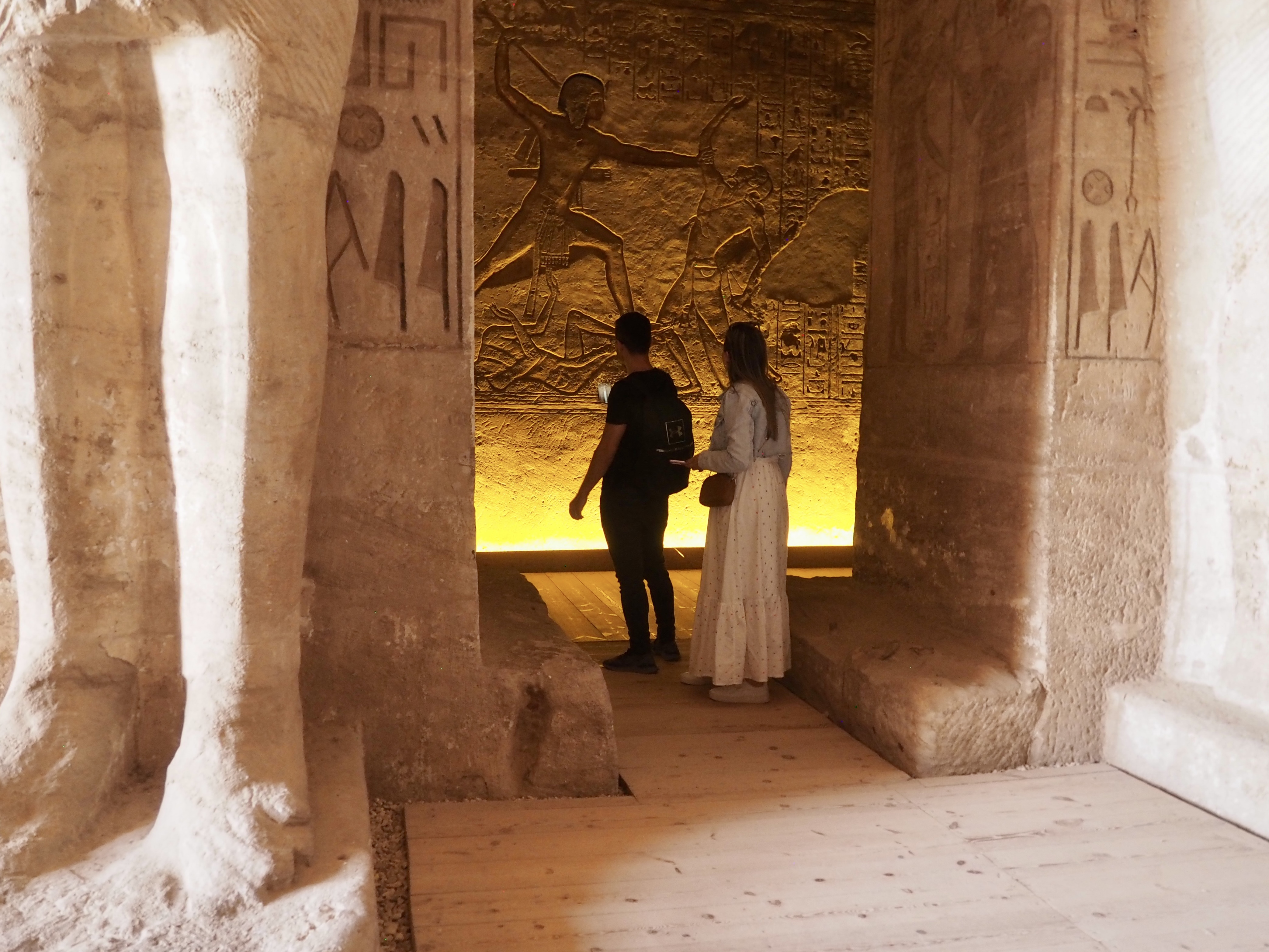
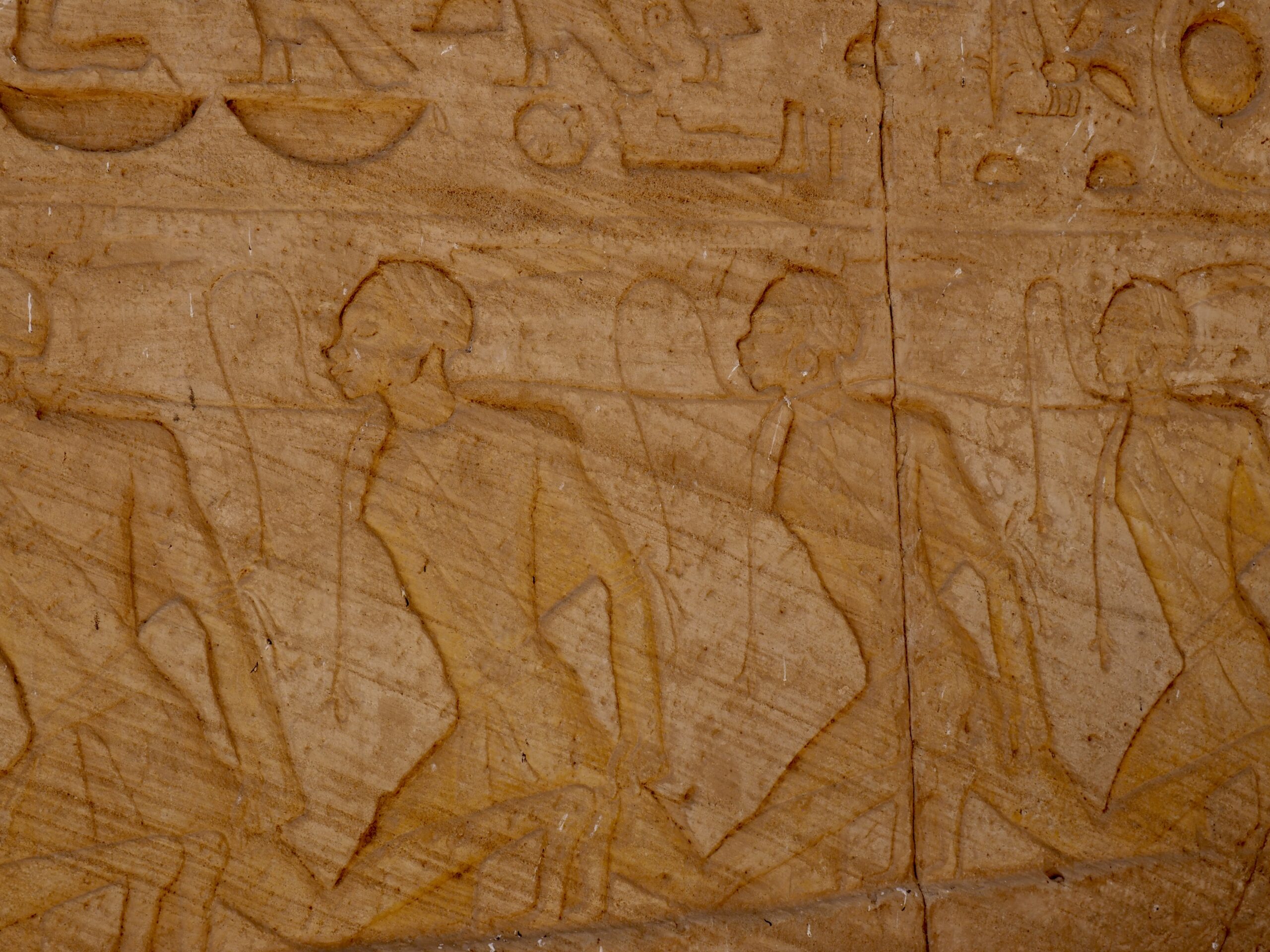
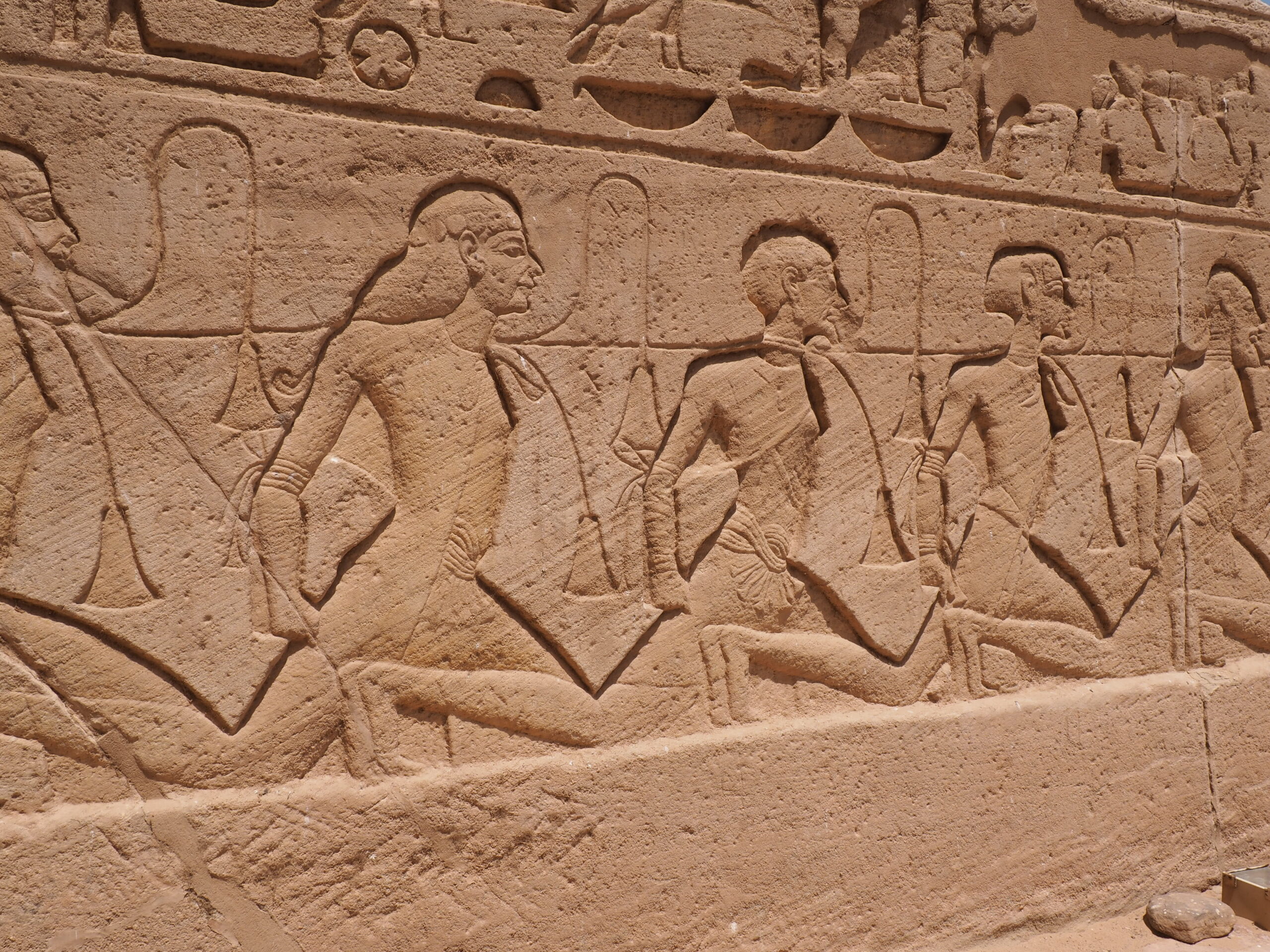
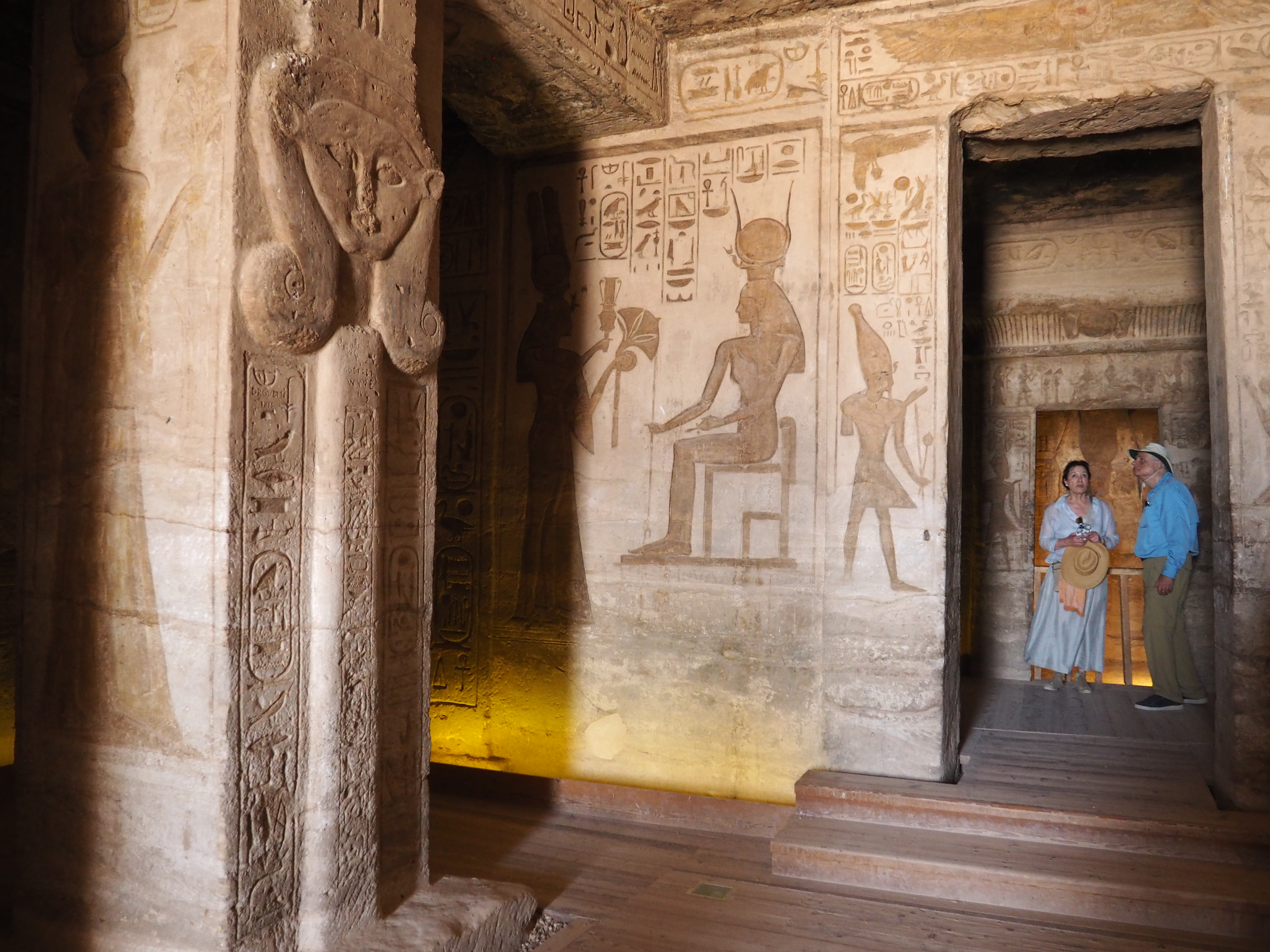
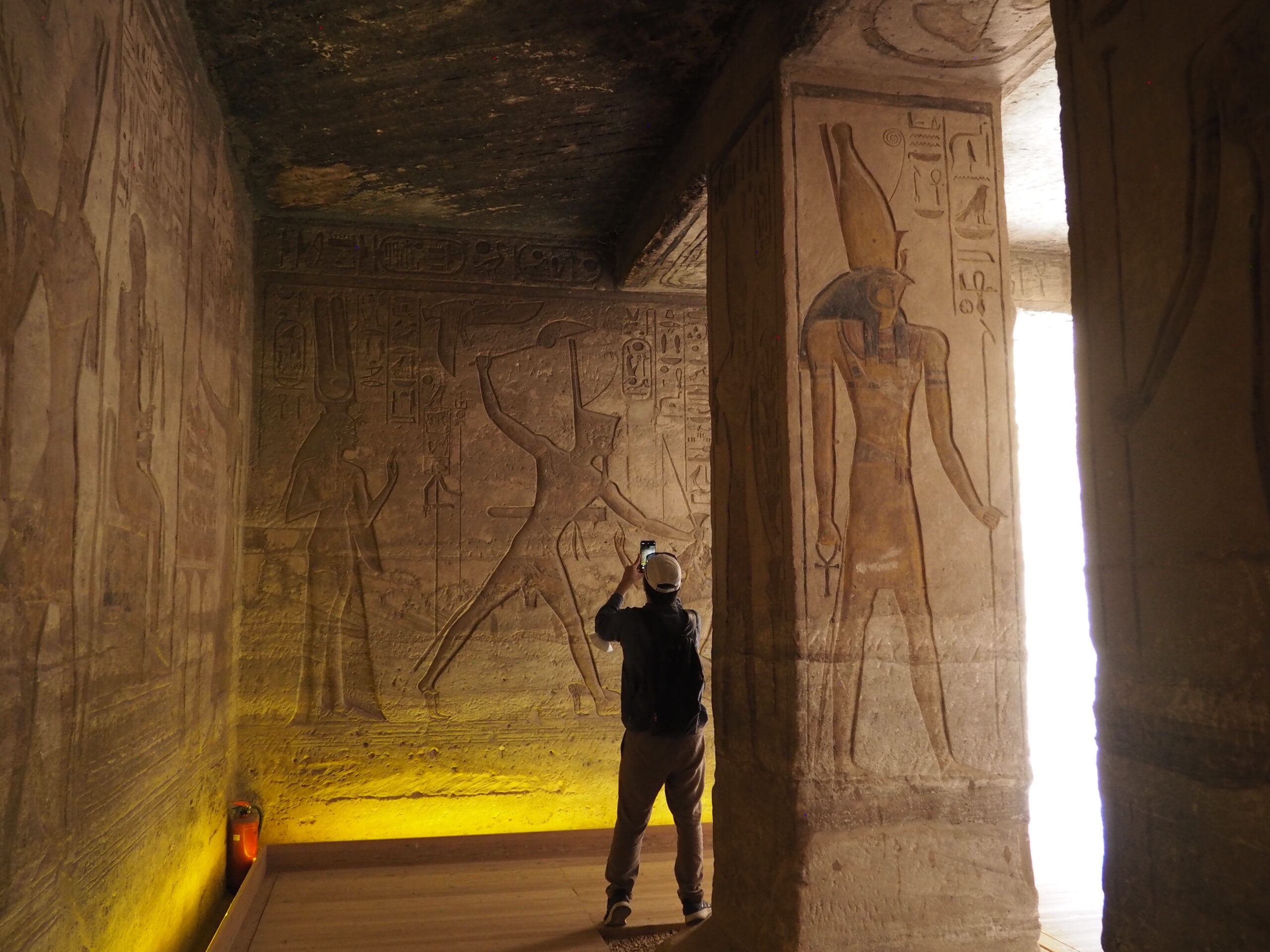
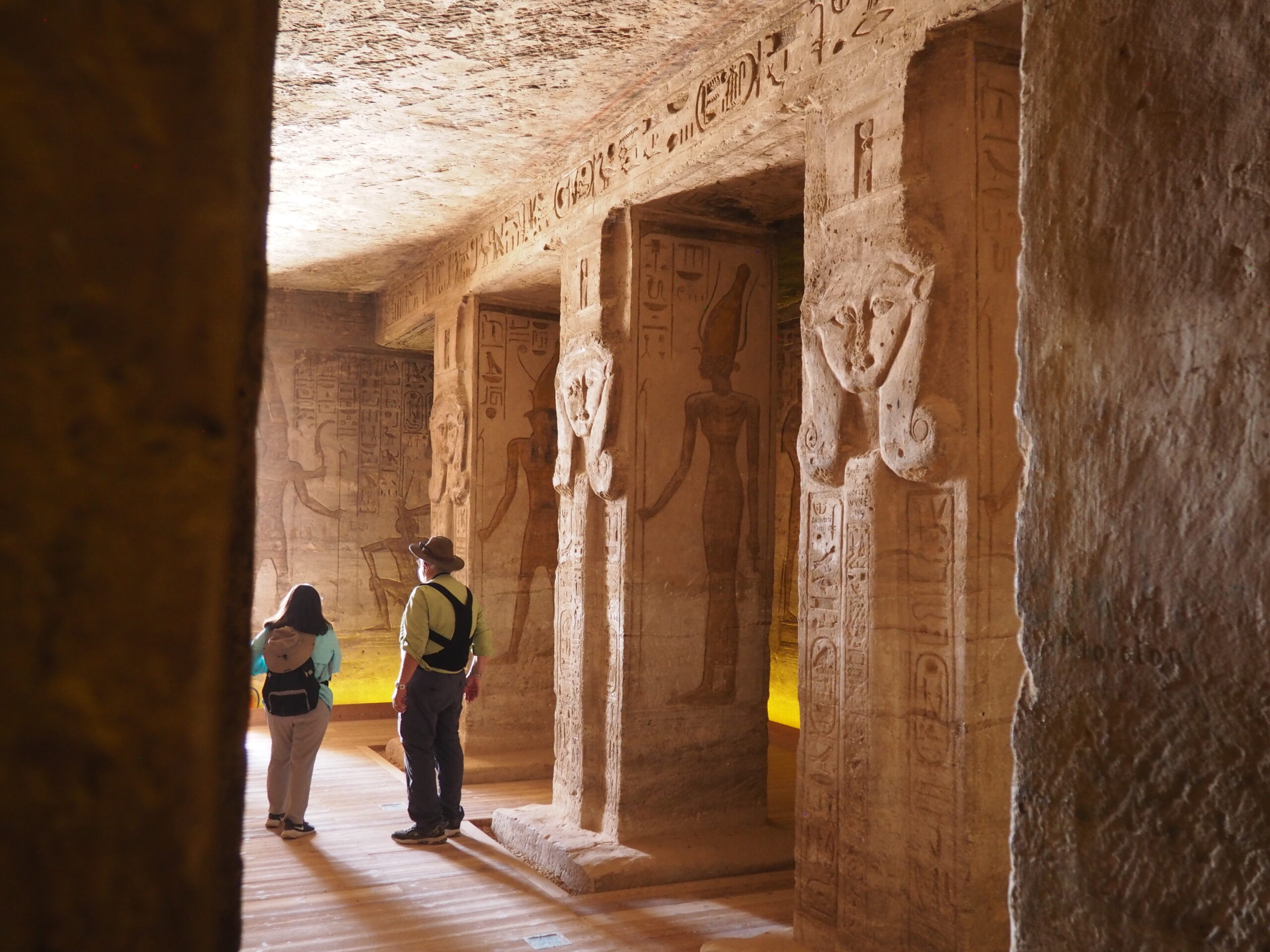
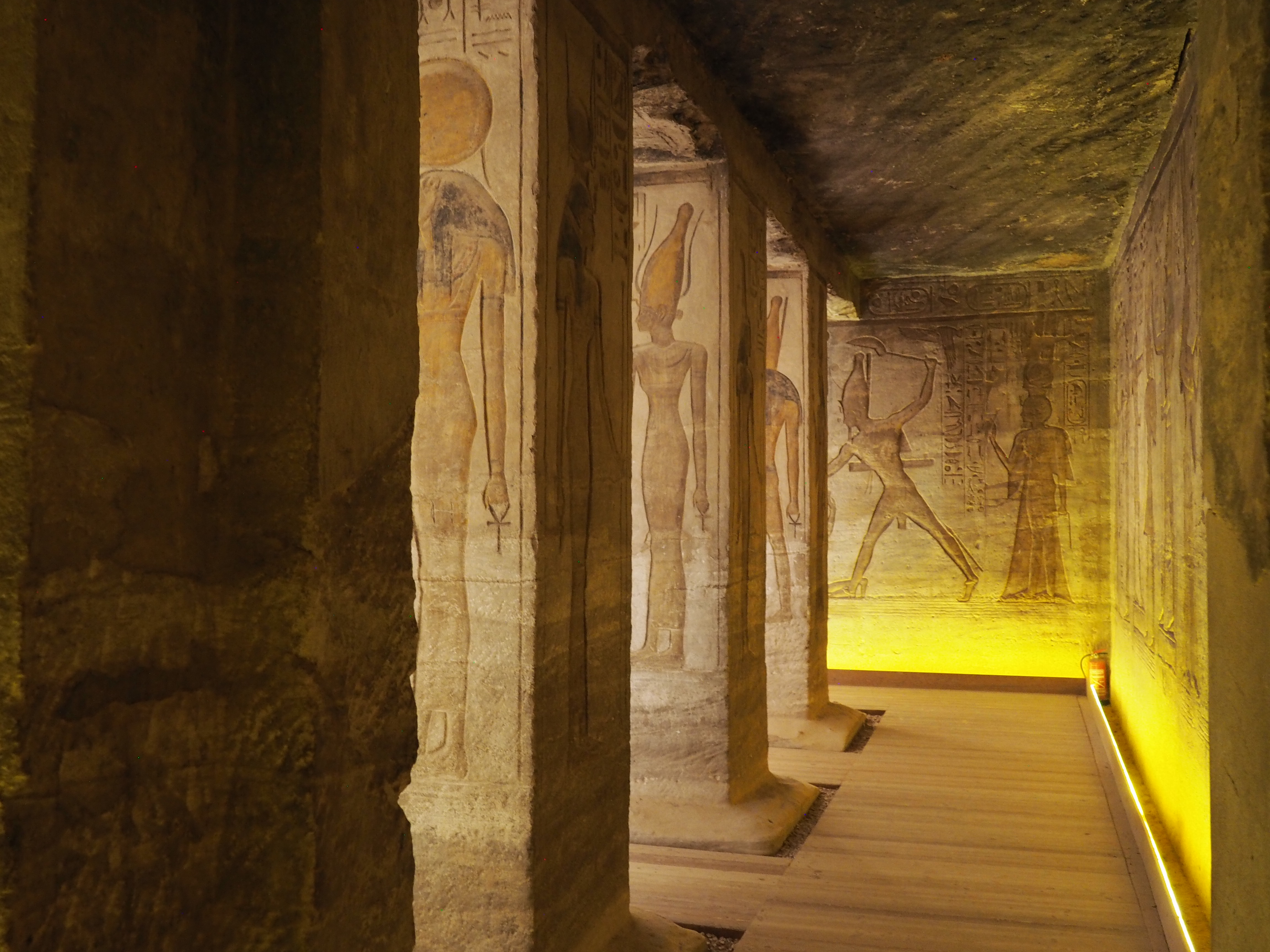
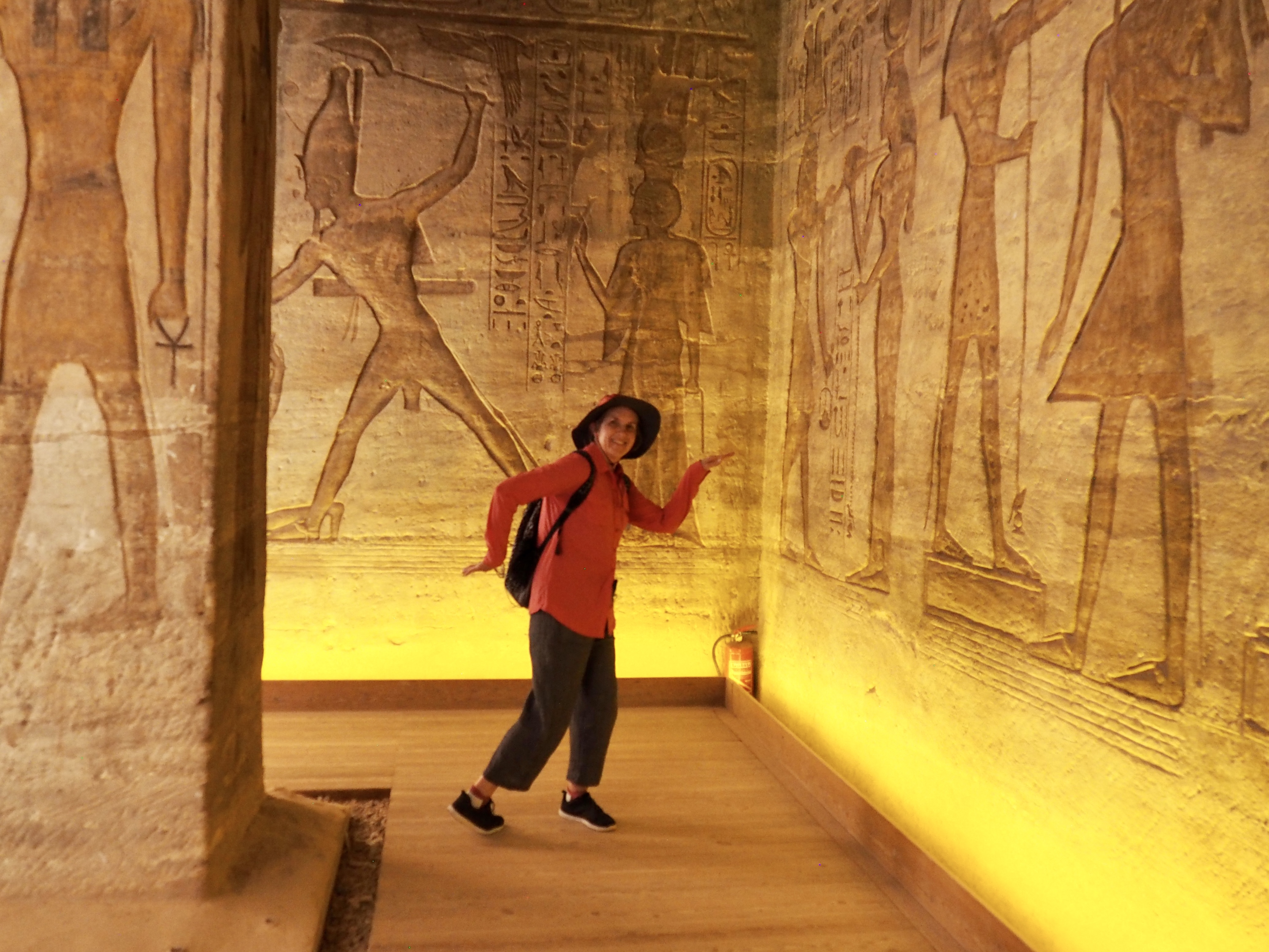
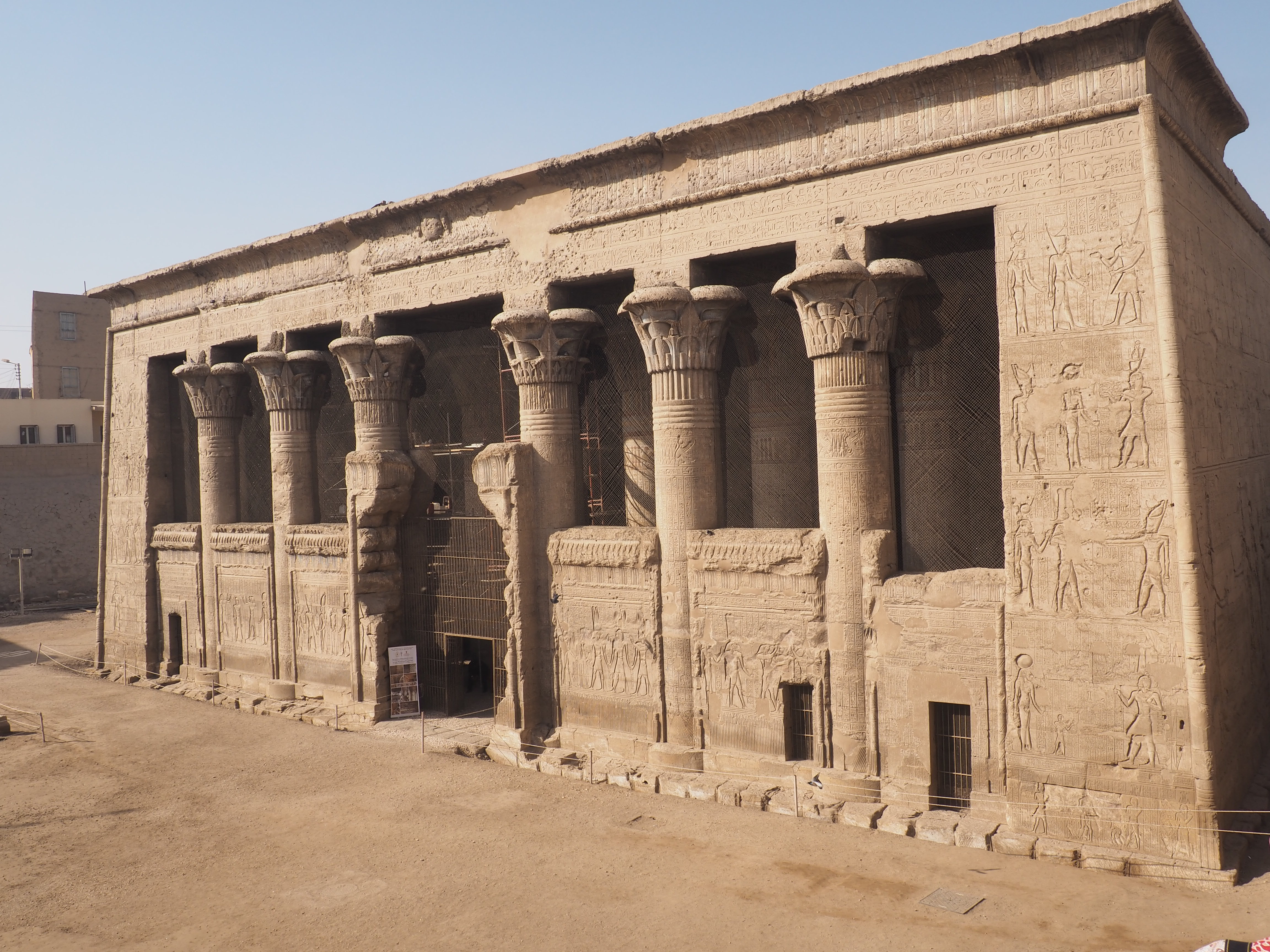
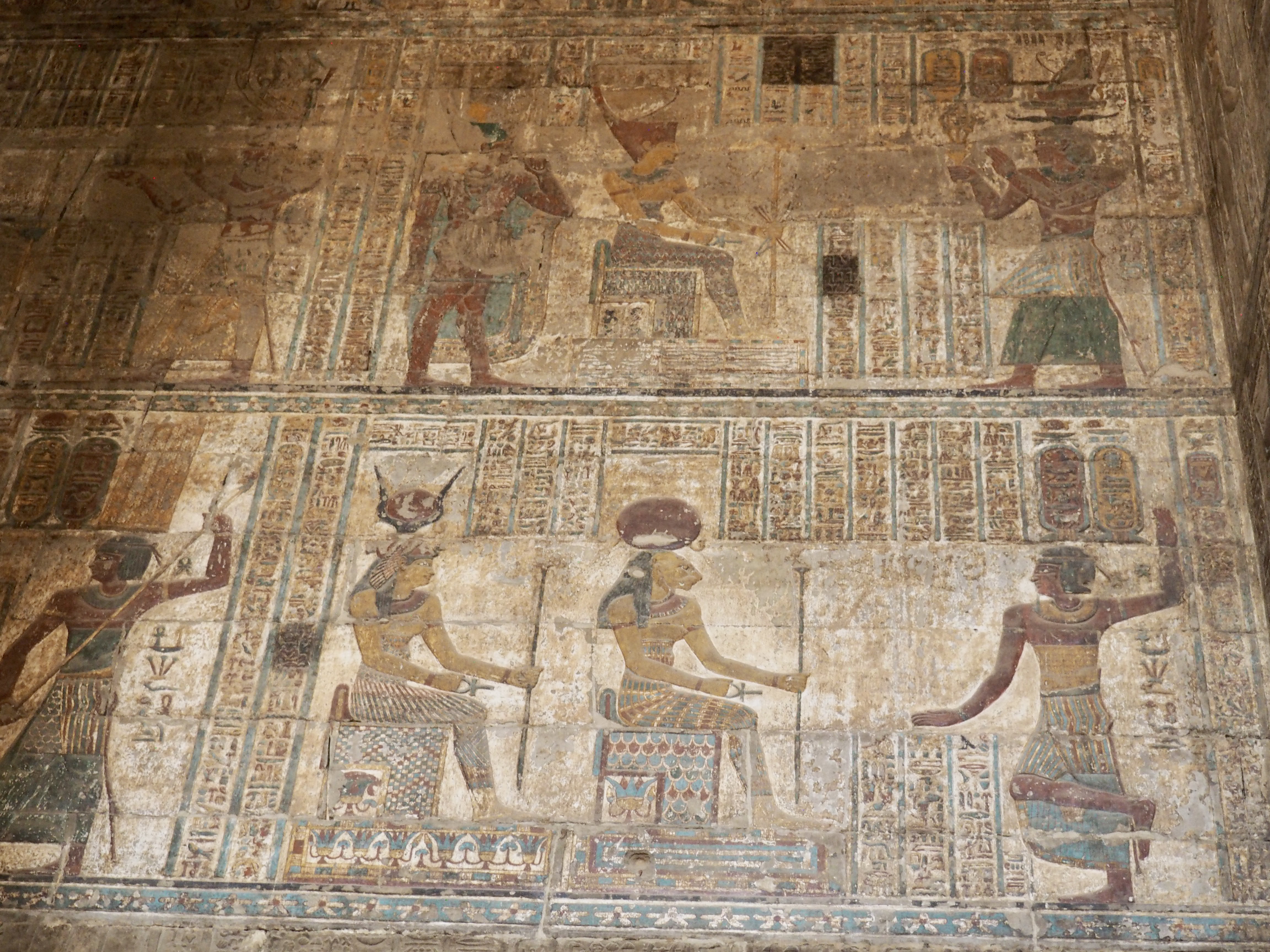
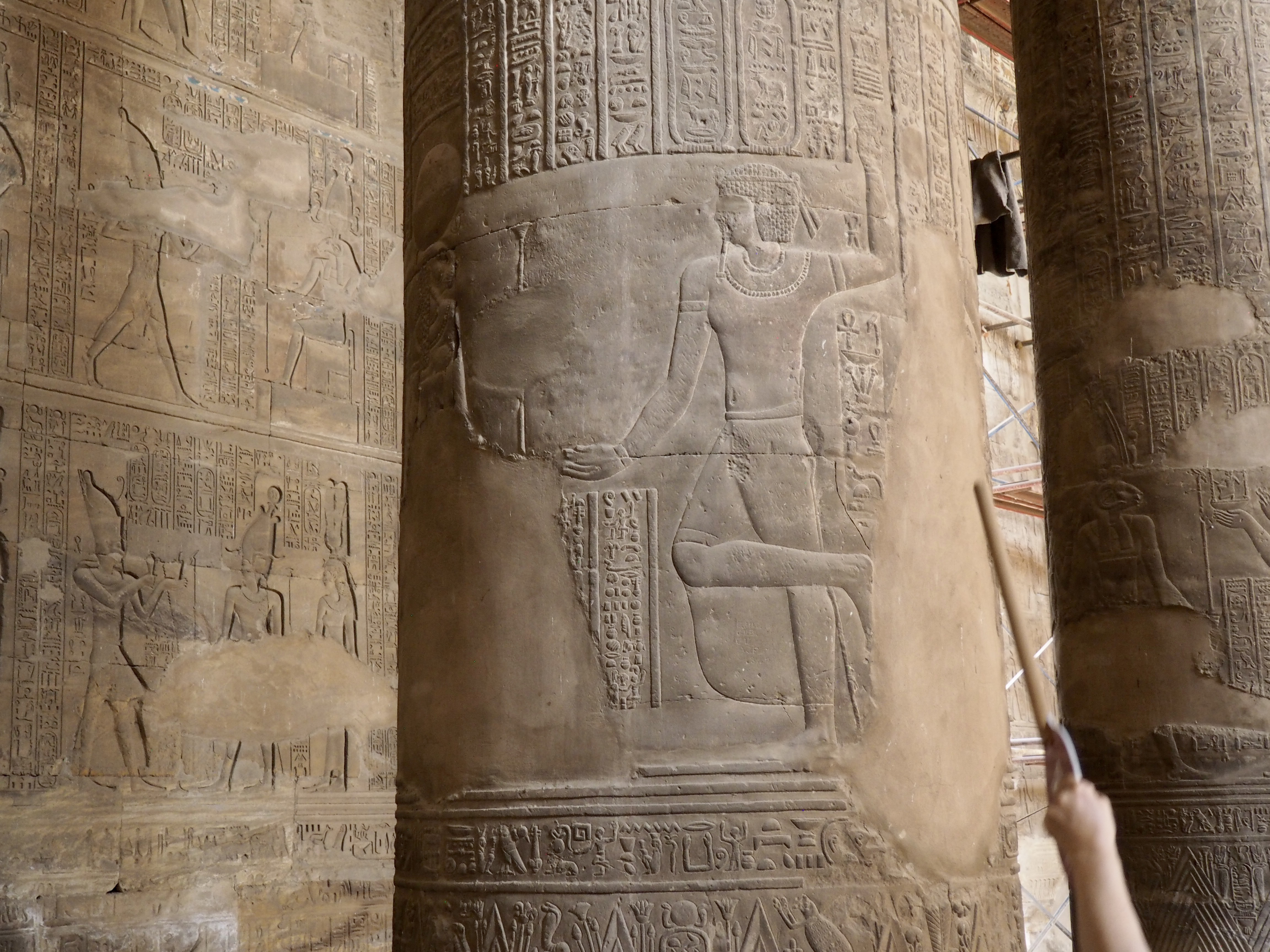
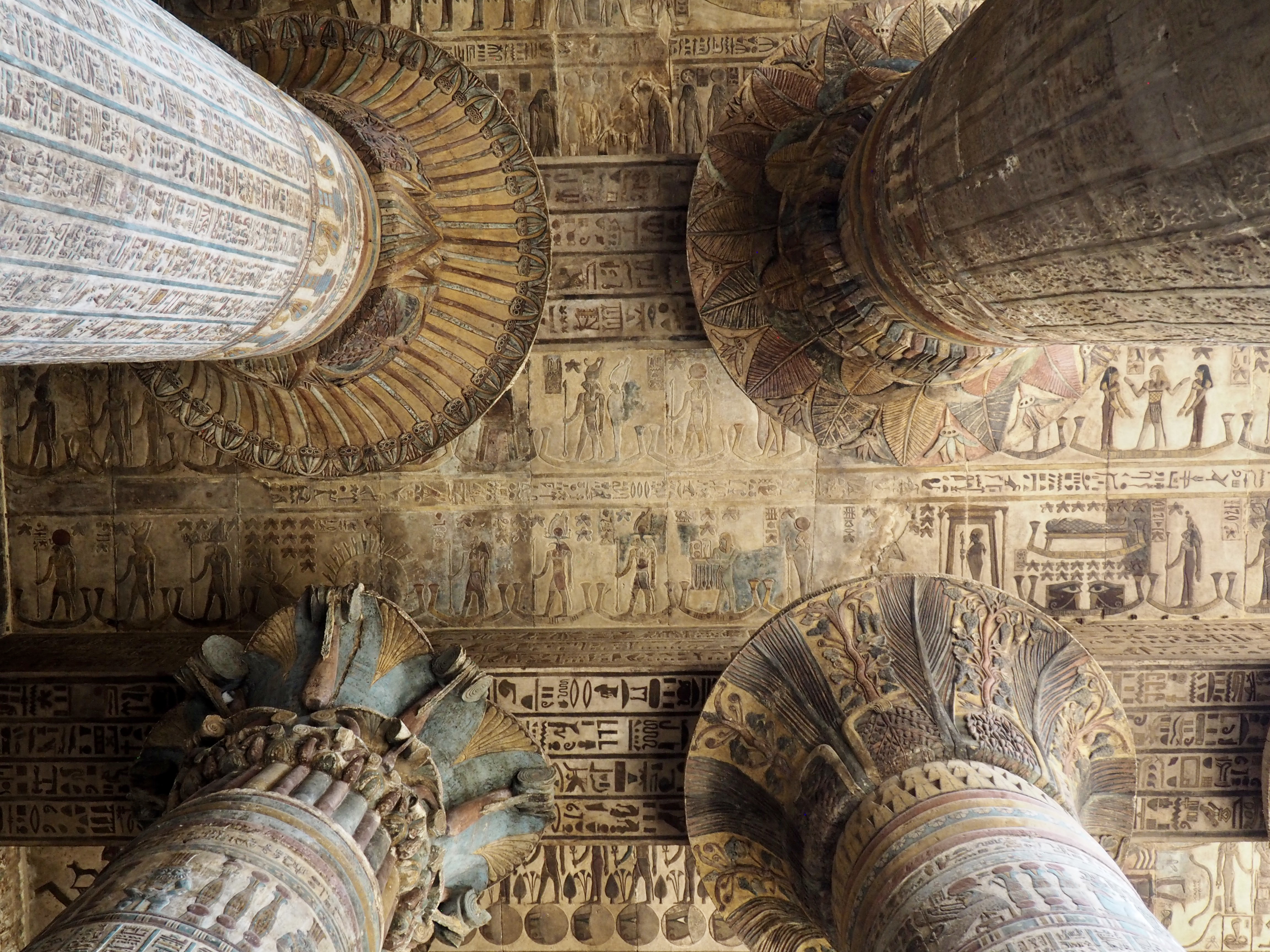
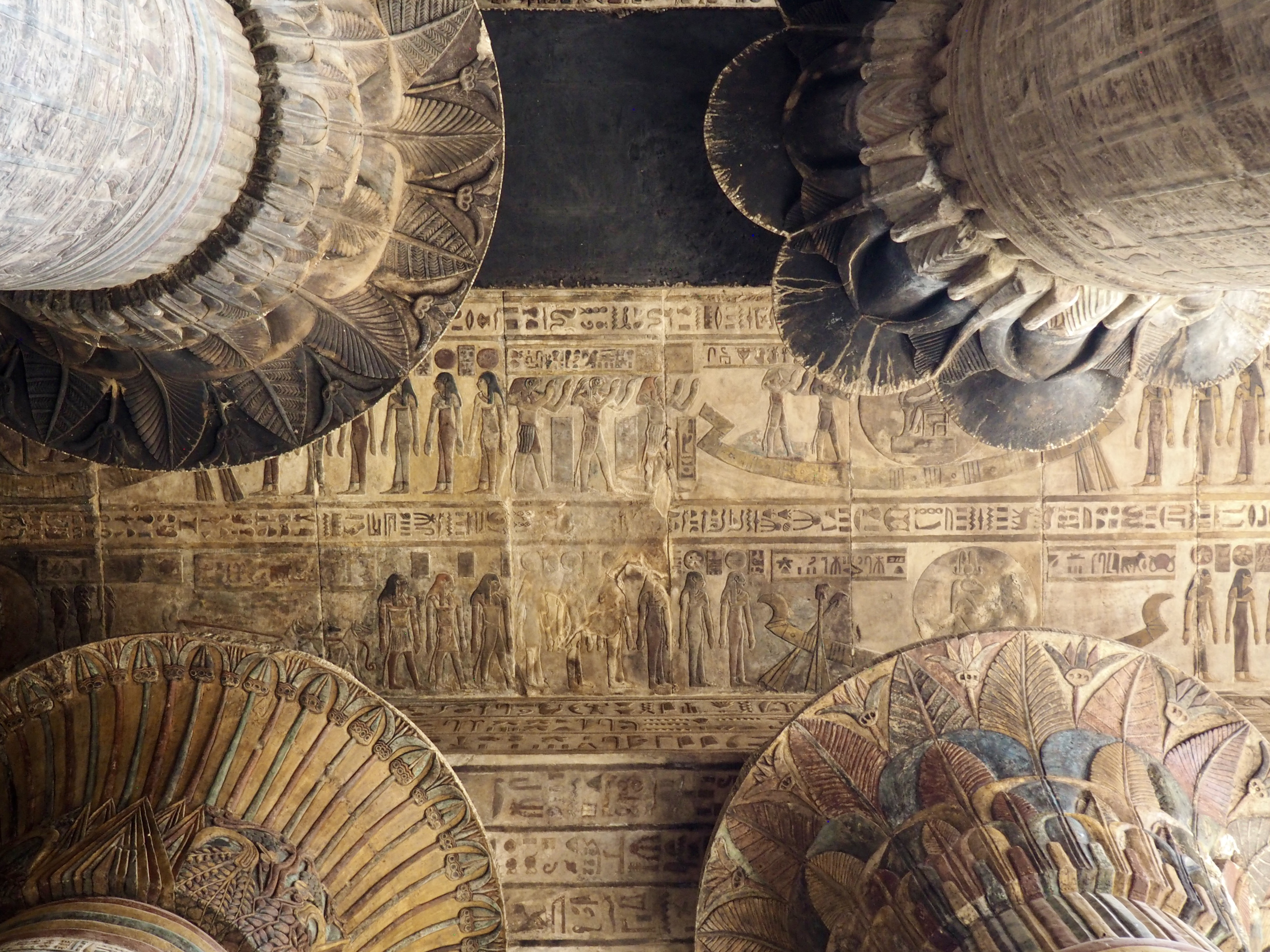
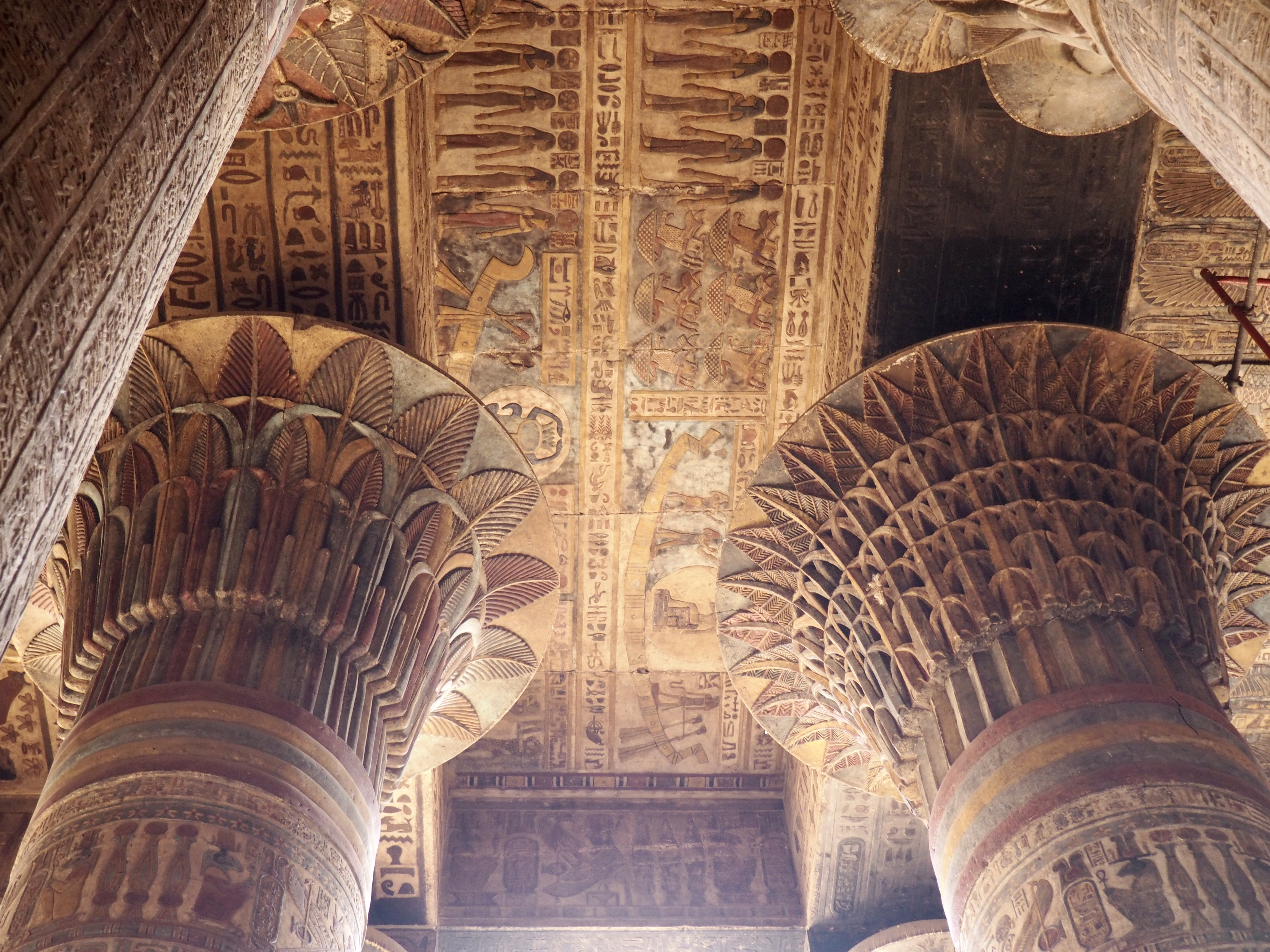
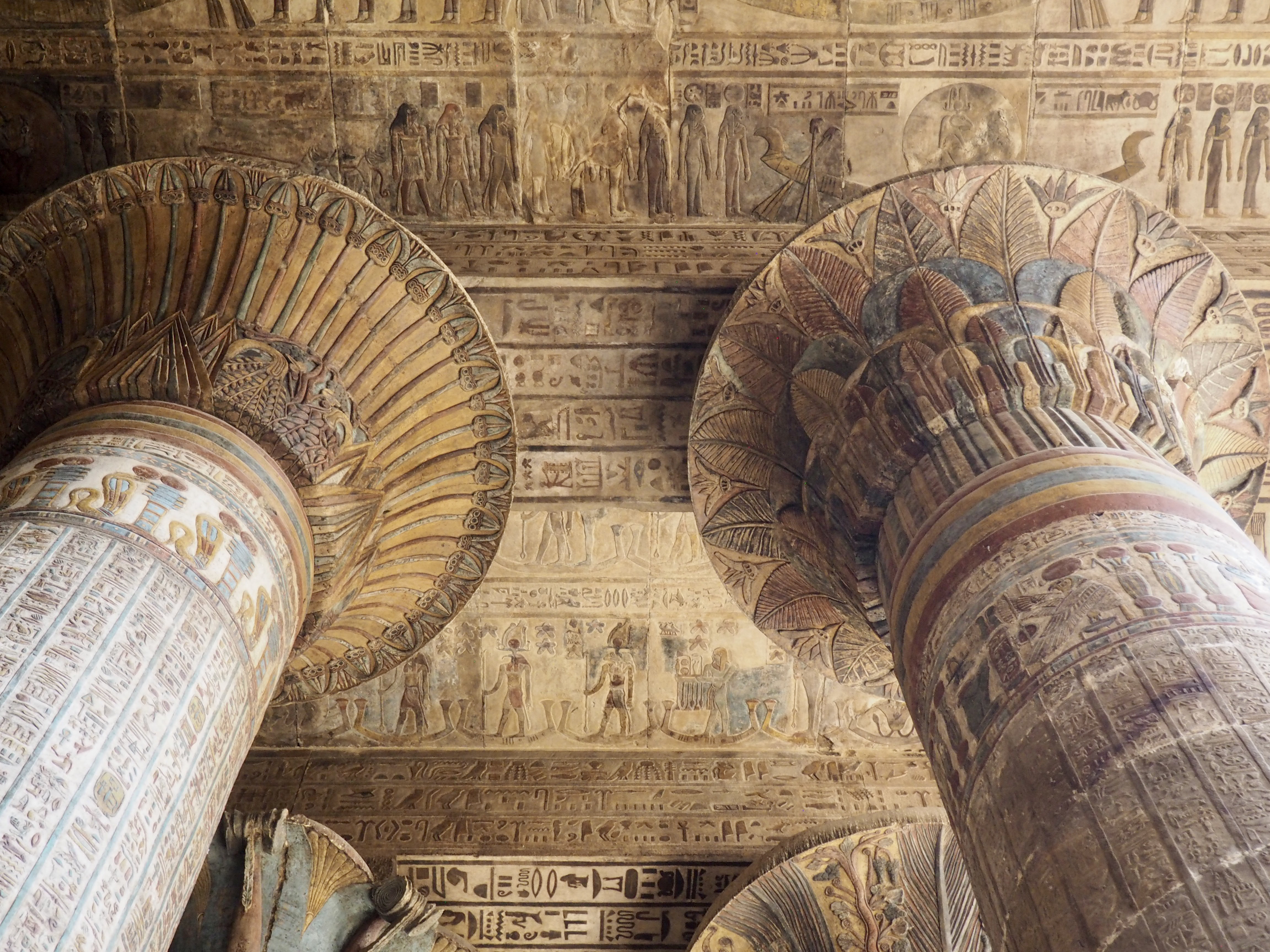
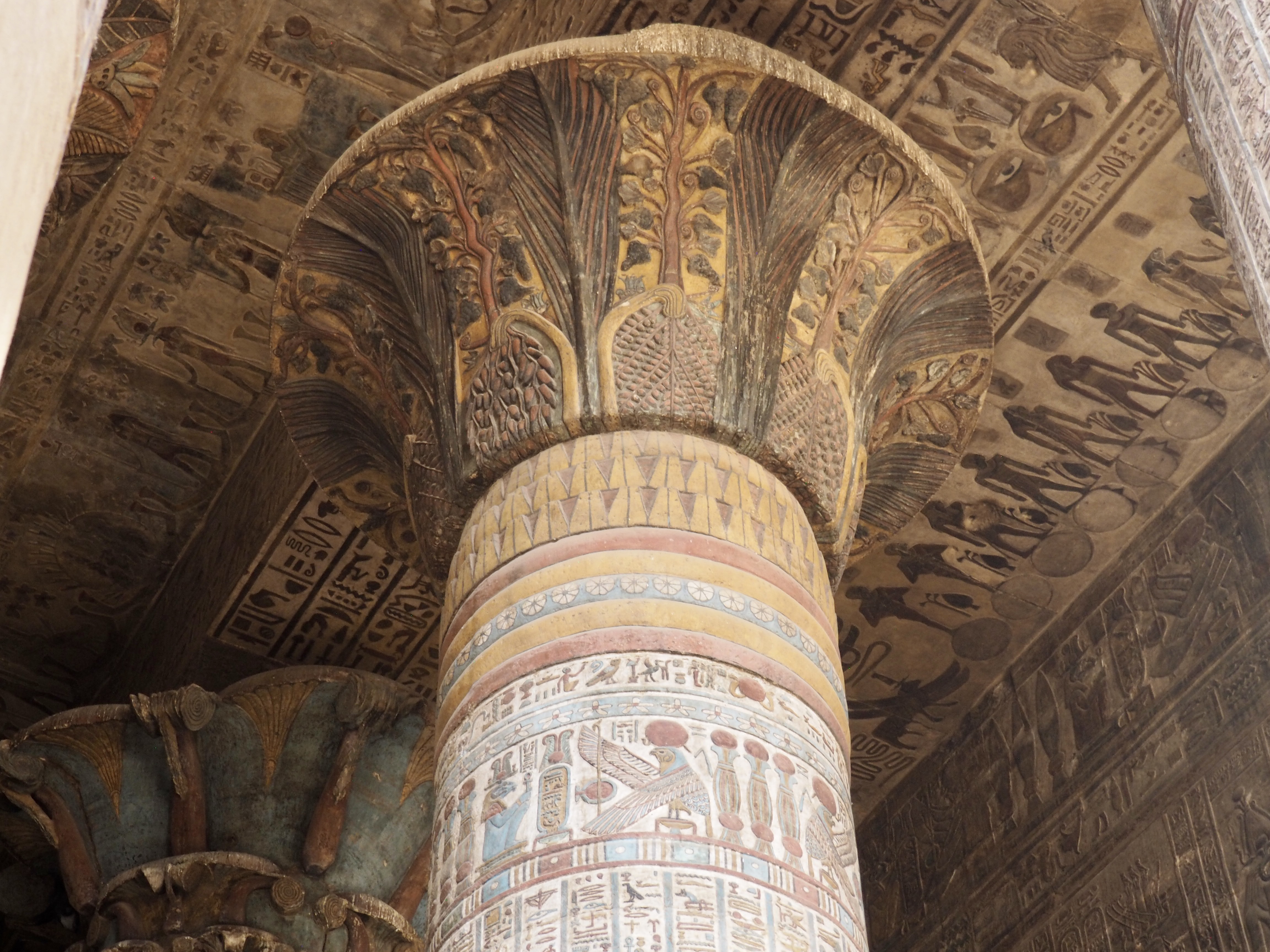
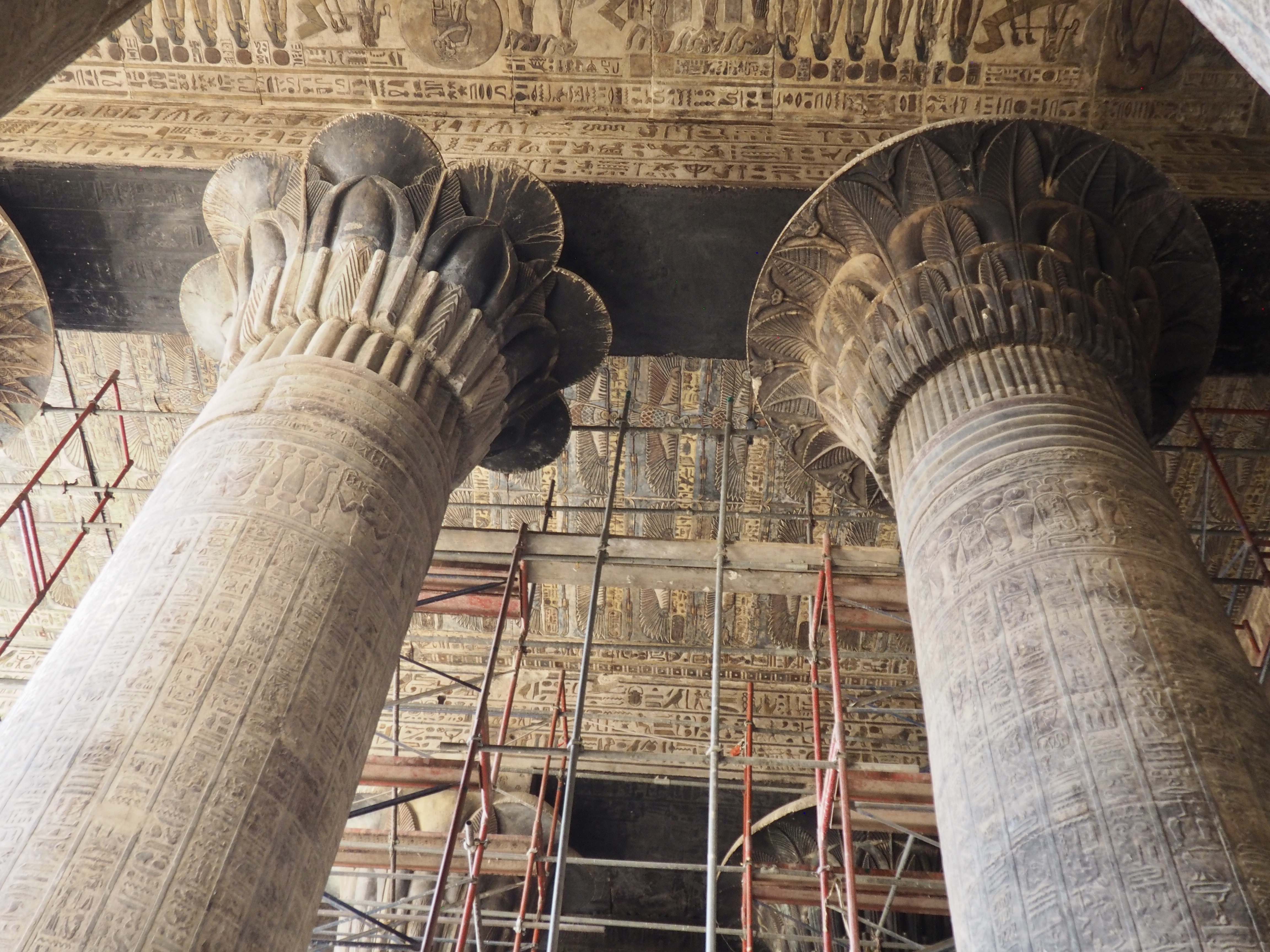
The ancient Egyptians were master tellers of gripping stories that propelled their civilization and kept it going for thousands of years. The Divine Right of Kings (in fact, the actual divinity of kings), the Resurrection of the Dead (for everyone), the Unitary Nation State (with the Pharaoh’s crown itself incorporating the symbols of both Upper and Lower Egypt), the Great Battle between Good and Evil, miraculous conception by the gods, the underworld, all go back to Egypt and all that writing on the columns and the wall.
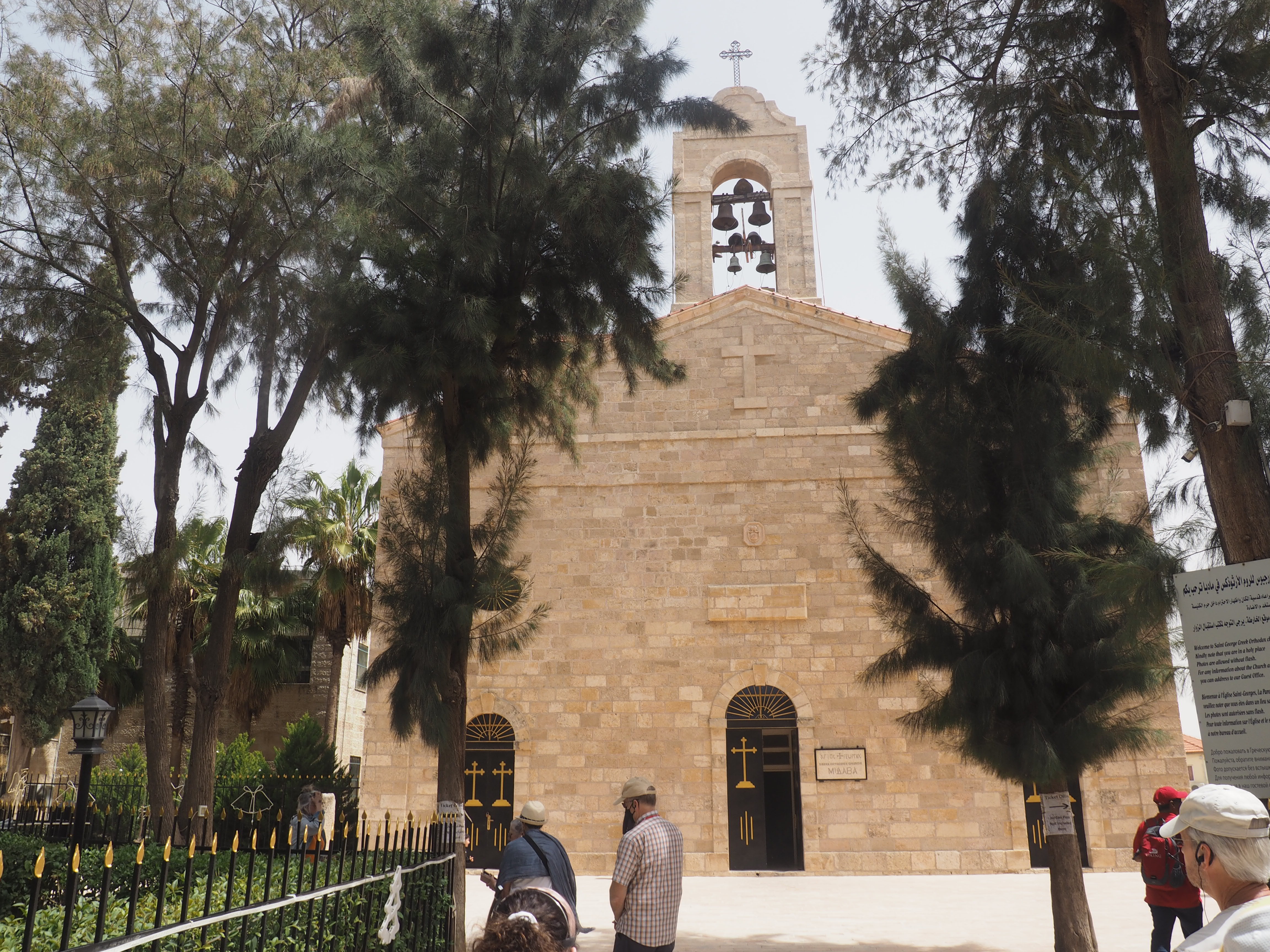
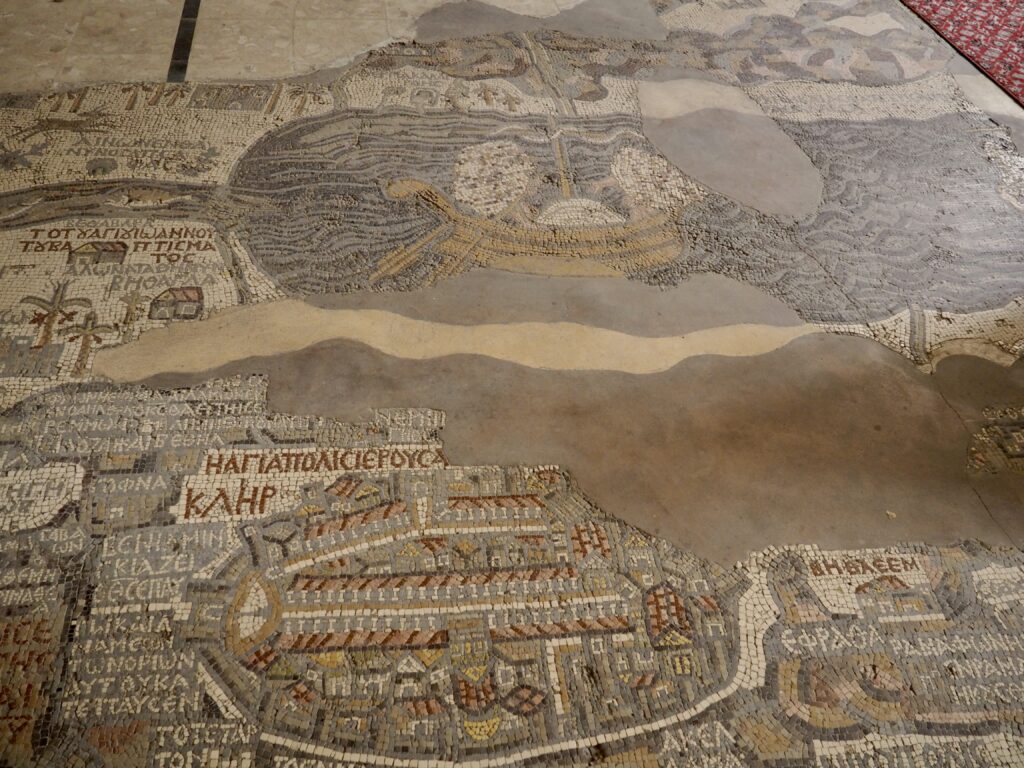
The stories of Egypt, Israel and Jordan are linked tightly together, both in the past and to the present day. In the biblical accounts, Egypt is a place of both exile and refuge. Our guide in Jordan was Palestinian with family he could not visit in the West Bank. Geographically, Cairo is significantly closer to Jerusalem than to Aswan. And culturally, everyone looks back to Abraham and the prophets.
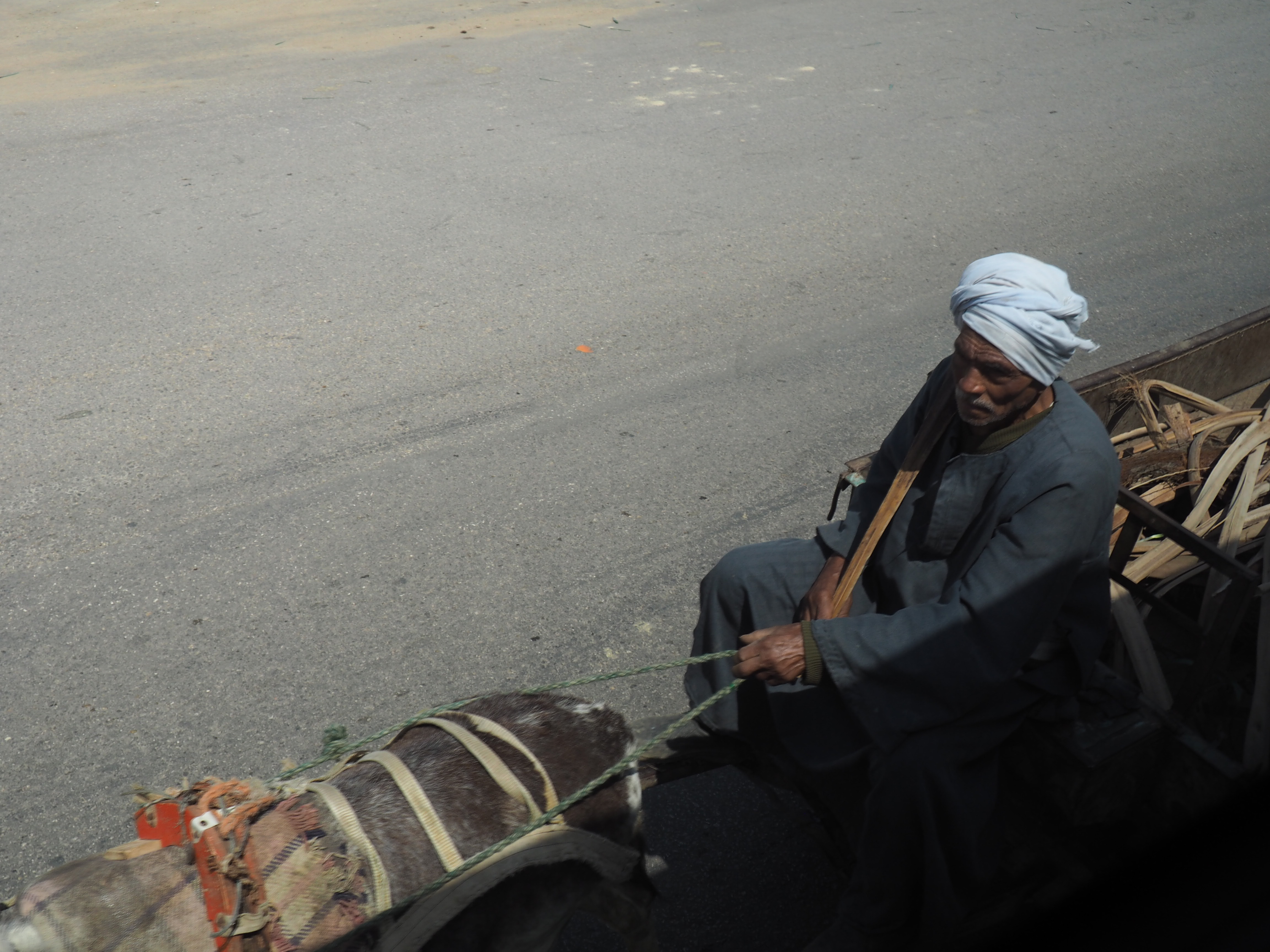

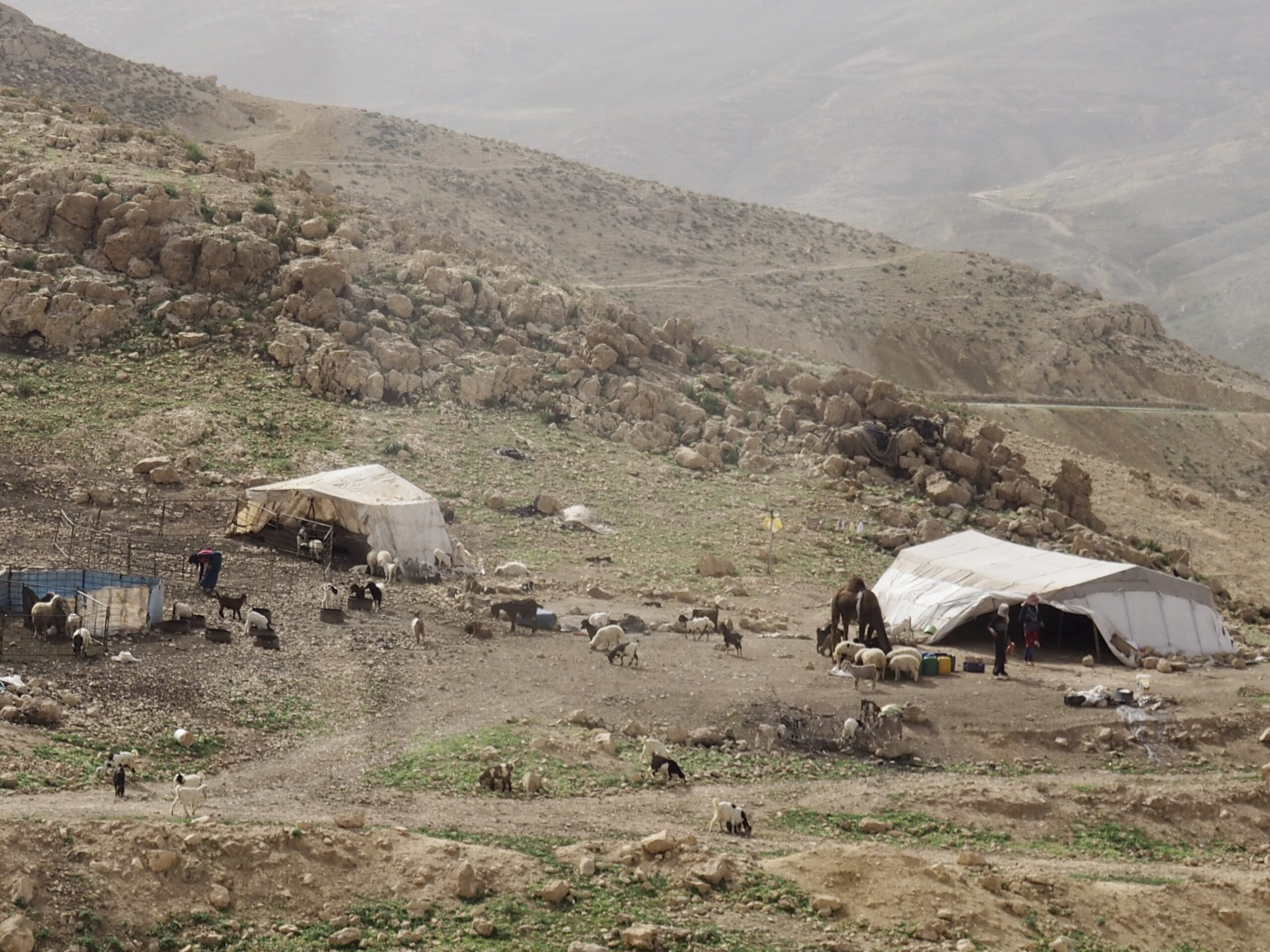
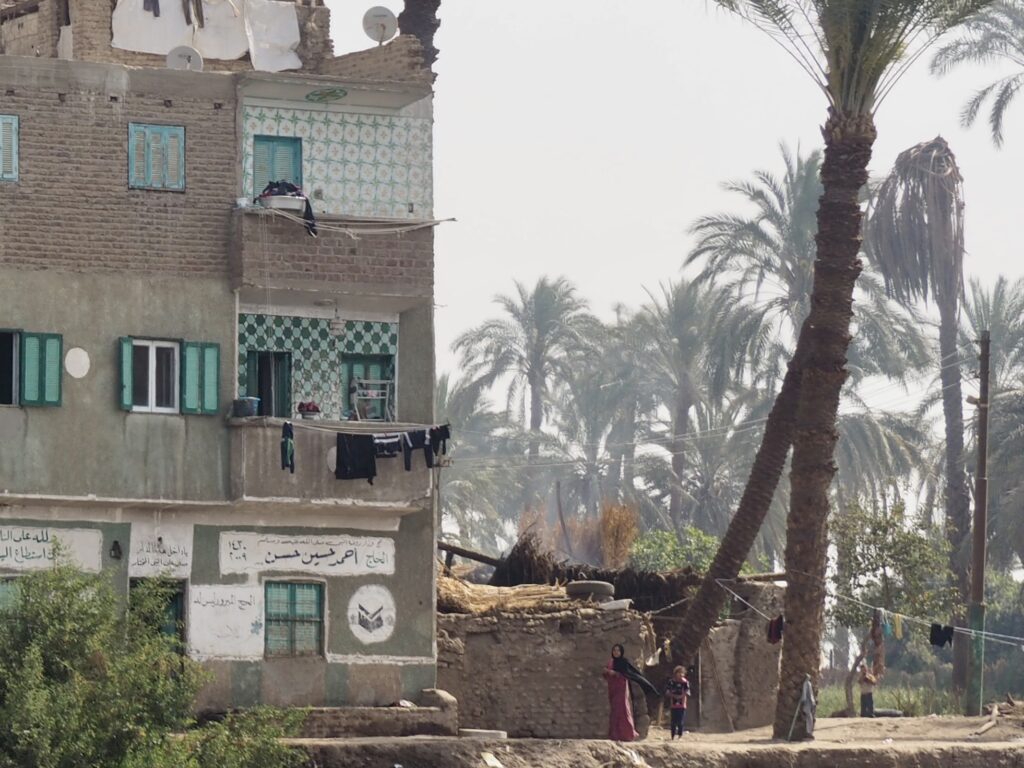
Egypt struggles. In Cairo, thousands of people make their home in the mausoleums of an enormous cemetery known as the City of the Dead (of course, in America thousands sleep homeless on the street). In the country, our guide assures us that conditions are pretty good and that there are many prosperous farmers who choose to live in the old way.




In Israel and Egypt, we had to be conscious of different expectations separating the sexes, whether at airport or other security checks where it would be men on the left, women on the right, or approaching the Western Wall where there are two sections of wall, one for men and the much more crowded one for women.
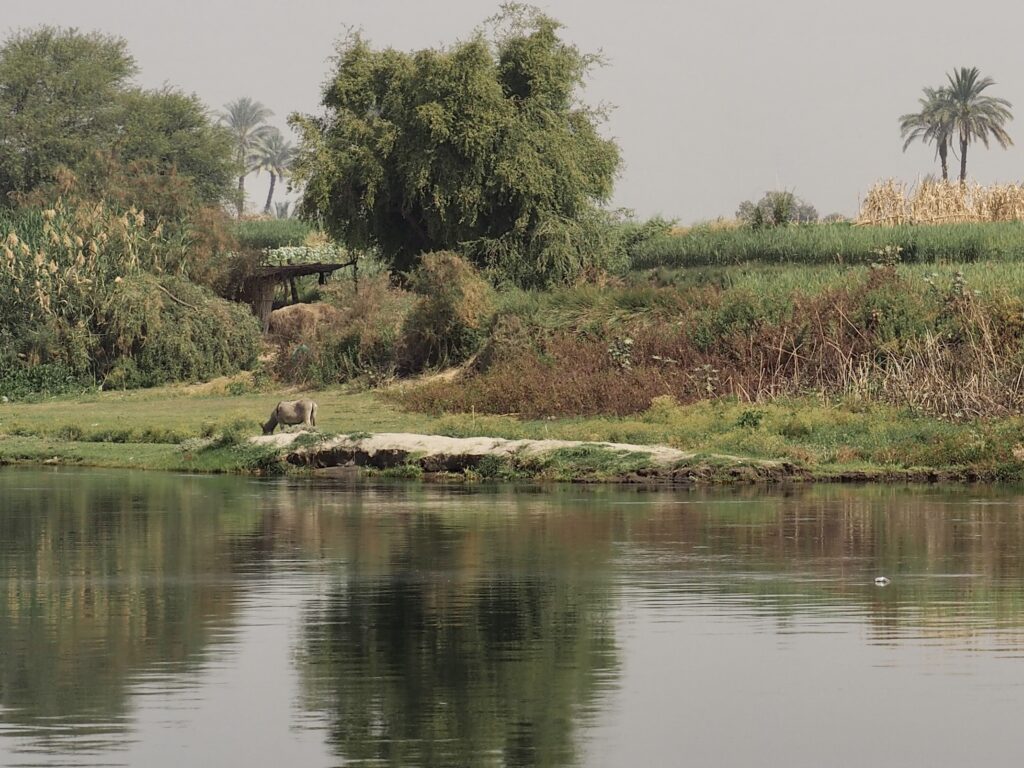
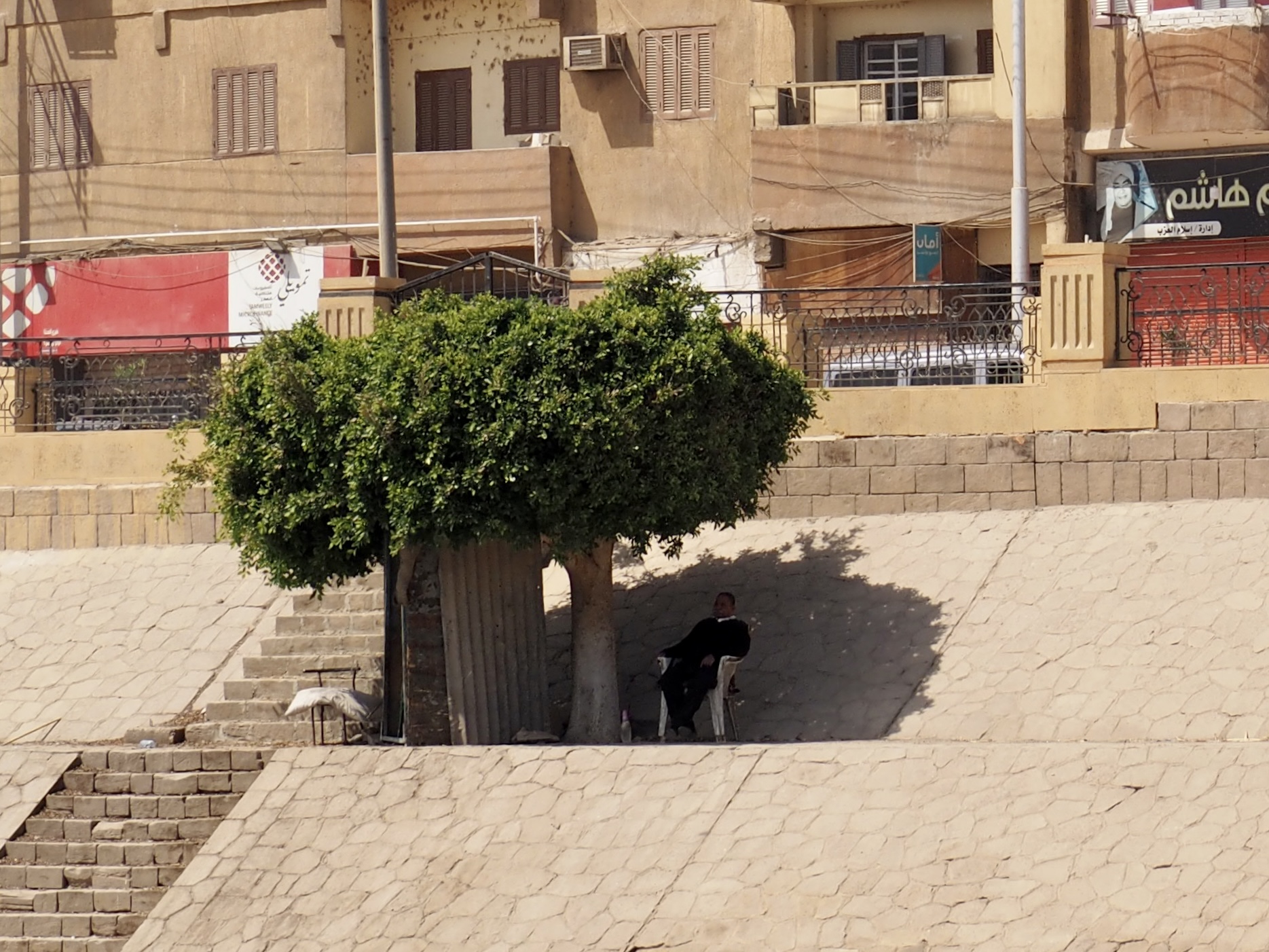
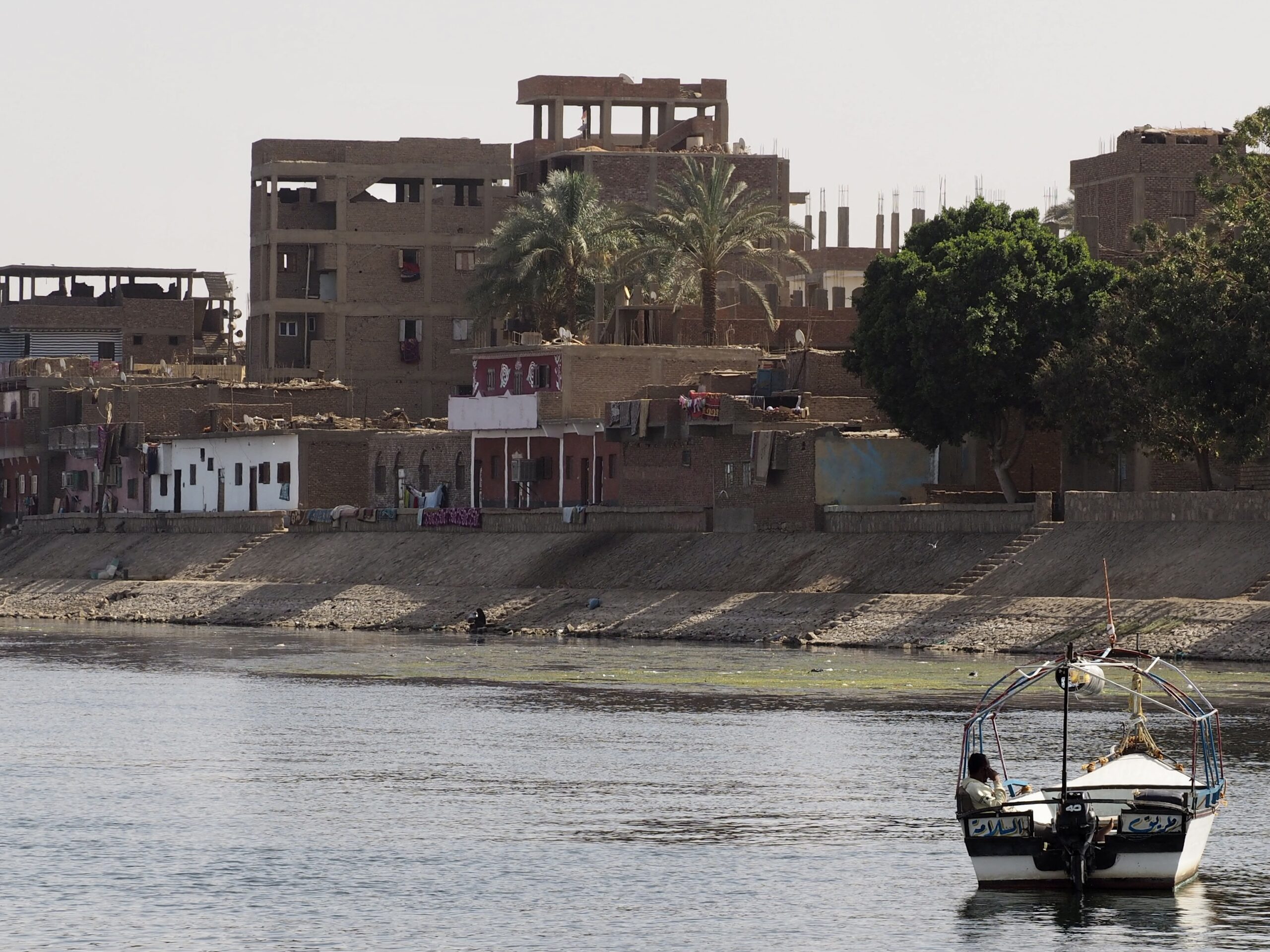
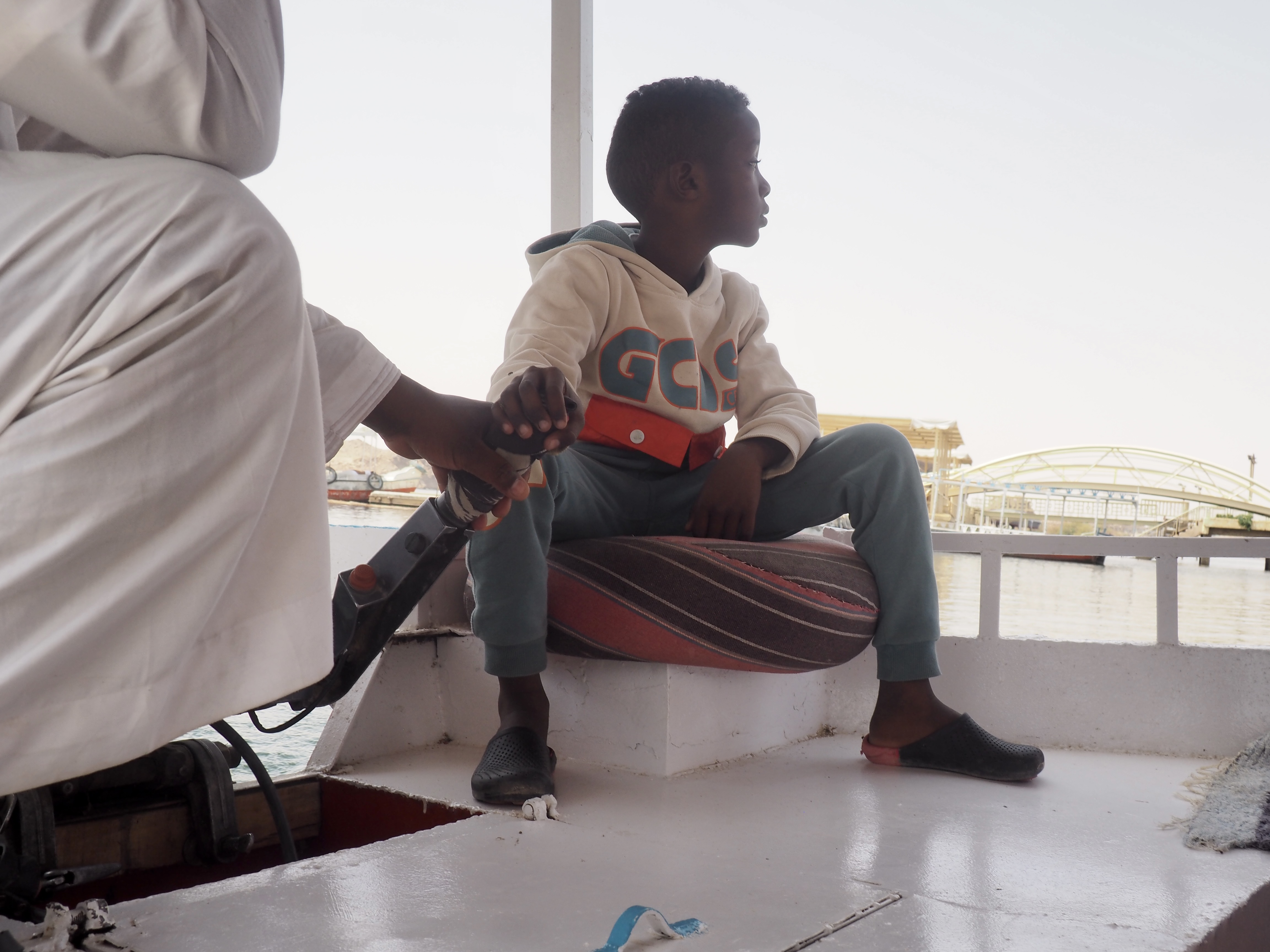
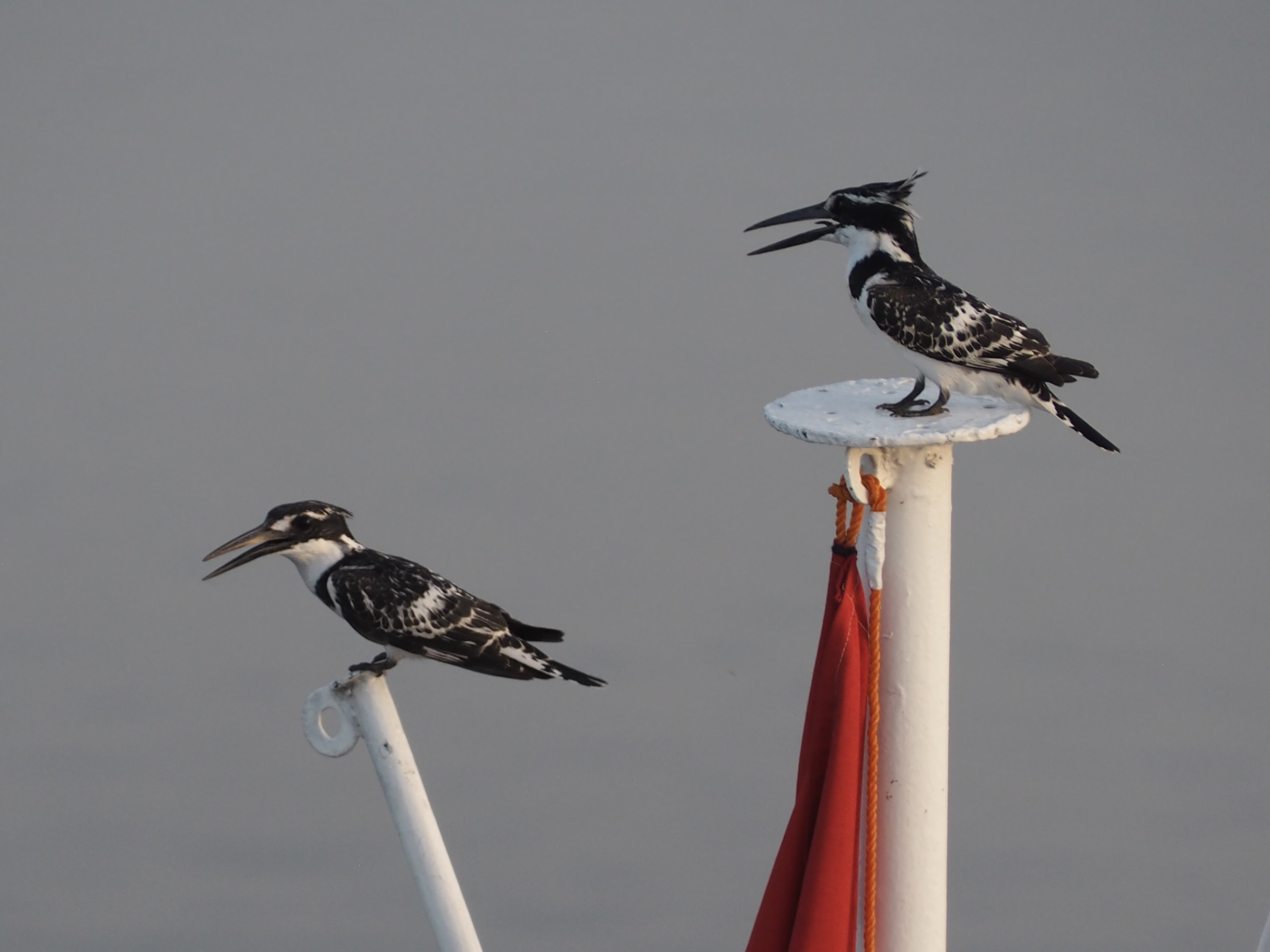



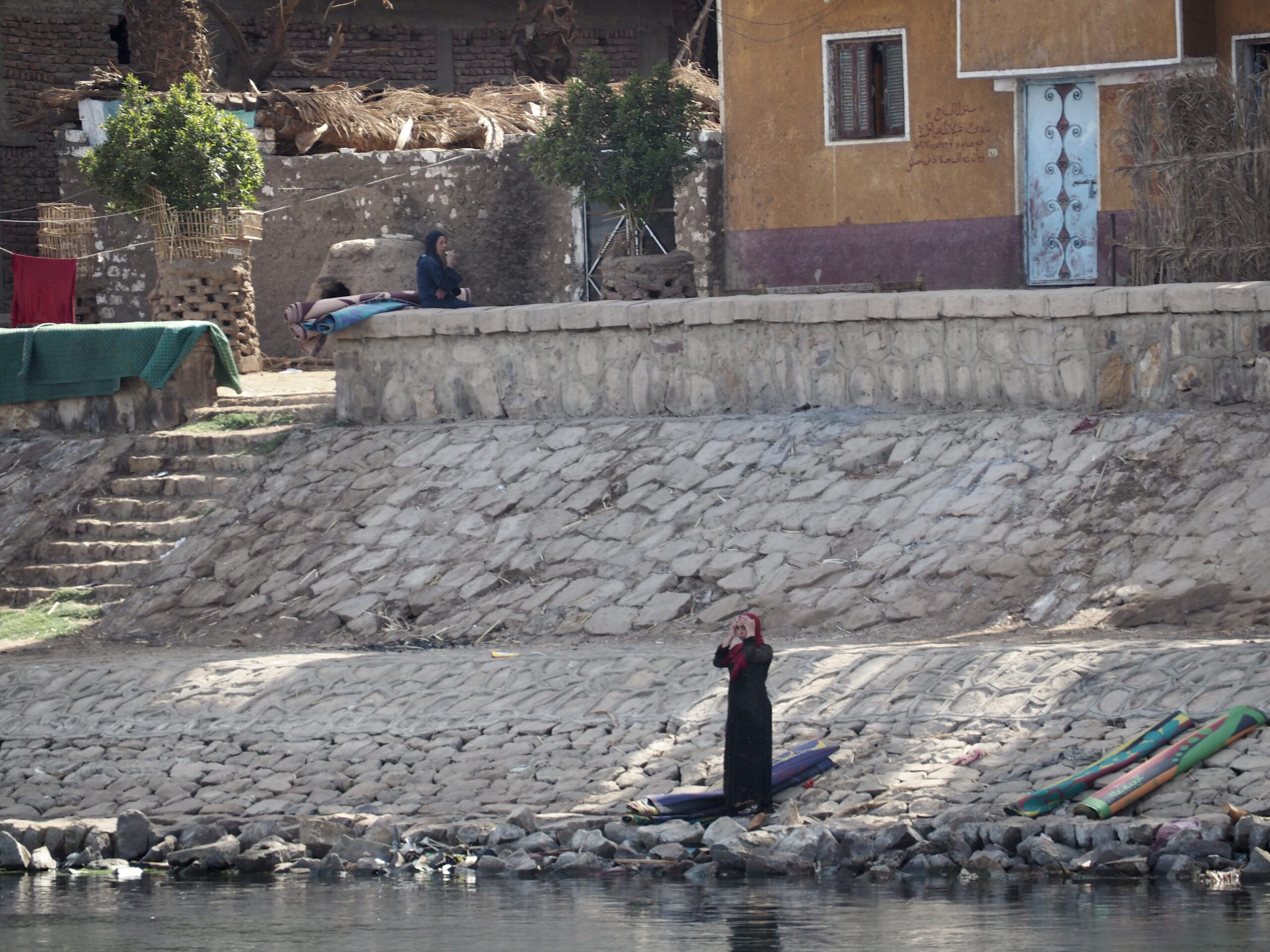




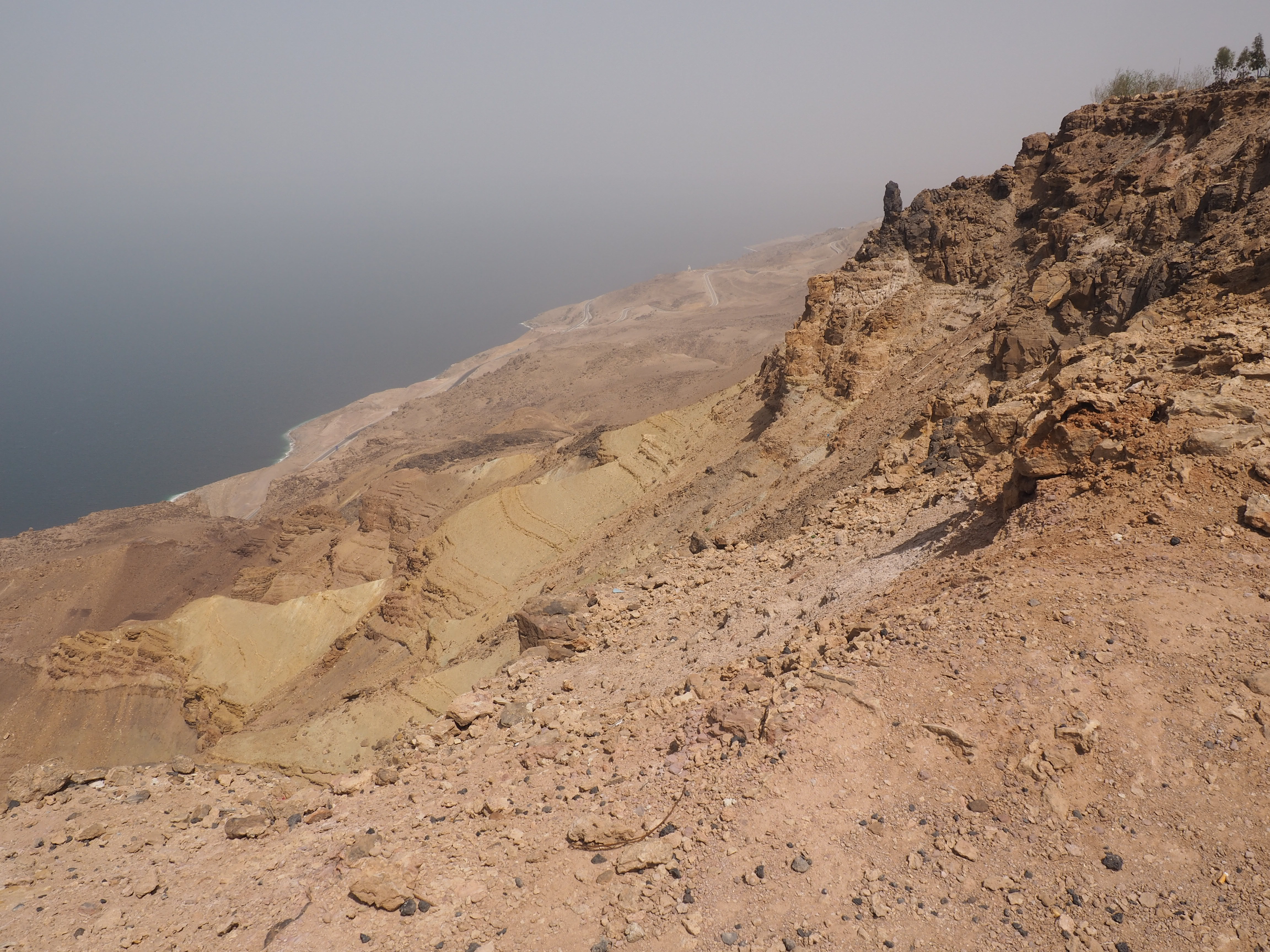
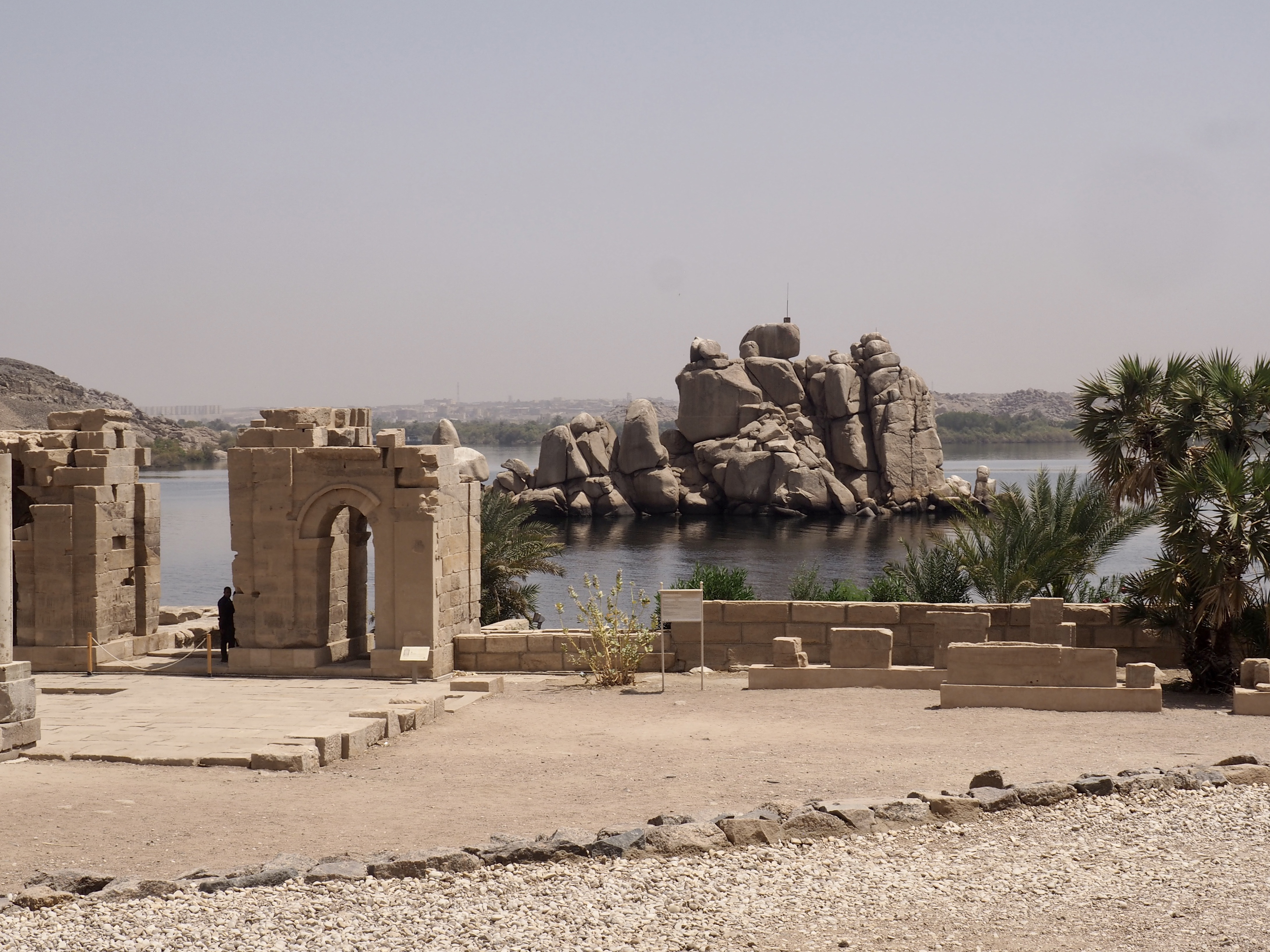
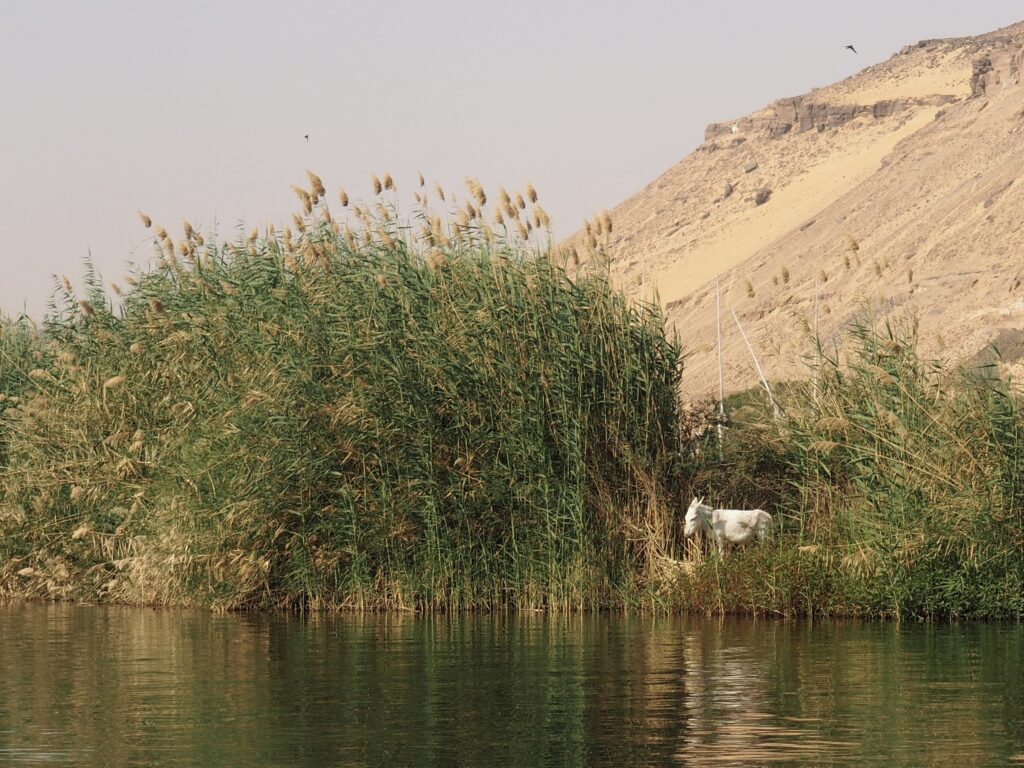
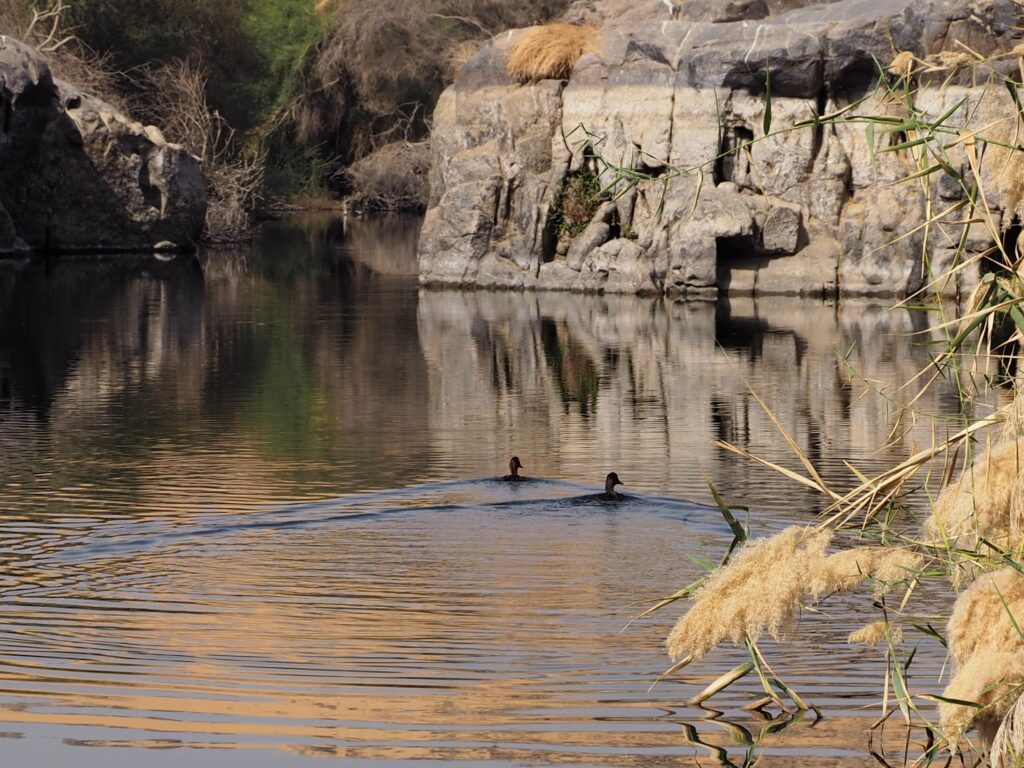
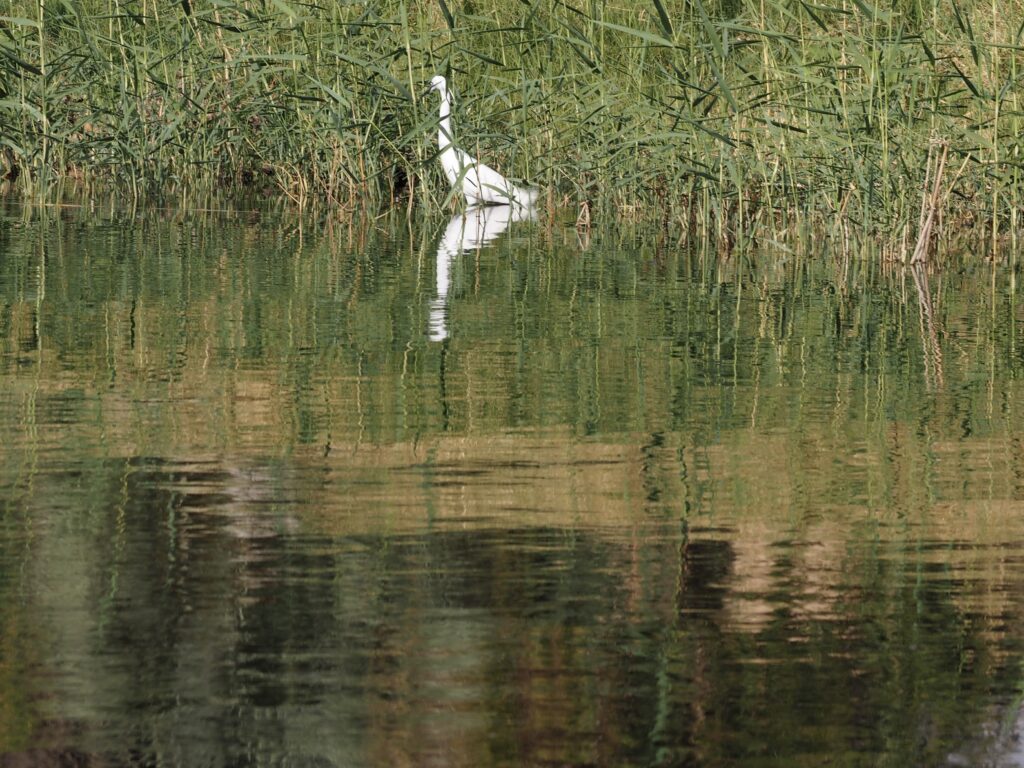
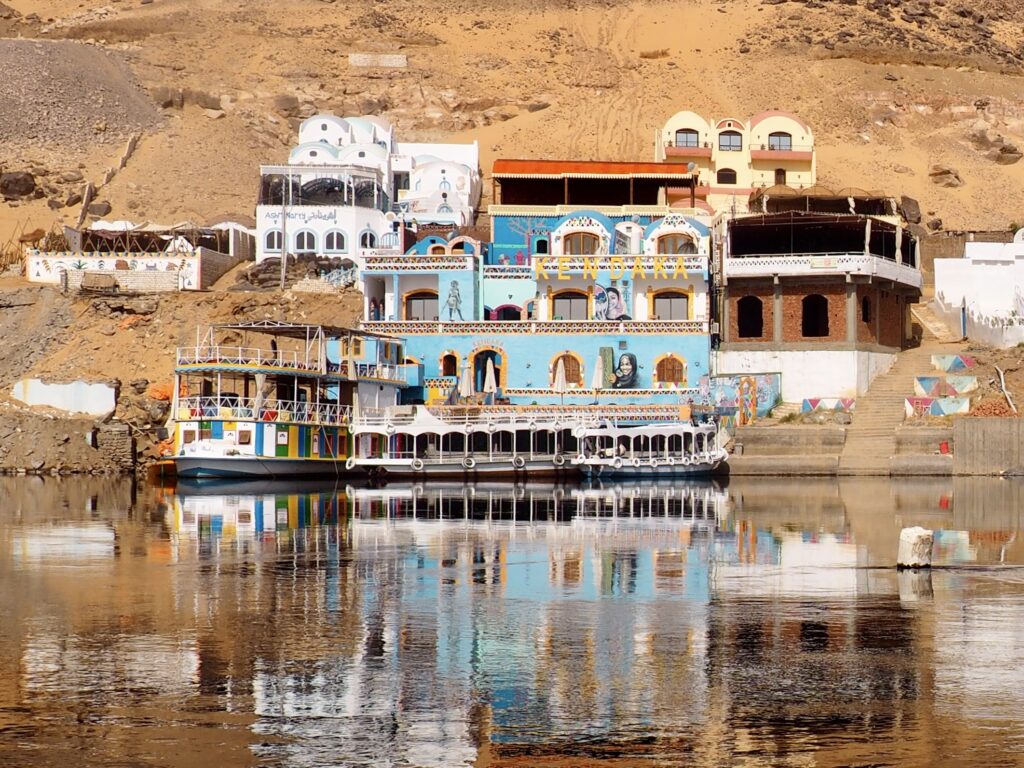
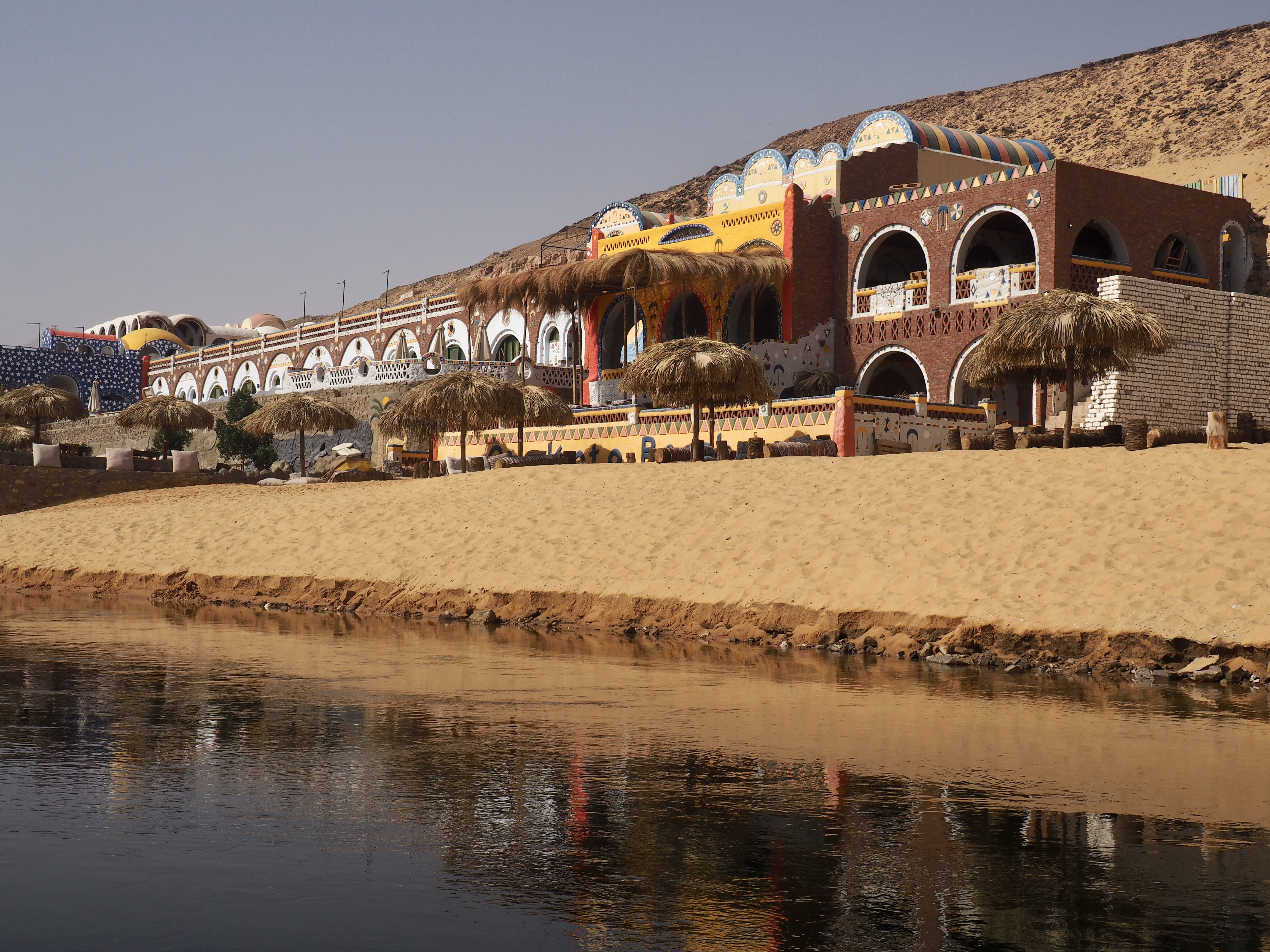
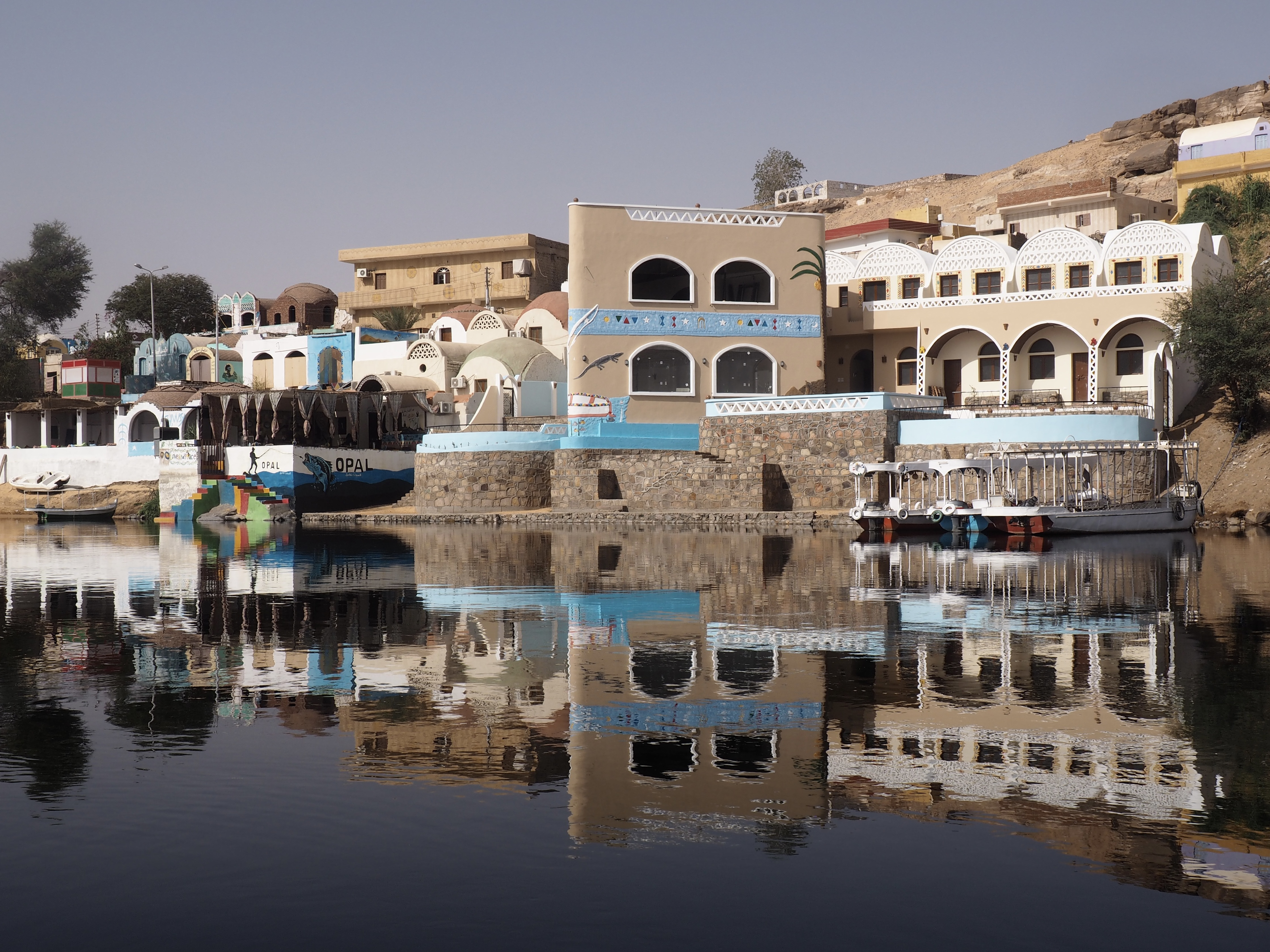
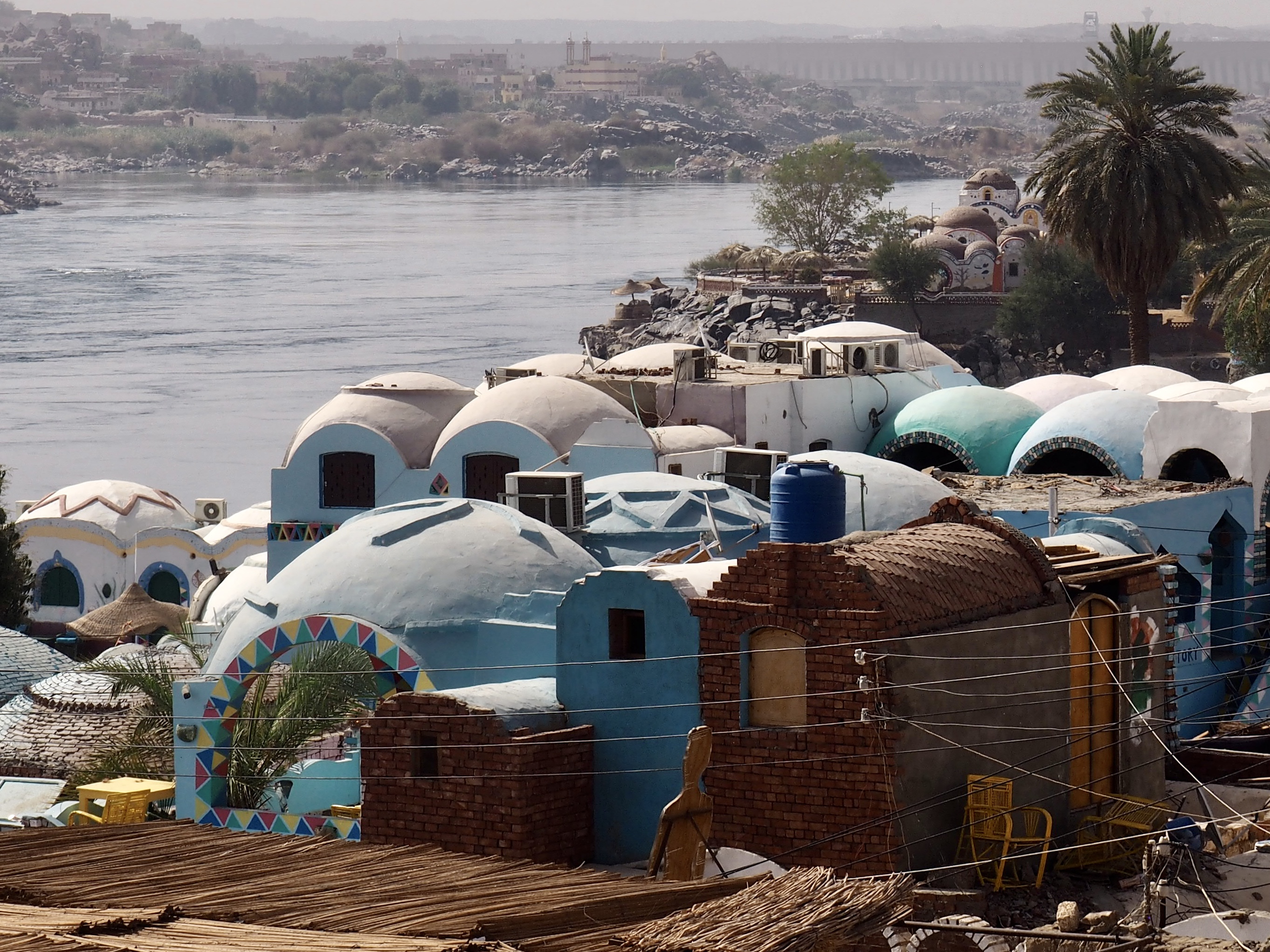
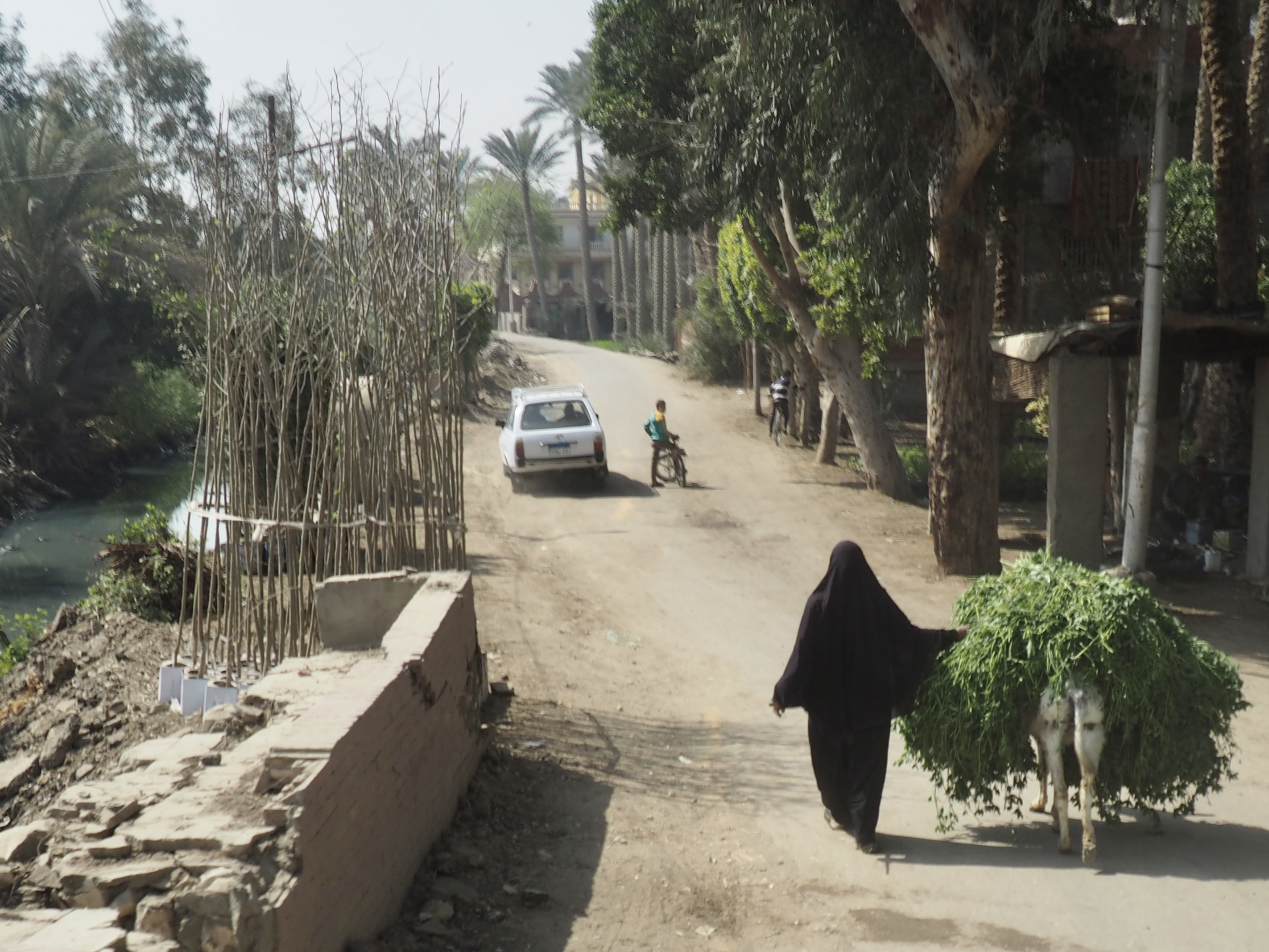
In Egypt, the Nile is everything. Life revolves around it and the water it has provided as a gift since before we knew of a thing called time.

Throughout the region, reminders of conflict are never far. An armed and very alert escort wearing a suit was almost always with us in Egypt (sometimes police cars fore and aft with Tourist Police markings). In Jordan, we only had a guard when crossing the desert (“because the King insists,” according to our guide). Despite this, despite the consistently heavy police and army presence in Israel, and despite the x-ray machines and metal detectors when entering any tourist destination, we felt safe.
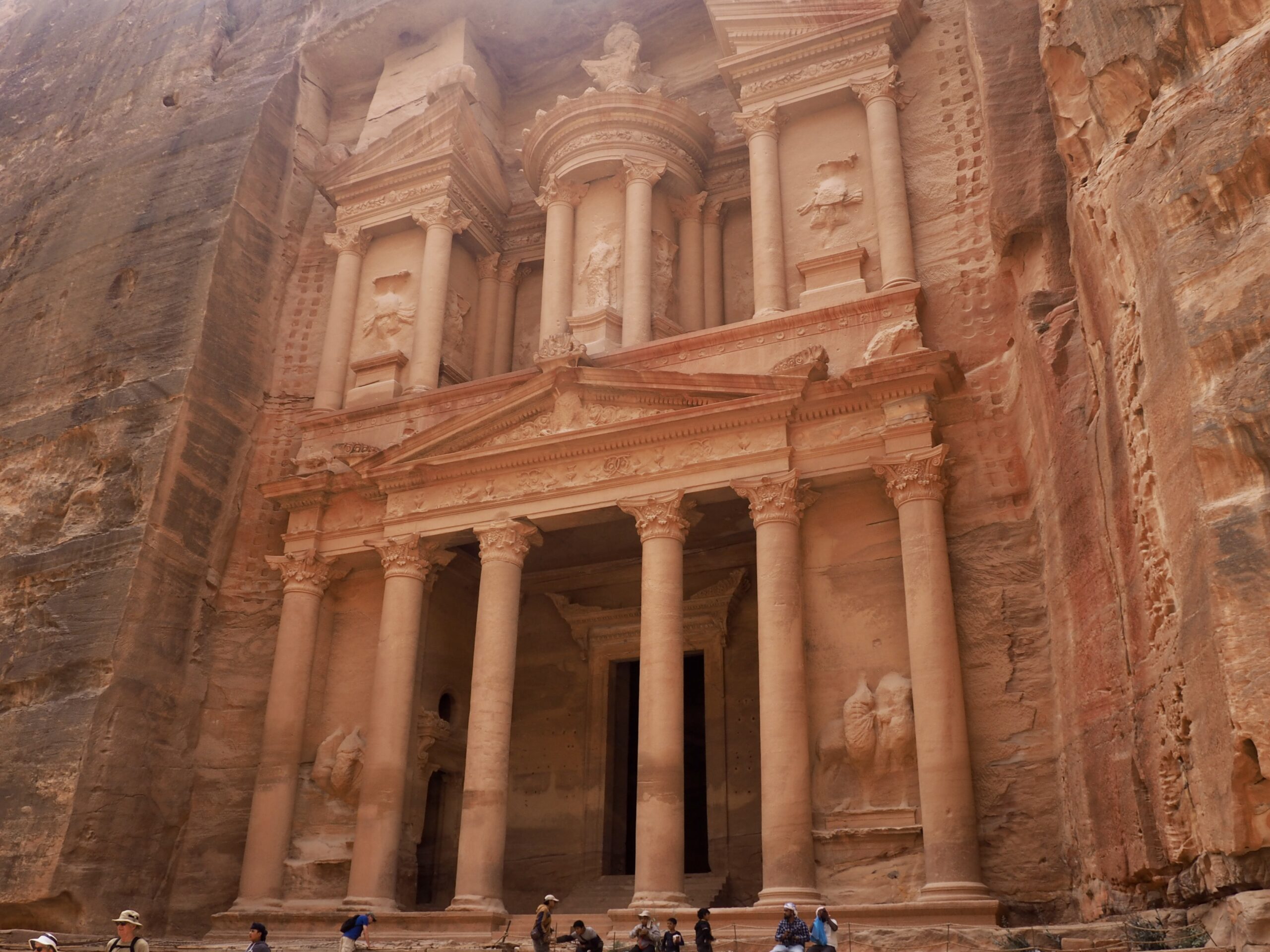
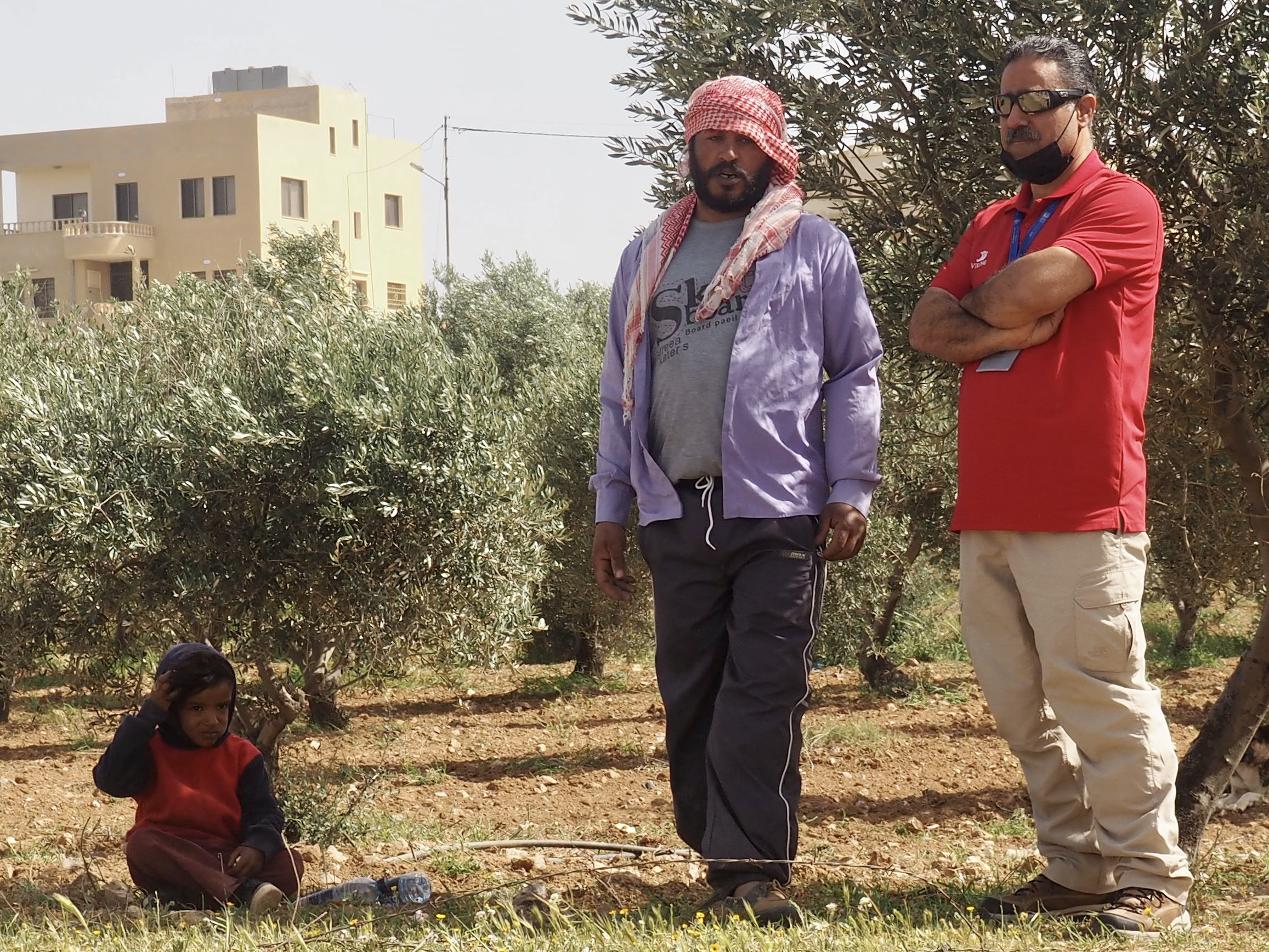
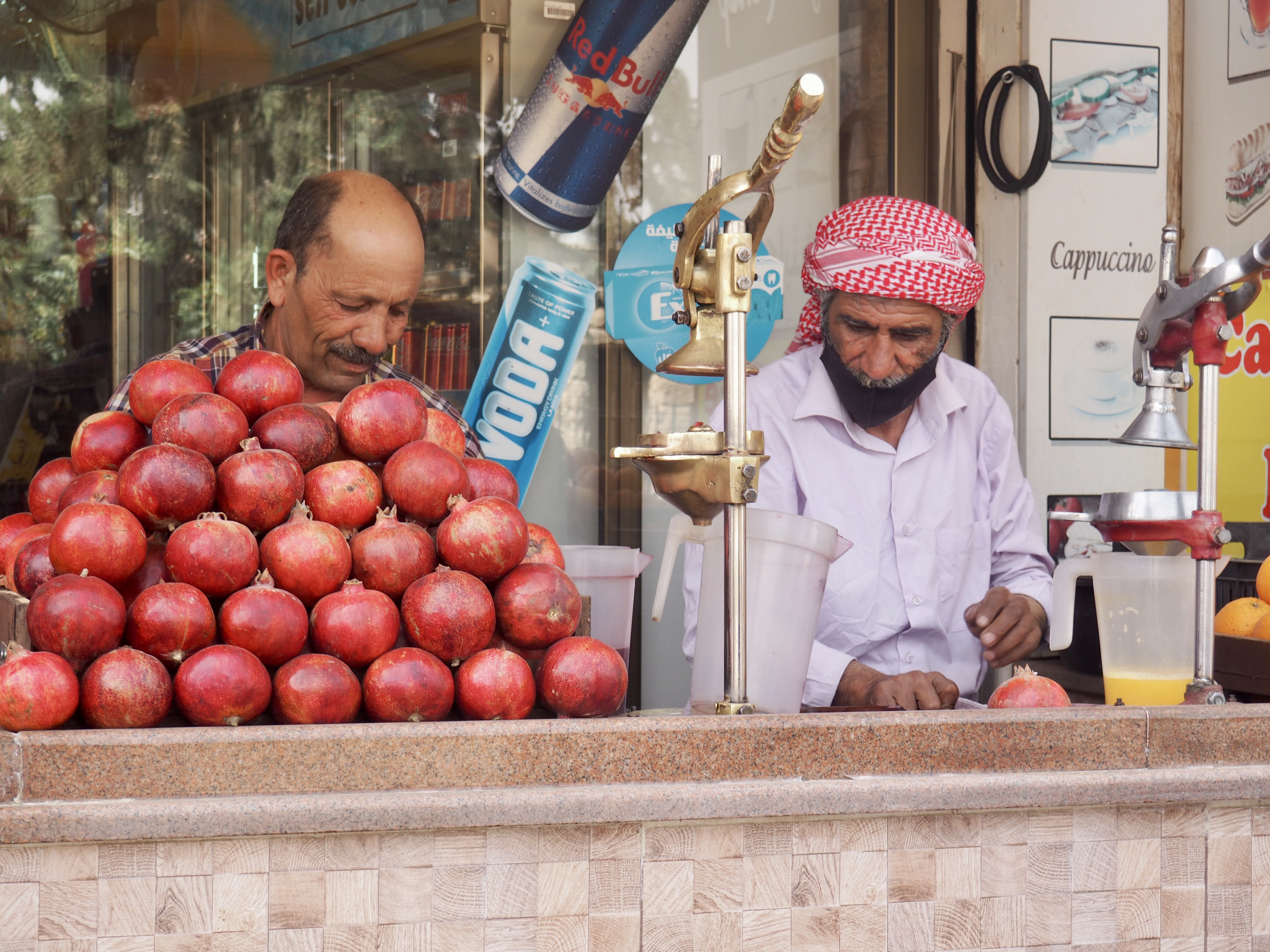
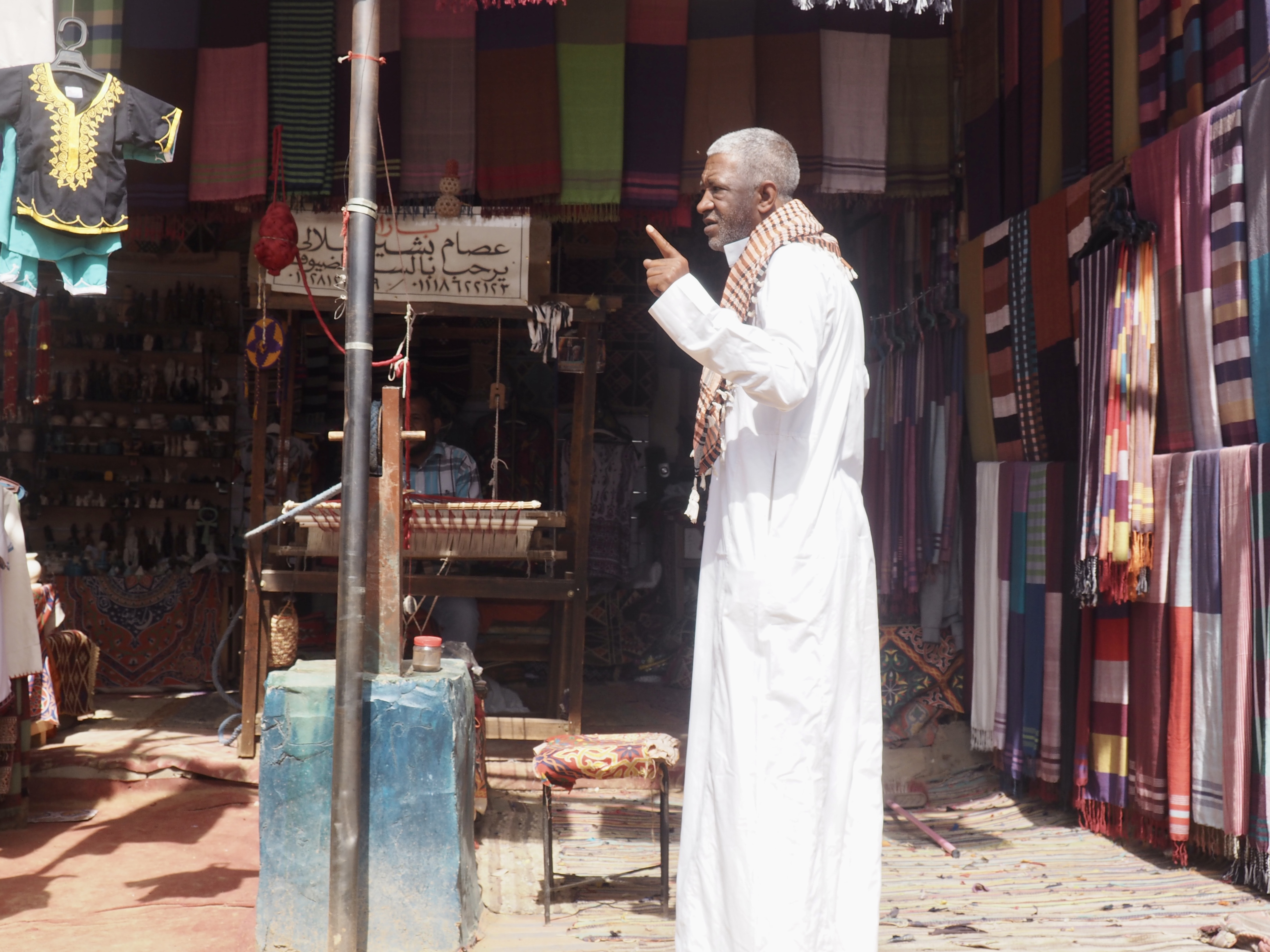
We felt genuinely welcomed by the communities into which we traveled and never sensed any hostility or resentment. We not only were cheered by people on the street in that Egyptian town, a waitress at our hotel in Petra, the two men checking passports on leaving Jordan, engaged us in friendly banter and urged us to come back to stay with them longer. And, our guide in, again, Jordan gave a very moving little farewell speech, “I know your friends and family all told you that you were crazy to come to the Middle East, that this is a dangerous place to be and you came anyway.” (Not a dry eye in the house.) Our Egyptian guide, who took any opportunity to correct the misunderstandings most Americans have about Islam (“all that is just politics, it is not Islam”), also went out of her way to encourage us to buy from the mobs of vendors we encountered at every tourist stop and to even do an occasional sales pitch for one of them, pointing out that we were among the first tourists to be coming back in force after two years of covid when they were just beginning to recover from the chaos of the Arab Spring.
On our last evening, anticipating an extraordinarily early departure for the airport the next day, we walked from our Amman hotel (the one with the artificial Siq) to a nearby large modern shopping area to look for a light supper. We came to an open air multilevel mall lined with restaurants on both sides and noticed just one restaurant with lots of people sitting at tables outside, so we asked for a table and placed our order. Only after sipping our water and eating the complimentary snack did we notice that no one else was eating or drinking anything, but sitting there talking with their untouched food and drinks in front of them. Oops. It was still Ramadan. At first, we felt bad and embarrassed. Then we noticed that no one really noticed or cared. There were no dirty looks. After a while, the main courses came rolling out of the kitchen and ours also came out in the order of ordering. Still, no one else ate or drank until one of the waiters came out and announced that the sun had set.
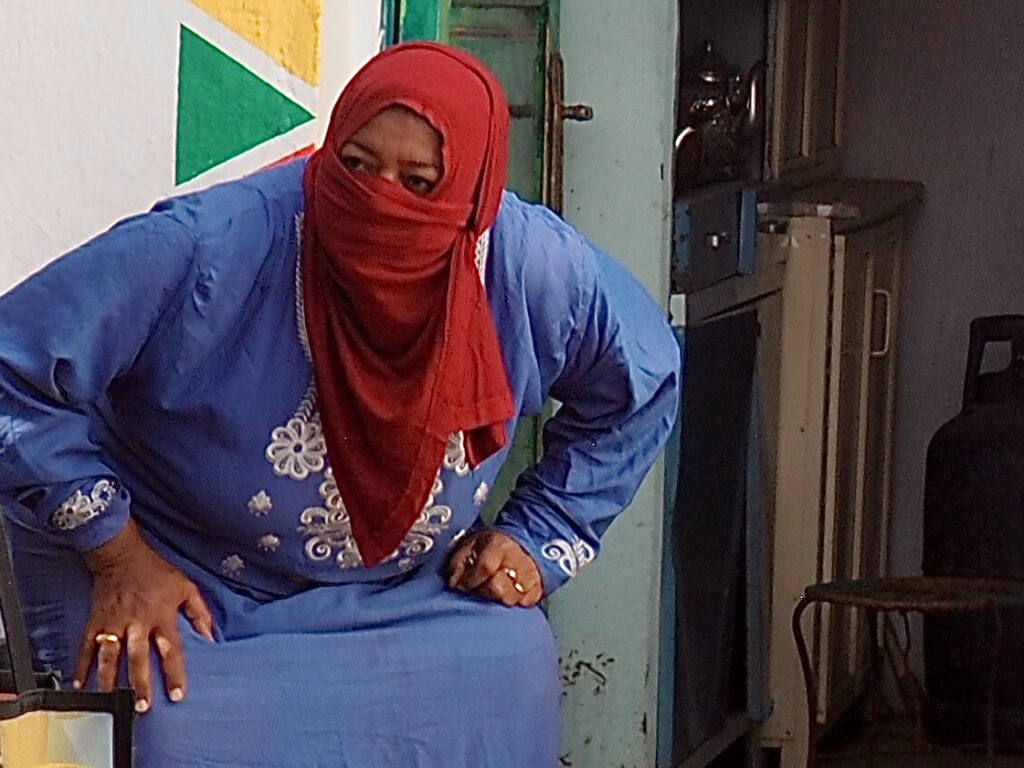

We hope our heart is equally open to welcome the stranger.